Background: Cariprazine is an atypical antipsychotic currently under investigation as adjunctive therapy in patients with major depressive disorder (MDD) who have inadequate response to standard antidepressant therapy.
Method: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, flexible-dose study was conducted from December 2011 to December 2013 in adults who met DSM-IV-TR criteria for MDD and had an inadequate antidepressant response. Eligible patients were randomized to 8-week adjunctive treatment with placebo (n = 269), cariprazine 1-2 mg/d (n = 274), or cariprazine 2-4.5 mg/d (n = 276). The primary efficacy parameter was change from baseline to week 8 in Montgomery-Asberg Depression Rating Scale (MADRS) total score; P values were adjusted for multiple comparisons. Safety assessments included adverse events, clinical laboratory tests, vital signs, electrocardiograms (ECGs), and suicidality.
Results: Compared with placebo, reduction in MADRS total score at week 8 was significantly greater with adjunctive cariprazine 2-4.5 mg/d (least squares mean difference [LSMD] = -2.2; adjusted P = .0114), but not with cariprazine 1-2 mg/d (LSMD = −0.9; adjusted P = .2404). Significant LSMDs for MADRS total score change were detected at all earlier study visits (weeks 2, 4, 6) in the 2- to 4.5-mg/d group and at weeks 2 and 4 in the 1- to 2-mg/d group (all P values < .05). Treatment-emergent adverse events reported in ≥ 10% of patients in either cariprazine dosage group were akathisia (22.3%), insomnia (13.6%), and nausea (12.8%) (all in 2- to 4.5-mg/d group). Mean changes in metabolic parameters, vital signs, and ECG parameters were generally similar between groups. No suicide-related adverse events were reported.
Discussion: These results show that adjunctive cariprazine 2-4.5 mg/d was effective and generally well tolerated in adults with MDD who had inadequate responses to standard antidepressants. Further clinical studies to confirm these results are warranted.
Trial Registration: ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT01469377
Efficacy and Safety of Adjunctive Cariprazine
in Inadequate Responders to Antidepressants:
A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Study
in Adult Patients With Major Depressive Disorder
ABSTRACT
Background: Cariprazine is an atypical antipsychotic currently under investigation as adjunctive therapy in patients with major depressive disorder (MDD) who have inadequate response to standard antidepressant therapy.
Method: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, flexible-dose study was conducted from December 2011 to December 2013 in adults who met DSM-IV-TR criteria for MDD and had an inadequate antidepressant response. Eligible patients were randomized to 8-week adjunctive treatment with placebo (n = 269), cariprazine 1–2 mg/d (n = 274), or cariprazine 2–4.5 mg/d (n = 276). The primary efficacy parameter was change from baseline to week 8 in Montgomery-Asberg Depression Rating Scale (MADRS) total score; P values were adjusted for multiple comparisons. Safety assessments included adverse events, clinical laboratory tests, vital signs, electrocardiograms (ECGs), and suicidality.
Results: Compared with placebo, reduction in MADRS total score at week 8 was significantly greater with adjunctive cariprazine 2–4.5 mg/d (least squares mean difference [LSMD] = –2.2; adjusted P = .0114), but not with cariprazine 1–2 mg/d (LSMD = −0.9; adjusted P = .2404). Significant LSMDs for MADRS total score change were detected at all earlier study visits (weeks 2, 4, 6) in the 2- to 4.5-mg/d group and at weeks 2 and 4 in the 1- to 2-mg/d group (all P values < .05). Treatment-emergent adverse events reported in ≥ 10% of patients in either cariprazine dosage group were akathisia (22.3%), insomnia (13.6%), and nausea (12.8%) (all in 2- to 4.5-mg/d group). Mean changes in metabolic parameters, vital signs, and ECG parameters were generally similar between groups. No suicide-related adverse events were reported.
Discussion: These results show that adjunctive cariprazine 2–4.5 mg/d was effective and generally well tolerated in adults with MDD who had inadequate responses to standard antidepressants. Further clinical studies to confirm these results are warranted.
Trial Registration: ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT01469377
J Clin Psychiatry 2016;77(3):371–378
dx.doi.org/10.4088/JCP.15m10070
© Copyright 2016 Physicians Postgraduate Press, Inc.
aForest Research Institute (an Allergan affiliate), Jersey City, New Jersey
bGedeon Richter Plc, Budapest, Hungary
cDepartment of Psychiatry, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston
dImperial College School of Science and Medicine, University of London, London, United Kingdom
*Corresponding author: Suresh Durgam, MD, Forest Research Institute, Clinical Development, Harborside Financial Center, Jersey City, NJ 07311 ([email protected]).
Despite many available approved drugs for major depressive disorder (MDD), approximately half of patients fail to achieve adequate response to initial antidepressant treatment and effective management of MDD remains a considerable challenge.1,2 In addition to antidepressant switching,3 augmentation with different classes of drugs may provide advantages for achieving optimal treatment effects.4 Atypical antipsychotics have been used adjunctively with antidepressant treatment to improve response, with some demonstrating efficacy in randomized, controlled trials.5,6 Currently, aripiprazole, quetiapine extended release, and brexpiprazole are the only antipsychotics approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for the adjunctive treatment of MDD.7–9 When adding an antipsychotic to an antidepressant regimen, it is important to consider the risk for adverse effects associated with this class of medication (eg, weight gain, extrapyramidal symptoms).5,6
Cariprazine, a dopamine D3 and D2 receptor partial agonist with preferential binding to D3 receptors, is an investigational drug in late-stage development for bipolar mania and schizophrenia. Cariprazine differs from other antipsychotics by exhibiting a 10-fold greater in vitro affinity for D3 versus D2 receptors10 and high and balanced in vivo occupancy of both D2 and D3 receptors at clinically relevant doses.11,12 Since the D3 receptor is preferentially expressed in areas of the brain associated with motivation and reward-related behavior,13 it has been identified as a potential pharmacologic target for depression treatment.14 Cariprazine also acts as a partial agonist at serotonin 5-HT1A receptors,10 which is a mechanism thought to enhance the neurochemical and behavioral effects of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs).15 These pharmacologic characteristics suggest that cariprazine may have potential clinical utility as an adjunctive treatment for MDD; the exact mechanisms by which cariprazine may alleviate depressive symptoms remain unknown.
In a previous phase 2 study16 of adjunctive cariprazine in adult MDD patients, cariprazine did not statistically separate from placebo at dose levels of 0.1–0.3 mg/d or 1–2 mg/d. The present phase 2 study was conducted to further evaluate the effects of adjunctive cariprazine at higher dosages (1–2 mg/d and 2–4.5 mg/d) in a larger sample of patients.
METHOD
Study Design
This was a multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group study (NCT01469377) of adjunctive flexible-dose cariprazine in adults with MDD and inadequate response to ongoing antidepressant treatment. The study was conducted from December 2011 to December 2013 at 76 study centers in the United States (41 centers) and Europe (35 centers) in compliance with International Council for Harmonisation (ICH) E6 Good Clinical Practice guidelines and the Declaration of Helsinki. All sites required institutional review board (US sites) or ethics committee/government agency (non-US sites) approval. All patients provided written, informed consent.
