Abstract
Pseudobulbar affect (PBA) is a socially debilitating condition that primarily affects people with neurologic diseases, such as Alzheimer’s disease or multiple sclerosis. This condition is characterized by uncontrolled, exaggerated expressions of laughing or crying—often when the situation does not warrant this behavior. Although the true prevalence of PBA is surprisingly high, this condition remains widely misdiagnosed and underdiagnosed. While its exact etiology is unknown, PBA likely results from disruptions in the brain structures and/or neurotransmitters that regulate emotions. Differential diagnosis of PBA includes ruling out depression or other psychiatric conditions. Treatment of PBA has traditionally centered on antidepressant therapies, but newer therapeutic options include combination agents employing multiple modalities. Therapy should include patient counseling to reassure patients and families that PBA is not the fault of the individual. Counseling should also emphasize safety precautions to minimize adverse events and maximize appropriate adherence to the selected therapies.
Find more articles on this and other psychiatry and CNS topics:
The Journal of Clinical Psychiatry
The Primary Care Companion for CNS Disorders
This CME activity is expired. For more CME activities, visit CMEInstitute.com.
Find more articles on this and other psychiatry and CNS topics:
The Journal of Clinical Psychiatry
The Primary Care Companion for CNS Disorders
Abstract
Pseudobulbar affect (PBA) is a socially debilitating condition that primarily affects people with neurologic diseases, such as Alzheimer’s disease or multiple sclerosis. This condition is characterized by uncontrolled, exaggerated expressions of laughing or crying—often when the situation does not warrant this behavior. Although the true prevalence of PBA is surprisingly high, this condition remains widely misdiagnosed and underdiagnosed. While its exact etiology is unknown, PBA likely results from disruptions in the brain structures and/or neurotransmitters that regulate emotions. Differential diagnosis of PBA includes ruling out depression or other psychiatric conditions. Treatment of PBA has traditionally centered on antidepressant therapies, but newer therapeutic options include combination agents employing multiple modalities. Therapy should include patient counseling to reassure patients and families that PBA is not the fault of the individual. Counseling should also emphasize safety precautions to minimize adverse events and maximize appropriate adherence to the selected therapies.
Case Presentation:
Jessica is a 52-year-old woman who has had multiple sclerosis (MS) since her mid-thirties. Her disease has remained relatively stable on an injectable disease-modifying therapy, with a breakthrough relapse every 2 to 3 years. Recently, her existing MS symptoms have started to become more bothersome, including fatigue, spasticity affecting her right side, and what she describes as “forgetfulness.” During a recent follow-up visit, Jessica’s husband mentions that he thinks she is becoming depressed because she is frequently tearful and has “emotional outbursts.”
Overview
It is said that laughter is the best medicine, but involuntary laughing (or crying) can be socially debilitating and embarrassing. Pseudobulbar affect (PBA) is an uncontrollable response of the central nervous system in which an individual has emotional eruptions such as outbursts of crying or laughing.1 These expressions may not have precipitating stimuli and are often disruptive, unrelated to mood, and incongruent with or disproportionate to the context. Despite its common occurrence among patients with neurologic disorders, PBA has low recognition among health care professionals (AV 1).1
AV 1. Overview of PBA Underrecognition and Undertreatment (01:42)
Epidemiology of PBA
PBA has also been known by a variety of other terms, including affective lability, involuntary emotional expression disorder, or simply pathological laughing and crying.2–4 The 6 neurologic conditions most commonly associated with PBA are Alzheimer’s disease, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), MS, Parkinson’s disease, stroke, and traumatic brain injury (TBI).1 An online survey by Work et al1 screened 2,318 patients with these conditions for PBA, and, using disease population estimates from government agencies and professional organizations, the investigators reported a US prevalence of PBA ranging from 1.8 million to 7.1 million people, depending on the screening tools and thresholds used.1 The highest prevalence (a mean rate of 37.5%) was found using the Center for Neurologic Study-Lability Scale (CNS-LS) with a cutoff score of 13.