After 7–14 days of screening and washout of prohibited medications, eligible patients entered an 8-week, double-blind treatment period in which they continued antidepressant treatment and were randomized (1:1:1) to adjunctive cariprazine 1–2 mg/d, cariprazine 2–4.5 mg/d, or placebo. After double-blind treatment, patients entered a 1-week safety follow-up period.
Patients and study staff were blinded throughout treatment; patient identification and randomization codes were generated by an interactive voice/web system, and study medication was identical in appearance. Breaking the blind resulted in discontinuation from the study.
Participants
Male or female outpatients, ages 18 to 65 years, met DSM-IV-TR17 criteria for MDD without psychotic features and had a current depressive episode (duration ≥ 8 weeks to ≤ 24 months) before screening. All patients were required to have ongoing inadequate response during the current episode to antidepressant treatment for ≥ 6 weeks at recommended doses per label guidelines, as recorded using a psychotropic drug listing form. Per a protocol amendment, the Antidepressant Treatment History Form18 was implemented as a formal tool to document treatment history for the current depressive episode and allow investigators to indicate the reliability of their assessment; it was utilized with approximately 75% of enrolled patients. For these patients, inadequate response was defined as an antidepressant resistance rating score ≥ 3 (ie, failure to respond after ≥ 6 weeks of antidepressant treatment at the minimum FDA-recommended dosage or higher [matching the definition used since trial inception]) and global confidence score ≥ 3 (ie, adequate available information based on 1 or more reliable source).
Additional eligibility requirements included Montgomery-Asberg Depression Rating Scale (MADRS)19 total score ≥ 22, body mass index (kg/m2) ≥ 18 and ≤ 40, and normal results from physical examinations, clinical laboratory tests, and electrocardiogram (ECG) or abnormal results that were not considered clinically significant. The Structured Clinical Interview for DSM-IV-TR Axis I Disorders, Clinical Trials version (SCID-I-CT)20 was administered at screening.
Patients meeting any of the following DSM-IV-TR criteria were excluded: principal Axis I disorder other than MDD, or any Axis I disorder other than MDD that was the primary focus of treatment within 6 months of screening; any Axis II disorder that might interfere with participation as judged by the investigator; alcohol/substance abuse or dependence within 6 months of screening; or lifetime history of depressive episodes with psychotic or catatonic features, bipolar disorder, schizophrenia or other psychotic disorder, panic disorder, obsessive-compulsive disorder, anorexia or bulimia, and dementia or other cognitive disorder. Patients with suicide risk per investigator’s judgment, psychiatric interview, Columbia-Suicide Severity Rating Scale (CSSRS),21 or MADRS item 10 (suicidal thoughts, score ≥ 5) were not allowed to participate. Patients were excluded if they had a prior or concurrent medical condition that might interfere with study conduct, confound study results, or endanger patient well-being.
Treatment-related exclusion criteria included refractory depression (ie, inadequate response to ≥ 3 antidepressants at sufficient dosages and duration for the current episode); antidepressant augmentation with any medication (eg, antipsychotic, anticonvulsant/mood stabilizer, anxiolytic, benzodiazepines, second antidepressant) within 1 week of baseline (up to 4 weeks for some medications) or 5 half-lives of the medication, whichever was longer; concomitant use of antipsychotics, anxiolytics, mood stabilizers, or stimulants; or psychotherapy for depression within 3 months of screening.
Treatments
Antidepressant treatments were continued at stable doses per prescribing recommendations until the end of the study. All patients randomized to cariprazine started at 0.5 mg/d on days 1 and 2. In the cariprazine 1- to 2-mg/d group, dosage was increased to 1.0 mg/d on day 3 for at least the remainder of the first week of treatment. In the cariprazine 2- to 4.5-mg/d group, dosage was increased to 1.0 mg/d on day 3, 1.5 mg/d on day 4, and 2.0 mg/d on day 5 for at least the remainder of the first week. At the investigator’s discretion and as tolerated by the patient, cariprazine dosages were increased to 1.5 or 2.0 mg/d (1- to 2-mg/d group) or to 3.0 or 4.5 mg/d (2- to 4.5-mg/d group).
Efficacy Assessments
The primary and secondary efficacy parameters were change from baseline to week 8 in MADRS and Sheehan Disability Scale (SDS)22 total scores, respectively. Additional efficacy parameters included changes from baseline to week 8 in Clinical Global Impressions-Severity of Illness scale (CGI-S)23 score and SDS subscales; MADRS response, defined as ≥ 50% improvement from baseline in MADRS total score; CGI-Improvement scale (CGI-I)23 response, defined as CGI-I score ≤ 2; and MADRS remission, defined as MADRS total score ≤ 10. The MADRS and CGI-S were conducted at screening, baseline (week 0), and weeks 1, 2, 4, 6, and 8. The SDS was conducted at screening, baseline, and weeks 2, 4, 6, and 8; and the CGI-I at weeks 1, 2, 4, 6, and 8.
Safety Assessments
Adverse events, recorded at baseline and all subsequent visits, were defined as any untoward event that occurred between patient consent and 30 days after last dose of study drug. A nonleading question about overall well-being was asked to elicit volunteer adverse event reporting; patients were also queried about adverse events that had occurred since the previous visit. Severity, relationship to treatment, and seriousness were assessed by the investigator for each reported adverse event. Vital signs and body weight were recorded at screening, baseline, and all study visits. Electrocardiograms and laboratory tests were conducted at screening, week 4, and week 8. Extrapyramidal symptoms (EPS) were evaluated using the Barnes Akathisia Rating Scale (BARS),24 Abnormal Involuntary Movement Scale,25 and Simpson-Angus Scale (SAS).26 Suicidal ideation and behavior were monitored using the CSSRS.
Statistical Analyses
The safety population included all patients who received ≥ 1 dose of double-blind study drug. The intent-to-treat population included all patients in the safety population who had ≥ 1 postbaseline MADRS total score assessment.
MADRS, SDS, and CGI-S score changes were analyzed using a mixed-effects model for repeated measures with treatment group, study center, visit, and treatment group-by-visit interaction as fixed effects; baseline value and baseline-by-visit interaction were included as covariates. An unstructured covariance matrix was used to model the covariance of within-patient scores. For the primary and secondary end points (MADRS and SDS total scores, respectively), a matched parallel gatekeeping procedure was used to control the overall type I error rate for multiple comparisons of 2 active doses with placebo.27 The study was considered positive if at least 1 cariprazine dosage group was statistically superior to placebo for the primary end point after multiplicity adjustment. For response and remission, a logistic regression model was used to determine the odds ratio (OR) of active treatment versus placebo with last observation carried forward. For all efficacy outcomes, statistical hypothesis tests were 2-sided at a 5% level of significance for main effects. For applicable measures, 2-sided 95% confidence intervals (CIs) were also estimated. Descriptive statistics were used to summarize all safety outcomes.
On the basis of results from other MDD studies,16,28–30 it was estimated that 270 patients per treatment group would provide approximately 90% power to detect an effect size of 0.285 in at least 1 cariprazine dose group on the primary efficacy parameter at a 2-sided significance level of 5%.
RESULTS
Patients and Disposition
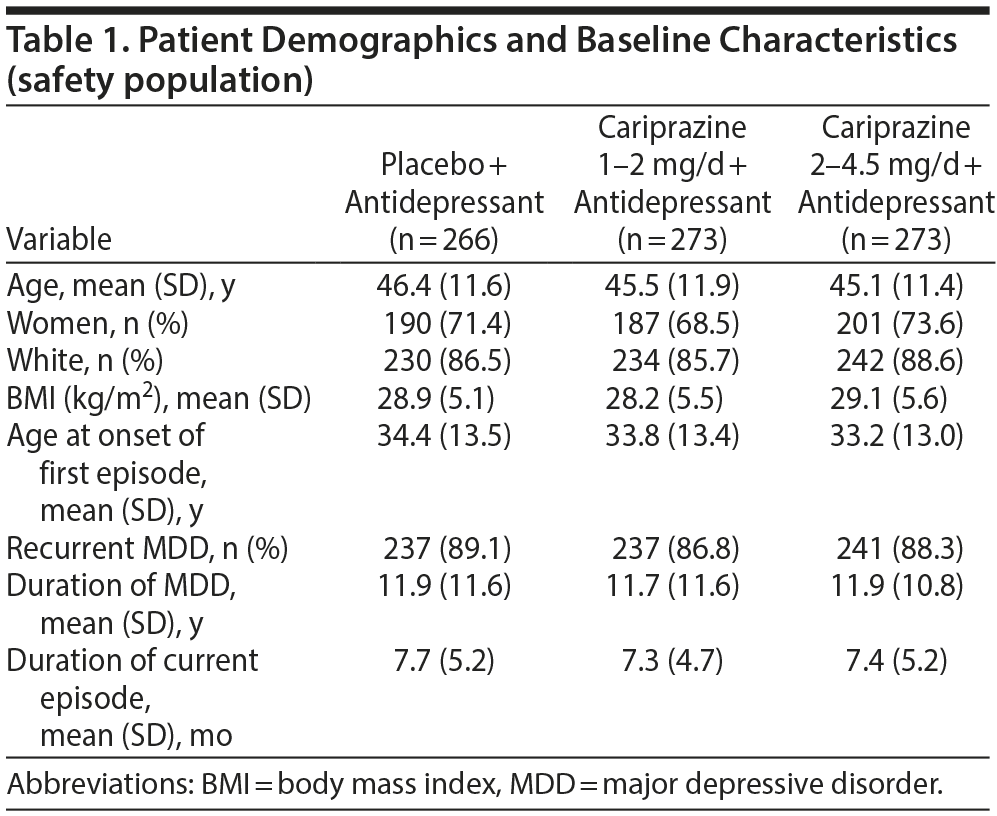
The safety population included 812 patients (Figure 1), 4 of whom (2 each for placebo and cariprazine 2–4.5 mg/d) did not have a postbaseline MADRS assessment and were excluded from efficacy analyses. Demographics and clinical characteristics were similar across groups (Tables 1 and 2). Of the patients in the safety population, 670 (82.5%) completed the study. Study completion was significantly lower in the cariprazine 2- to 4.5-mg/d group than in the placebo group (76.9% and 88.0%, respectively; P = .0010). Reasons for discontinuation were similar across all groups except for adverse events, which were more frequent with cariprazine 2–4.5 mg/d than placebo (13.2% and 3.0%, respectively; P < .0001).
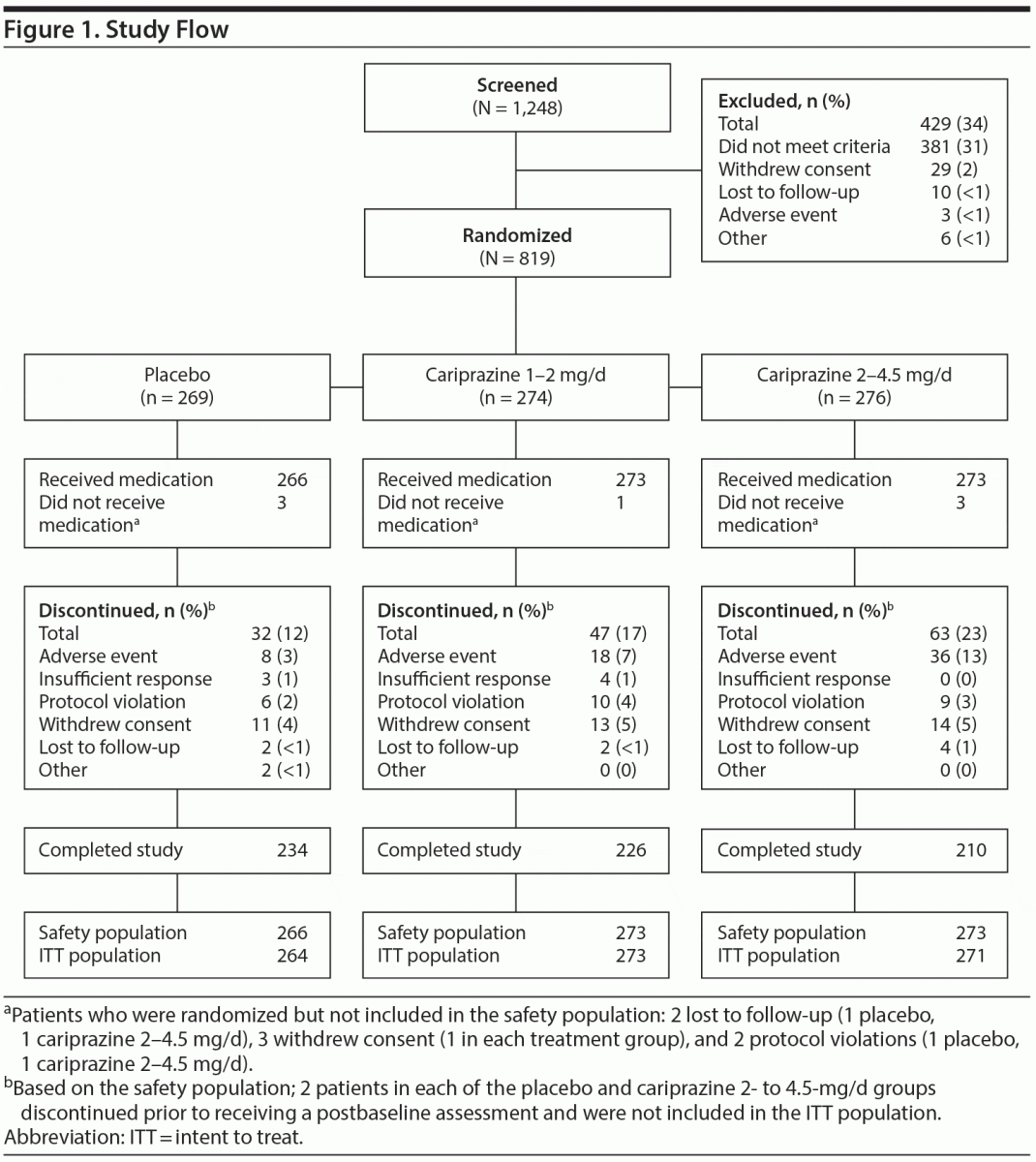
The Antidepressant Treatment History Form was administered to 615 patients in the safety population, 556 (90.4%) of whom had inadequate response to only 1 antidepressant (placebo, 90.5%; 1–2 mg/d, 91.0%; 2–4.5 mg/d, 89.7%). Sertraline (20.6%), citalopram (19.2%), escitalopram (18.2%), venlafaxine (11.8%), and duloxetine (10.8%) were the most common concurrent antidepressants in this study. Overall mean ± SD daily dose of cariprazine was 1.4 ± 0.3 mg/d and 2.6 ± 0.8 mg/d in the lower and higher dosage groups, respectively. Modal daily dose was 2 mg/d in > 40% of the patients in both cariprazine groups (1–2 mg/d, 42.1%; 2–4.5 mg/d, 44.0%). In the lower dosage group, 31.9% had a modal daily dose of 1 mg/d; 27.8% of patients in the higher dosage group had a modal daily dose of 4.5 mg/d.