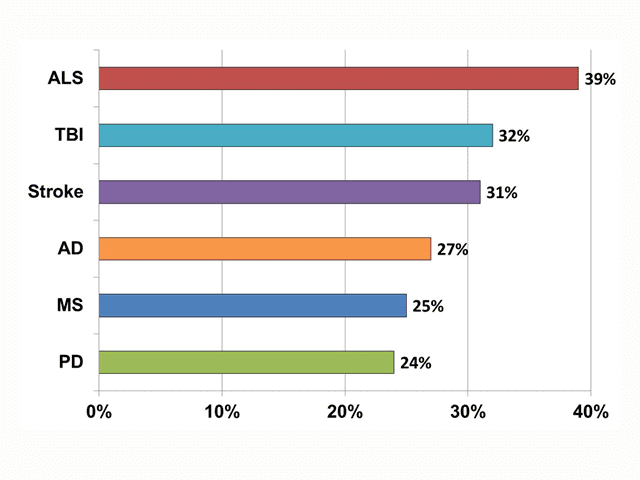
AV 2. Prevalence of PBA by Neurologic Condition in PRISM Study (01:29)
Reprinted with permission via Creative Commons Attribution License from Brooks et al.5
In a registry study called PRISM,5 Brooks and colleagues evaluated the prevalence of PBA by enrolling patients with these 6 neurologic diseases at 173 sites. Data from 5,290 patients showed an overall prevalence rate of 37%, ranging from 26% in Parkinson’s disease to 52% in TBI (AV 2).5
Due to the potential for an increasing incidence of neurologic conditions such as Alzheimer’s disease among the aging population,6 health care professionals may begin to encounter more patients with PBA.3 In the PRISM study, 58% of participants were aged 65 years and older, and in this subgroup the overall prevalence of PBA was 27% (AV 3).7
AV 3. Prevalence of PBA in Patients Aged ≥ 65 Years by Neurologic Condition (N=3,048)
Unfortunately, PBA has often been missed by clinicians. The survey1 by Work and colleagues indicated that, among patients who discussed their crying/laughing symptoms with a physician, 41% received a diagnosis, but none received a diagnosis of PBA. One-third of patients who were diagnosed received a major depressive disorder (MDD) diagnosis, 28% were told the symptoms were just part of the neurologic condition, and others received diagnoses of bipolar disorder, posttraumatic stress disorder, anxiety, or other conditions. About half of those diagnosed received a medication to treat their episodes.
Proposed Pathophysiology of PBA
The exact causes of PBA are unclear, although it is believed to be related to disruption of neural networks involving the limbic and paralimbic systems modulated by the cerebellum.4 PBA is believed to be a disorder of frontal dysregulation and disinhibition (AV 4).3 Several hypotheses describe proposed pathophysiologic processes involved.
AV 4. Proposed Pathophysiology of PBA (00:34)
Based on Miller et al.3
Release hypothesis. The release hypothesis posited by Wilson8 in 1924 holds that PBA is due to disruption of cortical inhibition to an upper brainstem center, followed by release of lower bulbar nuclei that affect the motor responses associated with laughing and crying.4 In a revised theory, Parvizi and colleagues suggested that brain lesions affect the cerebro-pontocerebellar pathways, meaning the cerebellar structures that would normally trigger laughing or crying in response to a stimulus are forced to “operate on the basis of incomplete information about that context.”9[p.1708]
Gate control theory. Studies of the etiology of PBA in patients with MS suggest that the disorder is due to disinhibition of the “gate control” mechanisms that normally hold emotional expressions in check.10 In this theory, neurologic damage from MS or another neurodegenerative disease disrupts activity in the cortical structures related to sensory-motor and emotional processing, as well as overactive involvement of motor cortical areas.