Efficacy
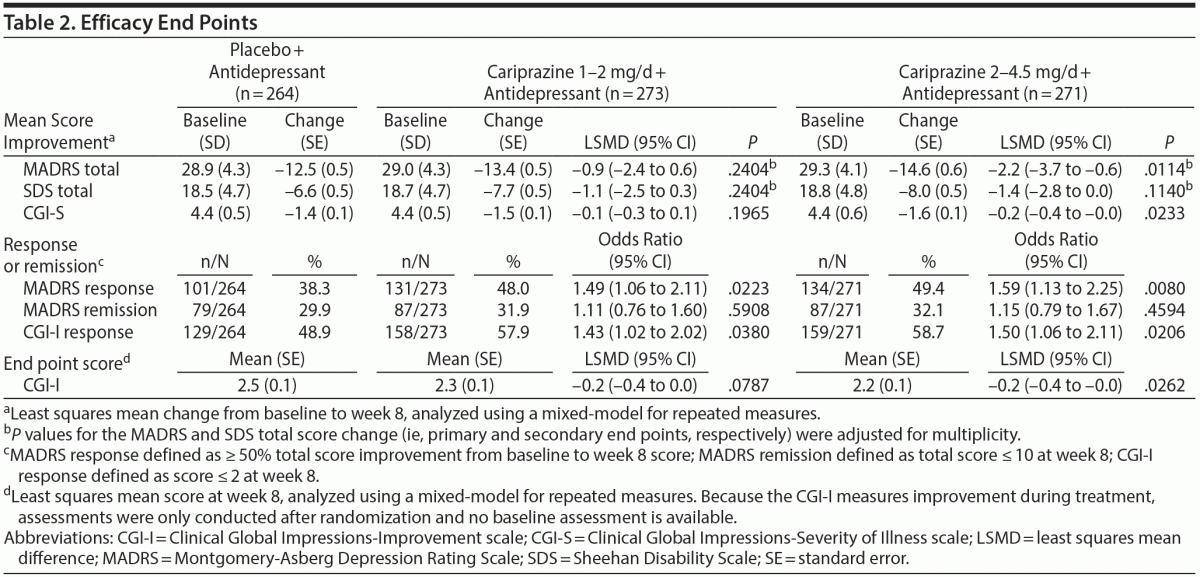
Patients receiving cariprazine 2–4.5 mg/d versus placebo had significantly greater mean reductions in MADRS total score by week 2 and at all subsequent study visits (Table 2, Figure 2A). At week 8, the least squares mean difference (LSMD) for cariprazine 2–4.5 mg/d versus placebo was –2.2 (95% CI, –3.7 to –0.6; P = .0057; adjusted, P = .0114). The LSMD at week 8 for cariprazine 1–2 mg/d was –0.9 (95% CI, –2.4 to 0.6; P = .2404; adjusted, P = .2404).
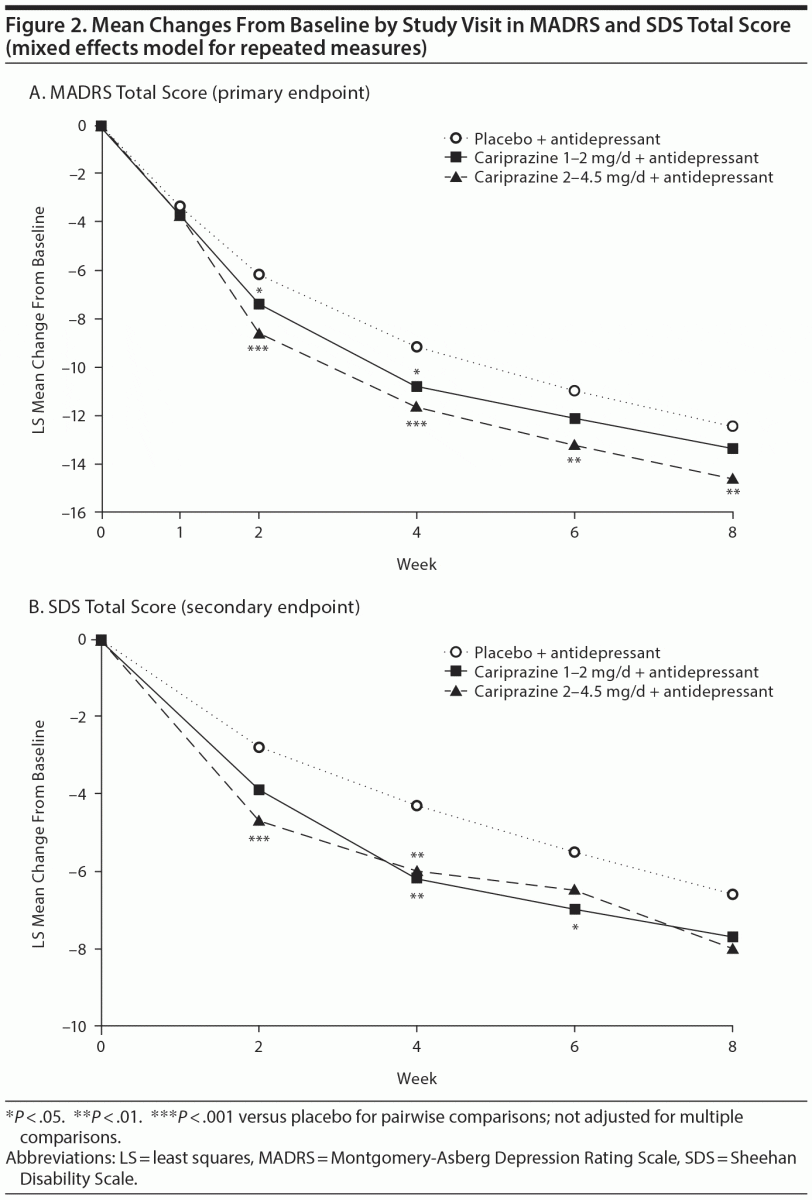
Significantly greater improvements in SDS total score were found in both cariprazine groups during double-blind treatment (Figure 2B), but no significant differences were detected at week 8 (Table 2). Mean change in SDS family/home was significantly greater with cariprazine 2–4.5 mg/d versus placebo at all study visits, including week 8 (placebo, –2.3; cariprazine 2–4.5 mg/d, –2.9; LSMD, –0.5; P = .0140). No significant improvements in SDS work/school and social life were found in either cariprazine group at week 8.
Additional efficacy results are presented in Table 2. Significantly greater global improvements and reduction in disease severity (CGI-I, CGI-S) were found with cariprazine 2–4.5 mg/d versus placebo. A significantly greater percentage of patients in both cariprazine groups met the criteria for MADRS response at week 8; significant differences from placebo for MADRS response were detected starting at weeks 2 and 3 in the cariprazine 2- to 4.5- and 1- to 2-mg/d groups, respectively (see Supplementary eFigure 1 at PSYCHIATRIST.COM). No statistically significant findings were detected for MADRS remission at week 8.
Safety
Adverse events. During double-blind treatment, serious adverse events were reported in < 1% of patients in all treatment groups (Table 3). These included 1 patient receiving placebo (depression) and 2 patients receiving cariprazine 2–4.5 mg/d (1 with agitation; 1 with panic attack, dyspnea, and noncardiac chest pain). No deaths occurred during the study. Treatment-emergent adverse events (TEAEs) that occurred in ≥ 10% of patients in either cariprazine group and at incidence greater than placebo were akathisia, insomnia, and nausea. Most TEAEs were judged by the investigator to be mild or moderate in intensity (placebo, 96.5%; 1–2 mg/d, 97.6%; 2–4.5 mg/d, 96.1%). Discontinuations due to adverse events occurred more frequently with cariprazine than with placebo. Akathisia was the only adverse event that led to discontinuation in ≥ 2% of patients in any treatment group (placebo, 0%; 1–2 mg/d, 0.4%; 2–4.5 mg/d, 4.8%).
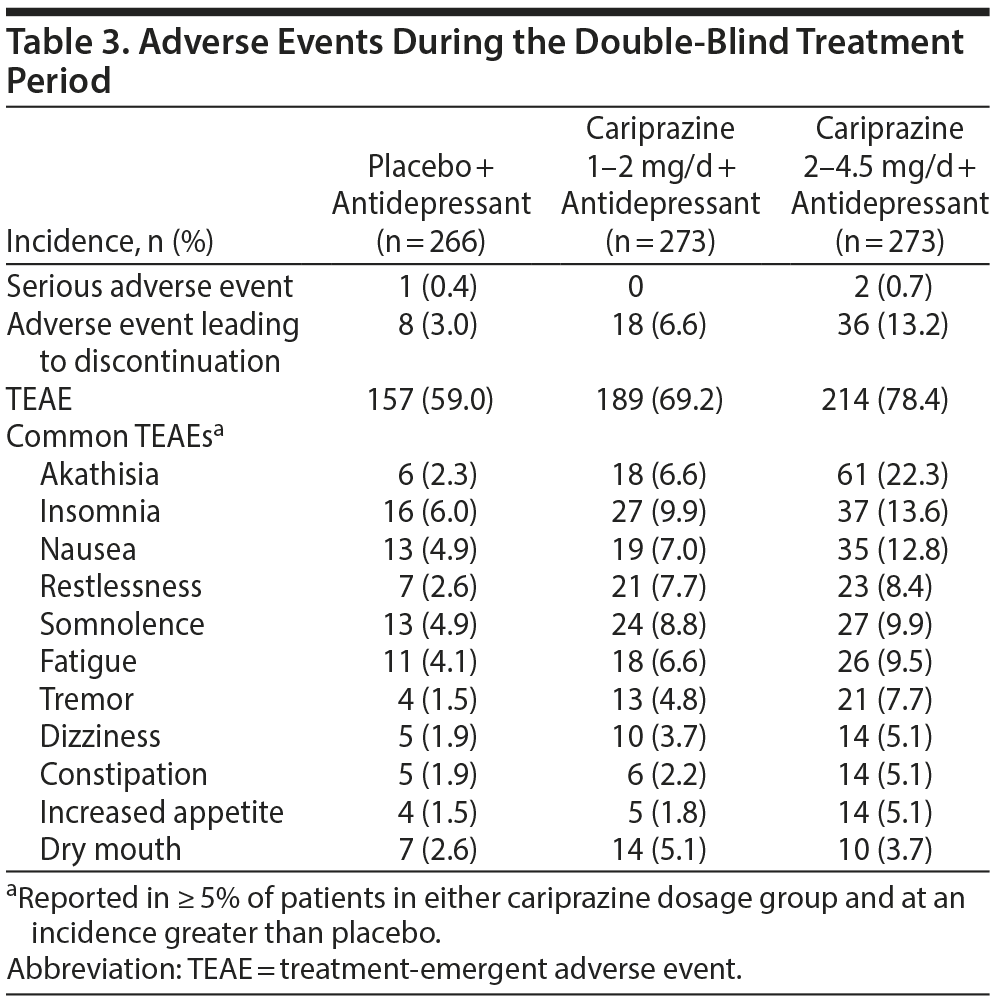
EPS-related events. Akathisia and restlessness occurred more frequently with cariprazine than with placebo (Table 3). Most incidences of akathisia were considered by the investigator to be mild or moderate in severity (placebo, 100%; cariprazine 1–2 mg/d, 100%; 2–4.5 mg/d, 93.4%). Excluding akathisia and restlessness, EPS-related TEAEs occurred in 6.2% and 11.0% of patients treated with cariprazine 1–2 and 2–4.5 mg/d, respectively, compared with 3.0% of placebo patients. Discontinuations due to these EPS-related TEAEs occurred in 0.7%, 1.1%, and 0.4% of patients in the cariprazine 1- to 2-mg/d, 2- to 4.5-mg/d, and placebo groups, respectively.
Per the SAS assessment (score ≤ 3 at baseline and > 3 postbaseline), treatment-emergent parkinsonism occurred in < 3% of patients in each treatment group. Treatment-emergent akathisia (BARS score ≤ 2 at baseline and > 2 postbaseline) occurred more frequently with cariprazine (1–2 mg/d, 8.1%; 2–4.5 mg/d, 21.4%) than with placebo (2.6%).
Vital signs, ECG, orthostatic hypotension. Mean changes in supine blood pressure and heart rate were similar across treatment groups (Table 4). The percentage of patients with ≥ 7% increase from baseline in body weight was low in all groups (placebo, 1.9%; 1–2 mg/d, 1.5%; 2–4.5 mg/d, 3.3%). The incidence of orthostatic hypotension was similar across treatment groups (placebo, 11.4%; 1–2 mg/d, 9.2%; 2–4.5 mg/d, 10.0%). Mean changes in ECG were also generally similar across groups, and no patient had a postbaseline QTc (Bazett or Fridericia correction) > 500 milliseconds.