Dysfunction of neurotransmitters theory. Disruption of cortico-limbic-subcortico-thalamic-pontocerebellar pathways that control human emotion is suggested in each of the previous theories.11 Key neurotransmitters, including serotonin, dopamine, glutamate, and sigma-1, are involved in carrying signals between neurologic structures to convey information about emotional expression.4 This suggests that interventions targeting these modulators may offer a possible avenue for treatment.11
Diagnosis of PBA
PBA can be confusing to the patient, family members, and social contacts because the behavior does not necessarily reflect how the affected person is actually feeling. PBA sometimes occurs as an exaggerated response to a predictable (and expected) emotion, but it also can occur as a completely paradoxical response to the circumstances.3 Diagnostic criteria for PBA include the following symptoms and impairment:2,3
- Involuntary or exaggerated emotional expression, including episodes of laughing, crying, or related emotional displays, resulting from a brain disorder (patients may have only laughing or only crying episodes, or they may have both)
- Episodes represent a change in the patient’s usual emotional reactivity, are exaggerated or incongruent with the patient’s subjective emotional state, and are independent or in excess of an eliciting stimulus
- Symptoms cause clinically significant distress or impairment in social or occupational functioning
- The person may also experience outbreaks of anger
- Symptoms cannot be attributed to another neurologic or psychiatric disorder or to the effects of a substance
In patients with neurologic disorders, clinicians must carefully differentiate PBA from other conditions affecting behavior and cognition, including MDD and psychosis. For example, depression occurs in roughly 20% to 45% of people with Parkinson’s disease and MS and about 10% to 35% of people with stroke.12 Depending on the criteria used, 35% to 54% of patients with Alzheimer’s disease have MDD.13 Psychotic symptoms have been found in 41% of people with Alzheimer’s disease14 and about 25% of individuals with Parkinson’s disease.15,16
AV 5. Distinguishing PBA From Depression (01:56)
When distinguishing symptoms of depression from those of PBA, it is important to remember that depression is a disorder of mood, while PBA is a disorder of affect (AV 5).3 A depressed person can often mask or hide feelings of pain or hopelessness, and his or her affect is frequently flat. In PBA, crying or laughing outbursts are not able to be controlled and occur regardless of the person’s mood. However, given the high prevalence of depression among people with the neurologic conditions associated with PBA, it is not uncommon for these conditions to present concomitantly.17 An evidence-based guideline statement18 from the American Academy of Neurology (AAN) on assessment and management of psychiatric disorders in patients with MS recommends using the CNS-LS to screen for PBA (AV 6).19 The AAN recommends using the Beck Depression Inventory (BDI)20 and a 2-question tool that asks about mood and anhedonia21 to screen for depressive disorders and the General Health Questionnaire22 to screen for broadly defined emotional disturbances.
Family members are frequently the first to notice the onset of PBA symptoms—often before the patient does. However, because of the relatively low awareness and understanding of PBA, friends and family members may assume that the behavior is conscious or voluntary on the part of the patient. PBA can cause embarrassment in social situations, but many family members will not bring up the issue with a health care professional unless they are asked. If PBA is suspected, questioning family members separately may assist in the diagnostic process. The provider should first confirm that the individual is authorized to share the patient’s health care information.
Case Continuation
After speaking with Jessica’s husband, you consider the possibility of PBA, which affects close to half of people with MS.5 Because depression is also a common comorbidity in MS,12 you ask an advanced practice nurse to administer both the BDI and the CNS-LS. Jessica’s CNS-LS result of 18 and her normal BDI score suggest that PBA is more likely the cause of her emotional outbursts than depression. In subsequent conversation, Jessica says her outbursts seem to be brief and can “crop up out of nowhere.” Neither Jessica nor her husband had heard of PBA before. She is relieved to know that she is not alone and that her “overreacting” has a physical cause.
Treatment of PBA
PBA is an added burden to the significant difficulty of coping with a neurologic disease, making recognition and treatment important.3 Treatment options for PBA historically have centered on the antidepressant categories, including tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs) and selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs). The mechanisms of these agents are thought to act on diffuse neural networks. Thus, the use of antidepressants for PBA may be accompanied by unwanted adverse effects.23
Evidence supporting the off-label use of SSRIs and TCAs in PBA has come largely from case reports and small trials.3,17,24 The few placebo-controlled trials have mostly had small samples, often did not use validated measures or standardized PBA criteria, and did not systematically report adverse event data.3,17,24 In the largest placebo-controlled study,25 91 patients with previous stroke were treated for “emotional incontinence”; the use of the SSRI fluoxetine resulted in significant improvement over placebo in scores for “excessive or inappropriate crying.” The differences were not significant for “excessive or inappropriate laughter.”