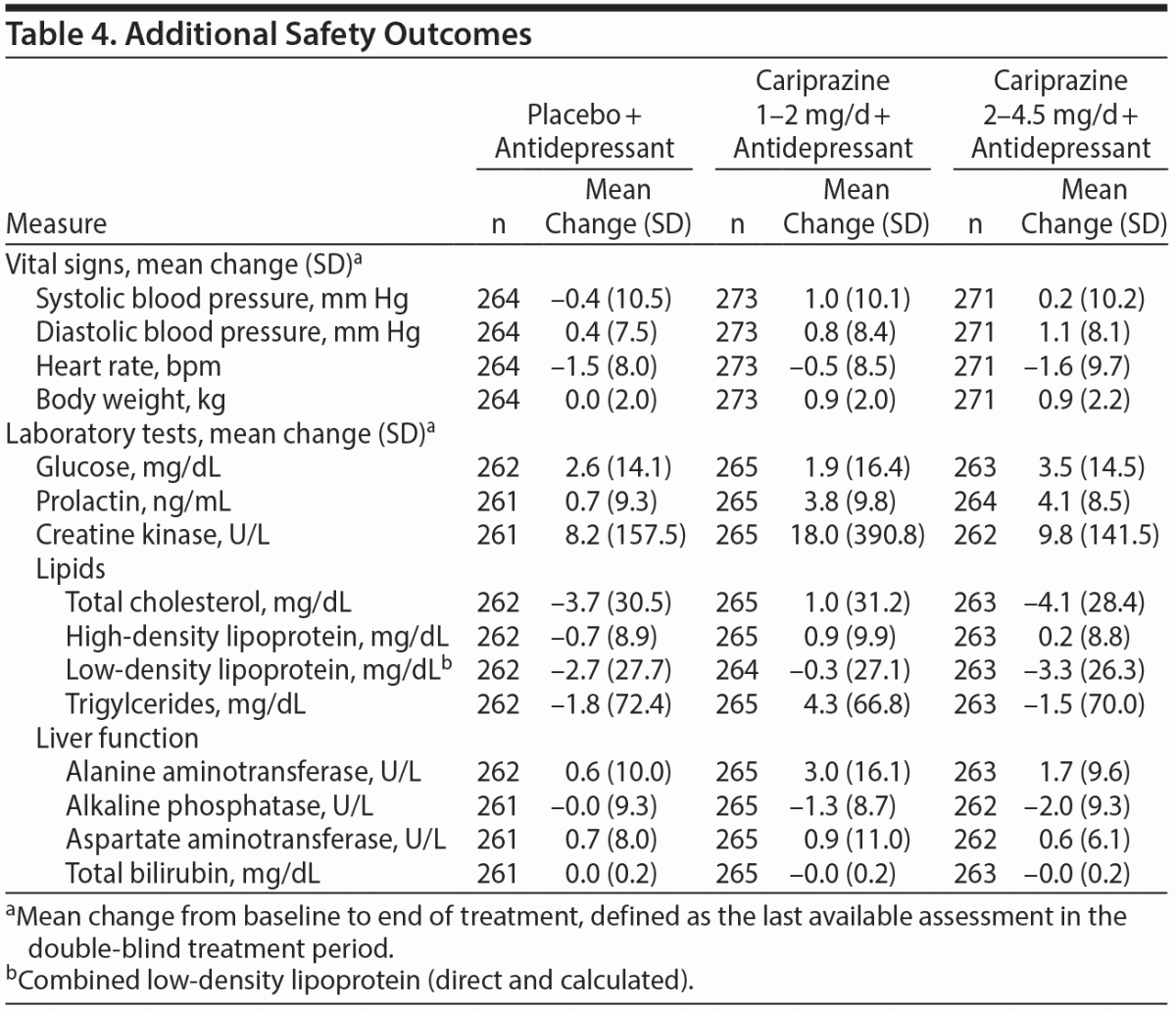
Clinical laboratory tests. Mean changes in clinical laboratory parameters were generally similar across treatment groups (Table 4). Small increases in prolactin were observed in all 3 groups, with larger increases with cariprazine (1–2 mg/d, 3.8 ng/mL; 2–4.5 mg/d, 4.1 ng/mL) than with placebo (0.7 ng/mL).
Suicidality. No patient reported suicidal ideation or behavior as a TEAE or serious adverse event. Per the C-SSRS assessment, there was no suicidal behavior during this study. The percentage of patients with CSSRS suicidal ideation was similar across treatment groups (placebo, 7.2%; 1–2 mg/d, 7.7%; 2–4.5 mg/d, 8.1%).
DISCUSSION
In this study, cariprazine 2–4.5 mg/d showed superior efficacy to placebo as measured by change in MADRS total score and was generally well tolerated as an adjunctive treatment in adult MDD patients with inadequate antidepressant response. The LSMD in MADRS total score change for cariprazine 2–4.5 mg/d versus placebo was –2.2 points, which exceeds the 2-point threshold that is commonly used to indicate a clinically relevant treatment effect.31 In addition, patients receiving higher-dose cariprazine also had significantly greater MADRS and CGI-I response rates relative to placebo. The 1–2 mg/d group did not show statistical significance versus placebo on the primary efficacy end point, although this dose group did show significantly higher MADRS and CGI-I response rates relative to placebo at week 8.
The significant effect of cariprazine 2–4.5 mg/d on the MADRS outcomes at week 2 suggests a fast onset of treatment effect, although more rapid effects (1 week) have been found with adjunctive antipsychotics in other MDD studies.32–34 The current study was designed to investigate dose-titration regimens, with increases made per investigator judgment, which may have delayed the onset of cariprazine effect. It is possible that starting with a low 0.5-mg/d dose in both cariprazine groups may have compromised efficacy, especially since patients who were titrated to only a minimum 1-mg/d dose (starting on day 3) had smaller treatment effects than patients titrated to a minimum 2-mg/d dose (starting on day 5).
The magnitude of effect (LSMD) and treatment response rates in this study were comparable to analyses of antidepressant efficacy in MDD trials that have been submitted to the FDA35,36 and European Union37 for approval. MADRS remission rates were also higher in both cariprazine groups relative to placebo, but the differences were not statistically significant. As is standard for acute MDD studies, this 8-week trial was not powered or designed to detect between-group differences for remission.
Based on MADRS response rates, the numbers needed to treat (NNTs) for cariprazine 1–2 mg/d and 2–4.5 mg/d were 11 and 9, respectively, with the higher dose meeting the generally accepted threshold of NNT ≤ 10 for clinical relevance in MDD patients.31 In making treatment decisions, results need to be weighed against the risk of adverse effects that may be unacceptable to some patients. Based on the number of patients who discontinued the study due to adverse events, the numbers needed to harm were 28 and 10 for cariprazine 1–2 and 2–4.5 mg/d, respectively.
Other safety considerations include the incidence of serious adverse events (< 1% in all treatment groups), the potential for suicidal ideation/behavior (no TEAEs reported in any treatment group), and TEAE severity (> 95% classified as mild or moderate in all treatment groups). The types and frequency of TEAEs in this study were generally similar to cariprazine monotherapy in bipolar mania.38,39 As seen with adjunctive antipsychotics in other MDD studies, TEAEs of potential concern (eg, akathisia, metabolic changes, weight gain) were found in the present study, with cariprazine results being generally comparable to published findings with other antipsychotics. For example, the reported incidence of akathisia with cariprazine 2–4.5 mg/d (22%) was similar to that reported for adjunctive aripiprazole treatment (25%).7 Clinically significant weight gain occurred less frequently with cariprazine 2–4.5 mg/d (3.3%) than previously reported for adjunctive aripiprazole or quetiapine (both 5%).7,8
The percentage of patients taking sertraline, citalopram, and escitalopram in this study was similar to general SSRI use, as indicated by health care utilization data from 2005 to 200740; however, use of serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor was slightly higher than previously reported (10% vs 6%). The minimum antidepressant resistance rating score of 3 on the Antidepressant Treatment History Form, which was used to define inadequate response in this study, is consistent with Stage I of the treatment-resistant depression model proposed by Thase and Rush and the definition of nonresponse proposed by Souery et al.41 Mean baseline MADRS total scores (approximately 30) also suggest that many patients in the study could have been considered nonresponders. Approximately 10% of patients did have an inadequate antidepressant response to > 1 medication; if from different drug classes, these patients would have met the Stage II criteria of the Thase and Rush model and the definition of treatment resistance used by European Medicines Agency.41 Although no conclusions can be drawn regarding patients with potential treatment resistance due to the relatively low sample size, further research is warranted to better understand the efficacy of adjunctive cariprazine in patients with various degrees of treatment nonresponse.
Limitations included the short study duration and no active comparator. Additionally, although the flexible-dose design may better represent real-world practice, no conclusions can be drawn about specific cariprazine dosages. Moreover, the 2-mg/d dose was allowed in both groups, which further confounds identification of optimal dosing for adjunctive cariprazine. By selecting for patients with inadequate antidepressant response, these results may not be generalizable to all patients with MDD. The exclusion of patients with primary Axis I disorders other than MDD and a lifetime history of various other disorders further limits the generalizability of these data. Patients were not stratified by treatment history; in clinical settings, decisions about whether individual patients should receive higher antidepressant dosages, be switched to a different antidepressant class, or receive an adjunctive antipsychotic remains a management issue for health care providers. Further studies are also needed to elucidate the optimal duration of adjunctive antipsychotic treatment and characterize the effect of switching adjunctive antipsychotic treatments.
Results from the present study compared favorably with a previous phase 2 study16 in which adjunctive cariprazine at very low doses (0.1–0.3 mg/d) was not effective but higher doses (1–2 mg/d) showed a signal toward efficacy. It seems likely that cariprazine doses were too low in the previous study considering the similar cariprazine 1- to 2-mg/d results in the 2 studies and the demonstrated efficacy with higher cariprazine 2–4.5 mg/d in the present study. Future studies are warranted to characterize the efficacy, safety, tolerability, and optimal dosing of cariprazine as an adjunctive treatment for adults with MDD.
Submitted: April 20, 2015; accepted October 1, 2015.
Drug names: aripiprazole (Abilify and others), brexpiprazole (Rexulti), cariprazine (Vraylar), citalopram (Celexa and others), duloxetine (Cymbalta and others), escitalopram (Lexapro and others), quetiapine (Seroquel and others), sertraline (Zoloft and others), venlafaxine (Effexor and others).
Potential conflicts of interest: Drs Durgam, Earley, Li, and Guo acknowledge a potential conflict of interest as employees of Forest Research Institute, an Allergan affiliate. Drs Durgam and Guo are stock shareholders of Forest Laboratories, an Allergan affiliate. Drs Németh and Laszlovszky acknowledge a potential conflict of interest as employees of Gedeon Richter Plc. Drs Németh and Laszlovszky are patent owners of the trial medication used in this study. Dr Fava’s disclosures can be viewed online at http://mghcme.org/faculty/faculty-detail/maurizio_fava. Dr Montgomery has been a consultant/speaker for or received consulting fees from Alkermes, AstraZeneca, Lundbeck, Pfizer, Pierre-Fabre Médicament, and Servier; has been a consultant for Gedeon Richter; and a consultant/speaker for Forest Laboratories (an Allergan affiliate).
Funding/support: Supported by funding from Forest Laboratories, LLC (Jersey City, New Jersey), an Allergan affiliate and Gedeon Richter Plc (Budapest, Hungary).
Role of the sponsor: Forest Laboratories, LLC, and Gedeon Richter Plc were involved in the study design, collection (via contracted clinical investigator sites), analysis and interpretation of data, and the decision to present these results.
Previous presentations: Presented at the 29th CINP World Congress; June 22–26, 2014; Vancouver, Canada ▪ the 53rd Annual Meeting of the American College of Neuropsychopharmacology; December 7–11, 2014; Phoenix, Arizona.
Acknowledgments: Writing assistance and editorial support for the preparation of this article were provided by Mildred Bahn, MA, and Paul Ferguson, MS, of Prescott Medical Communications Group, Chicago, Illinois, a contractor of Forest Research Institute, an Allergan affiliate.
Supplementary material: Available at PSYCHIATRIST.COM.
REFERENCES
1. Fava M. Diagnosis and definition of treatment-resistant depression. Biol Psychiatry. 2003;53(8):649–659. doi:10.1016/S0006-3223(03)00231-2 PubMed
2. Nemeroff CB. Prevalence and management of treatment-resistant depression. J Clin Psychiatry. 2007;68(suppl 8):17–25. PubMed
3. Fava M. Management of nonresponse and intolerance: switching strategies. J Clin Psychiatry. 2000;61(suppl 2):10–12. PubMed
4. Han C, Wang SM, Kato M, et al. Second-generation antipsychotics in the treatment of major depressive disorder: current evidence. Expert Rev Neurother. 2013;13(7):851–870. doi:10.1586/14737175.2013.811901 PubMed
5. Nelson JC, Papakostas GI. Atypical antipsychotic augmentation in major depressive disorder: a meta-analysis of placebo-controlled randomized trials. Am J Psychiatry. 2009;166(9):980–991. doi:10.1176/appi.ajp.2009.09030312 PubMed
6. Wright BM, Eiland EH 3rd, Lorenz R. Augmentation with atypical antipsychotics for depression: a review of evidence-based support from the medical literature. Pharmacotherapy. 2013;33(3):344–359. doi:10.1002/phar.1204 PubMed
7. Abilify (aripiprazole) [package insert]. Rockville, MD: Otsuka America Pharmaceutical, Inc; 2014.
8. Seroquel XR (quetiapine fumarate extended-release) [package insert]. Wilmington, DE: AstraZeneca Pharmaceuticals LP; 2013.
9. Rexulti (brexapiprazole) [package insert]. Rockville, MD: Otsuka America Pharmaceutical, Inc; 2015.
10. Kiss B, Horváth A, Némethy Z, et al. Cariprazine (RGH-188), a dopamine D(3) receptor-preferring, D(3)/D(2) dopamine receptor antagonist-partial agonist antipsychotic candidate: in vitro and neurochemical profile. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2010;333(1):328–340. doi:10.1124/jpet.109.160432 PubMed
11. Kiss B, Horti F, Bobok A. Cariprazine, a D3/D2 dopamine receptor partial agonist antipsychotic, displays greater D3 receptor occupancy in vivo compared with other antipsychotics. Schizophr Res. 2012;136(suppl 1):S190. doi:10.1016/S0920-9964(12)70588-1
12. Slifstein M, Abi-Dargham A, D’Souza DC, et al. Cariprazine demonstrates high dopamine D3 and D2 receptor occupancy in patients with schizophrenia: a clinical PET study with [11C]-(+)-PHNO. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2013;38(S2):S520.