Treatment options have recently expanded to include dextromethorphan plus quinidine, a sigma-1 agonist and a noncompetitive antagonist of the N-methyl-D-aspartate glutamate receptor.3,4 This agent is approved by the US Food and Drug Administration in a fixed-dose combination specifically for PBA.26
In a multicenter randomized study by Brooks et al,27 this fixed-dose combination was compared to either quinidine or dextromethorphan monotherapy for 28 days in 140 patients with ALS and PBA. On the primary efficacy outcome measure, the CNS-LS score, significantly greater improvements were found among patients treated with the combination compared with monotherapy with either dextromethorphan (P=.001) or quinidine (P<.001).27 Significantly lower episode rates were also found with the combination treatment than with either monotherapy (P<.01). In a 12-week placebo-controlled study by Panitch et al28 among 150 patients with MS, those treated with the combination had significantly lower CNS-LS scores (P<.0001) and experienced significantly fewer episodes consistent with PBA (P≤.0077) compared with those receiving placebo. Because of the low doses in the dextromethorphan/quinidine combination, safety concerns with either drug alone are less relevant.26 Nevertheless, patients with PBA, who often have medical problems and take multiple medications, should be assessed for drug interactions and monitored for tolerability, especially if they are at risk for torsades de pointes.26 Dizziness, nausea, fatigue, and weakness appear to be the most common adverse effects.26
The AAN guideline18 for managing psychiatric disorders in people with MS states that insufficient evidence is available to support or refute the use of antidepressants for PBA. The guideline18 states that the combination of dextromethorphan and quinidine may be considered.
Conclusion
PBA is a frustrating condition that frequently goes untreated. Increased recognition by health care professionals and the public may allow more affected individuals to be diagnosed and receive appropriate treatment. Patients with PBA and their families should be reassured that they are not alone. Treatment selection should be tailored for the individual, keeping in mind issues relating to safety and tolerability as well as the patient’s ability to adhere to treatment.
Drug Names
dextromethorphan/quinidine (Nuedexta), fluoxetine (Prozac and others)
Clinical Points
- Consider the possibility of an increasing prevalence of PBA due to the potential for an increasing incidence of neurologic conditions among the aging population
- Ask patients with neurologic conditions associated with PBA about the presence of PBA symptoms, as they may not bring them up; if symptoms are present, use a preferred screening tool such as the Center for Neurologic Study-Lability Scale (CNS-LS)
- Distinguish PBA from depression or other neuropsychiatric conditions
- Treat patients to reduce the frequency and/or severity of PBA symptoms, weighing individual patient characteristics and evidence of efficacy and safety
Abbreviations
AAN= American Academy of Neurology, AD=Alzheimer’s disease, ALS=amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, BDI= Beck Depression Inventory, CNS-LS= Center for Neurologic Study-Lability Scale, MDD=major depressive disorder, MS=multiple sclerosis, PBA=pseudobulbar affect, PD=Parkinson’s disease, SSRI=selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor, TBI=traumatic brain injury, TCA=tricyclic antidepressant.
References
- Work SS, Colamonico JA, Bradley WG, et al. Pseudobulbar affect: an under-recognized and under-treated neurological disorder. Adv Ther. 2011;28(7):586–601. doi:10.1007/s12325-011-0031-3. PubMed
- Cummings JL, Arciniegas DB, Brooks BR, et al. Defining and diagnosing involuntary emotional expression disorder. CNS Spectr. 2006;11(6):1–7. PubMed
- Miller A, Pratt H, Schiffer RB. Pseudobulbar affect: the spectrum of clinical presentations, etiologies and treatments. Expert Rev Neurother. 2011;11(7):1077–1088. doi:10.1586/ern.11.68. PubMed
- King RR, Reiss JP. The epidemiology and pathophysiology of pseudobulbar affect and its association with neurodegeneration. Degener Neurol Neuromuscul Dis. 2013;2013(3):23–31. doi:10.2147/DNND.S34160. Full Text
- Brooks BR, Crumpacker D, Fellus J, et al. PRISM: a novel research tool to assess the prevalence of pseudobulbar affect symptoms across neurological conditions. PloS One. 2013;8(8):e72232. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0072232. PubMed
- World Health Organization. Mental health and older adults: fact sheet. World Health Organization. http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs381/en/. Published April 2016. Accessed June 23, 2016.