13. Carnicella S, Drui G, Boulet S, et al. Implication of dopamine D3 receptor activation in the reversion of Parkinson’s disease-related motivational deficits. Transl Psychiatr. 2014;4(6):e401. doi:10.1038/tp.2014.43 PubMed
14. Leggio GM, Salomone S, Bucolo C, et al. Dopamine D(3) receptor as a new pharmacological target for the treatment of depression. Eur J Pharmacol. 2013;719(1–3):
25–33. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2013.07.022 PubMed
15. Celada P, Puig M, Amargós-Bosch M, et al. The therapeutic role of 5-HT1A and 5-HT2A receptors in depression. J Psychiatry Neurosci. 2004;29(4):252–265. PubMed
16. Hayes R, Bose A, Lu K, et al. A double-blind, placebo-controlled study of cariprazine as adjunctive therapy in major depressive disorder. Presented at: the Autumn Conference of the International Society for CNS Clinical Trials and Methodology; October 3–4, 2011; Amelia Island, Florida.
17. American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. Fourth Edition, Text Revision. Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Association; 2000.
18. Oquendo MA, Baca-Garcia E, Kartachov A, et al. A computer algorithm for calculating the adequacy of antidepressant treatment in unipolar and bipolar depression. J Clin Psychiatry. 2003;64(7):825–833. doi:10.4088/JCP.v64n0714 PubMed
19. Montgomery SA, Asberg M. A new depression scale designed to be sensitive to change. Br J Psychiatry. 1979;134(4):382–389. doi:10.1192/bjp.134.4.382 PubMed
20. First MB, Williams JBW, Spitzer RL, et al. Structured Clinical Interview for DSM-IV-TR Axis I Disorders, Clinical Trials Version (SCID-CT). New York, NY: Biometrics Research, New York State Psychiatric Institute; 2007.
21. Posner K, Brown GK, Stanley B, et al. The Columbia-Suicide Severity Rating Scale: initial validity and internal consistency findings from three multisite studies with adolescents and adults. Am J Psychiatry. 2011;168(12):1266–1277. doi:10.1176/appi.ajp.2011.10111704 PubMed
22. Sheehan DV, Harnett-Sheehan K, Raj BA. The measurement of disability. Int Clin Psychopharmacol. 1996;11(suppl 3):89–95. doi:10.1097/00004850-199606003-00015 PubMed
23. Guy W. ECDEU Assessment Manual for Psychopharmacology. US Dept Health, Education, and Welfare publication (ADM) 76-338. Rockville, MD: National Institute of Mental Health; 1976:218–222.
24. Barnes TR. A rating scale for drug-induced akathisia. Br J Psychiatry. 1989;154(5):672–676. doi:10.1192/bjp.154.5.672 PubMed
25. Guy W. ECDEU Assessment Manual for Psychopharmacology. US Dept Health, Education, and Welfare publication (ADM) 76-338. Rockville, MD: National Institute of Mental Health; 1976:534–537.
26. Simpson GM, Angus JW. A rating scale for extrapyramidal side effects. Acta Psychiatr Scand suppl. 1970;212(45):11–19. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0447.1970.tb02066.x PubMed
27. Chen X, Luo X, Capizzi T. The application of enhanced parallel gatekeeping strategies. Stat Med. 2005;24(9):1385–1397. doi:10.1002/sim.2005 PubMed
28. Bakish D, Bose A, Gommoll C, et al. Levomilnacipran ER 40 mg and 80 mg in patients with major depressive disorder: a phase III, randomized, double-blind, fixed-dose, placebo-controlled study. J Psychiatry Neurosci. 2014;39(1):40–49. doi:10.1503/jpn.130040 PubMed
29. Bauer M, Pretorius HW, Constant EL, et al. Extended-release quetiapine as adjunct to an antidepressant in patients with major depressive disorder: results of a randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind study. J Clin Psychiatry. 2009;70(4):540–549. doi:10.4088/JCP.08m04629 PubMed
30. El-Khalili N, Joyce M, Atkinson S, et al. Extended-release quetiapine fumarate (quetiapine XR) as adjunctive therapy in major depressive disorder (MDD) in patients with an inadequate response to ongoing antidepressant treatment: a multicentre, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2010;13(7):917–932. doi:10.1017/S1461145710000015 PubMed
31. Montgomery SA, Möller HJ. Is the significant superiority of escitalopram compared with other antidepressants clinically relevant? Int Clin Psychopharmacol. 2009;24(3):111–118. doi:10.1097/YIC.0b013e32832a8eb2 PubMed
32. Bauer M, El-Khalili N, Datto C, et al. A pooled analysis of two randomised, placebo-controlled studies of extended release quetiapine fumarate adjunctive to antidepressant therapy in patients with major depressive disorder. J Affect Disord. 2010;127(1–3):19–30. doi:10.1016/j.jad.2010.08.032 PubMed
33. Jon DI, Kim H, Seo HJ, et al. Augmentation of aripiprazole for depressed patients with an inadequate response to antidepressant treatment: a 6-week prospective, open-label, multicenter study. Clin Neuropharmacol. 2013;36(5):157–161. doi:10.1097/WNF.0b013e3182a31f3d PubMed
34. Pae CU, Jeon HJ, Lee BC, et al. Aripiprazole augmentation for treatment of patients with chronic or recurrent major depressive disorder: a 12-week prospective open-label multicentre study. Int Clin Psychopharmacol. 2013;28(6):322–329. doi:10.1097/YIC.0b013e3283643728 PubMed
35. Kirsch I, Deacon BJ, Huedo-Medina TB, et al. Initial severity and antidepressant benefits: a meta-analysis of data submitted to the Food and Drug Administration. PLoS Med. 2008;5(2):e45. doi:10.1371/journal.pmed.0050045 PubMed
36. Khin NA, Chen YF, Yang Y, et al. Exploratory analyses of efficacy data from major depressive disorder trials submitted to the US Food and Drug Administration in support of new drug applications. J Clin Psychiatry. 2011;72(4):464–472. doi:10.4088/JCP.10m06191 PubMed
37. Melander H, Salmonson T, Abadie E, et al. A regulatory Apologia—a review of placebo-controlled studies in regulatory submissions of new-generation antidepressants. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol. 2008;18(9):623–627. doi:10.1016/j.euroneuro.2008.06.003 PubMed
38. Durgam S, Starace A, Li D, et al. The efficacy and tolerability of cariprazine in acute mania associated with bipolar I disorder: a phase II trial. Bipolar Disord. 2015;17(1):63–75. doi:10.1111/bdi.12238 PubMed
39. Sachs GS, Greenberg WM, Starace A, et al. Cariprazine in the treatment of acute mania in bipolar I disorder: a double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase III trial. J Affect Disord. 2015;174:296–302. doi:10.1016/j.jad.2014.11.018 PubMed
40. Vlahiotis A, Devine ST, Eichholz J, et al. Discontinuation rates and health care costs in adult patients starting generic versus brand SSRI or SNRI antidepressants in commercial health plans. J Manag Care Pharm. 2011;17(2):123–132. PubMed
41. Souery D, Papakostas GI, Trivedi MH. Treatment-resistant depression. J Clin Psychiatry. 2006;67(suppl 6):16–22. PubMed
This PDF is free for all visitors!