- Crumpacker DW, Fellus JL, Kantor D, et al. PRISM: a novel research tool to assess the prevalence of pseudobulbar affect symptoms across neurological conditions. Am J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2014;22(3):S115–S116. doi:10.1016/j.jagp.2013.12.133. Full Text
- Wilson SAK. Some problems in neurology: no. II, pathological laughing and crying. J Neurol Psychopathol. 1924;4(16):299–333. Full Text
- Parvizi J, Anderson SW, Martin CO, et al. Pathological laughter and crying: a link to the cerebellum. Brain. 2001;124(Pt 9):1708–1719. PubMed
- Haiman G, Pratt H, Miller A. Brain responses to verbal stimuli among multiple sclerosis patients with pseudobulbar affect. J Neurol Sci. 2008;271(1-2):137–147. doi:10.1016/j.jns.2008.04.017. PubMed
- Rabins PV, Arciniegas DB. Pathophysiology of involuntary emotional expression disorder. CNS Spectr. 2007;12(4 Suppl 5):17–22. PubMed
- Rickards H. Depression in neurological disorders: Parkinson’s disease, multiple sclerosis, and stroke. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2005;76(suppl_1):i48–i52. doi:10.1136/jnnp.2004.060426. Full Text
- Engedal K, Barca ML, Laks J, et al. Depression in Alzheimer’s disease: specificity of depressive symptoms using three different clinical criteria. Int J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2011;26(9):944–951. doi:10.1002/gps.2631. PubMed
- Ropacki SA, Jeste DV. Epidemiology of and risk factors for psychosis of Alzheimer’s disease: a review of 55 studies published from 1990 to 2003. Am J Psychiatry. 2005;162(11):2022–2030. doi:10.1176/appi.ajp.162.11.2022. PubMed
- Lee AH, Weintraub D. Psychosis in Parkinson’s disease without dementia: common and comorbid with other non-motor symptoms. Mov Disord. 2012;27(7):858–863. doi:10.1002/mds.25003. PubMed
- Mack J, Rabins P, Anderson K, et al. Prevalence of psychotic symptoms in a community-based Parkinson disease sample. Am J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2012;20(2):123–132. doi:10.1097/JGP.0b013e31821f1b41. PubMed
- Ahmed A, Simmons Z. Pseudobulbar affect: prevalence and management. Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2013;9:483–489. doi:10.2147/TCRM.S53906. PubMed
- Minden SL, Feinstein A, Kalb RC, et al. Evidence-based guideline: assessment and management of psychiatric disorders in individuals with MS: report of the Guideline Development Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology. Neurology. 2014;82(2):174–181. doi:10.1212/WNL.0000000000000013. PubMed
- Moore SR, Gresham LS, Bromberg MB, et al. A self report measure of affective lability. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1997;63(1):89–93. PubMed
- Beck AT, Ward CH, Mendelson M, et al. An inventory for measuring depression. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1961;4:561–571. PubMed
- Whooley MA, Avins AL, Miranda J, et al. Case-finding instruments for depression. J Gen Intern Med. 1997;12(7):439–445. doi:10.1046/j.1525-1497.1997.00076.x. Full Text
- Rabins PV, Brooks BR. Emotional disturbance in multiple sclerosis patients: validity of the General Health Questionnaire (GHQ). Psychol Med. 1981;11(2):425–427. PubMed
- Ferguson JM. SSRI antidepressant medications: adverse effects and tolerability. Prim Care Companion J Clin Psychiatry. 2001;3(1):22–27. Full Text
- Pioro EP. Current concepts in the pharmacotherapy of pseudobulbar affect. Drugs. 2011;71(9):1193–1207. doi:10.2165/11591450-000000000-00000. PubMed
- Choi-Kwon S, Han SW, Kwon SU, et al. Fluoxetine treatment in poststroke depression, emotional incontinence, and anger proneness: a double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Stroke. 2006;37(1):156–161. doi:10.1161/01.STR.0000190892.93663.e2. PubMed
- Schoedel KA, Morrow SA, Sellers EM. Evaluating the safety and efficacy of dextromethorphan/quinidine in the treatment of pseudobulbar affect. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2014;10:1161–1174. doi:10.2147/NDT.S30713. PubMed
- Brooks BR, Thisted RA, Appel SH, et al. Treatment of pseudobulbar affect in ALS with dextromethorphan/quinidine: a randomized trial. Neurology. 2004;63(8):1364–1370. PubMed
- Panitch HS, Thisted RA, Smith RA, et al. Randomized, controlled trial of dextromethorphan/quinidine for pseudobulbar affect in multiple sclerosis. Ann Neurol. 2006;59(5):780–787. doi:10.1002/ana.20828. PubMed
Find more articles on this and other psychiatry and CNS topics:
The Journal of Clinical Psychiatry
The Primary Care Companion for CNS Disorders
CME Background Information
Supported by an educational grant from Otsuka America Pharmaceutical, Inc.
Brought to you through the joint providership of the CME Institute of Physicians Postgraduate Press, Inc., and CMEology.
Participants may receive credit by reading the activity, correctly answering the posttest questions, and completing the evaluation.
Objective
After completing this educational activity, you should be able to:
- Use appropriate validated instruments to screen for PBA
- Implement strategies for improving the differential diagnosis of PBA
- Provide evidence-based pharmacologic treatment for PBA
Financial Disclosure
The faculty for this CME activity and the CME Institute and CMEology staffs were asked to complete a statement regarding all relevant personal and financial relationships between themselves or their spouse/partner and any commercial interest. The CME Institute has resolved any conflicts of interest that were identified. No member of the CME Institute or CMEology staffs reported any relevant personal financial relationships. Faculty financial disclosure is as follows:
Dr David W. Crumpacker is a member of the speakers/advisory boards for Avanir, Otsuka, Merck, and Forest and is a stock shareholder of Pfizer.
Accreditation Statement
This activity has been planned and implemented in accordance with the Essential Areas and policies of the Accreditation Council for Continuing Medical Education (ACCME) through the joint providership of the CME Institute of Physicians Postgraduate Press, Inc., and CMEology. The CME Institute of Physicians Postgraduate Press, Inc., is accredited by the ACCME to provide continuing medical education for physicians.
Credit Designation
The CME Institute of Physicians Postgraduate Press, Inc., designates this enduring material for a maximum of 1 AMA PRA Category 1 Credit™. Physicians should claim only the credit commensurate with the extent of their participation in the activity.
The American Academy of Physician Assistants (AAPA) accepts certificates of participation for educational activities certified for AMA PRA Category 1 Credit™ from organizations accredited by ACCME or a recognized state medical society. Physician assistants may receive a maximum of 1 hour of Category I credit for completing this program.
To obtain credit for this activity, study the material and complete the CME Posttest and Evaluation.
Release, Review, and Expiration Dates
This Psychlopedia activity was published in July 2016 and is eligible for AMA PRA Category 1 Credit™ through July 31, 2017. The latest review of this material was June 2016.
Statement of Need and Purpose
Pseudobulbar affect (PBA) is a socially debilitating condition that affects a large portion of patients with neurologic diseases, such as multiple sclerosis, Parkinson’s disease, Alzheimer’s disease, and traumatic brain injury. This condition is widely underrecognized and misunderstood among the public and health care providers. With the association between PBA and some neurologic conditions related to aging, the incidence of this syndrome is likely to increase as the population ages. Because PBA is frequently mistaken for depression, psychiatrists need to be familiar with the differential diagnosis. Psychiatrists and other health care professionals who treat patients with neurologic conditions need updated guidance on how to screen patients for PBA, how to differentiate its symptoms from those of mood disorders, and how to implement evidence-based management approaches.
This activity was designed to meet the needs of participants in CME activities provided by the CME Institute of Physicians Postgraduate Press, Inc., who have requested information on pseudobulbar affect.
Disclosure of Off-Label Usage
Dr Crumpacker has determined that, to the best of his knowledge, dextromethorphan hydrobromide, fluoxetine, and quinidine sulfate are not approved by the US Food and Drug Administration for the treatment of pseudobulbar affect.
Review Process
The faculty reviewed the activity for accuracy and fair balance, and a member of the External Advisory CME Board who is without conflict of interest peer-reviewed the activity to determine whether the material is evidence-based and objective.
Acknowledgment
The opinions expressed herein are those of the faculty and do not necessarily reflect the opinions of the CME provider and publisher or the commercial supporter.