See letter by Fluegge

Intranasal Ketamine Treatment in an Adult With Autism Spectrum Disorder
Ketamine, a noncompetitive antagonist at the N-methyl-d-aspartate glutamate receptor, has been demonstrated in controlled clinical trials to rapidly decrease symptoms of depression in adults via intravenous infusion1 and has demonstrated promising results in an uncontrolled trial of intranasal infusion in adolescents with bipolar disorder.2 Other glutamatergic modulators, including d-cycloserine, amantadine, and memantine, have been the focus of drug development targeting core social impairment in autism spectrum disorder (ASD). However, to date, there have been no reports of ketamine treatment in individuals with ASD. In light of this, we present what is, to our knowledge, the first case report of an adult with ASD treated with intranasal ketamine.
Case report. Ms A, a 29-year-old woman with DSM-IV-defined ASD, major depressive disorder, anorexia nervosa, and obsessive-compulsive disorder, had a 15-year history of debilitating psychiatric illness including over 30 psychotropic medication trials, multiple hospitalizations, and electroconvulsive therapy. Despite extensive treatment, at presentation she suffered from social impairment, repetitive behaviors, sensory sensitivity, contamination fears, low weight, absent menstrual cycles, chronic purging, depressed mood, anhedonia, low energy, poor concentration, and chronic suicidality. Daily medications included selegiline transdermal, lamotrigine, naltrexone, and clonazepam when she consented to begin clinical treatment with intranasal ketamine in August 2013.
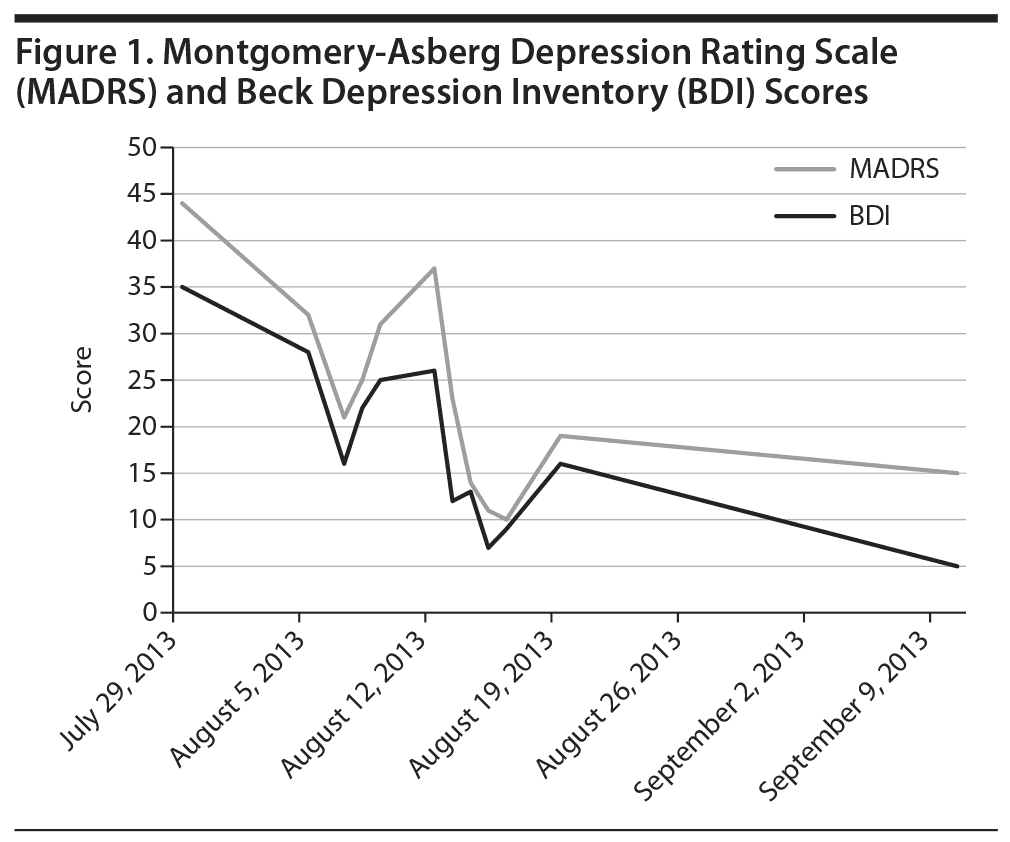
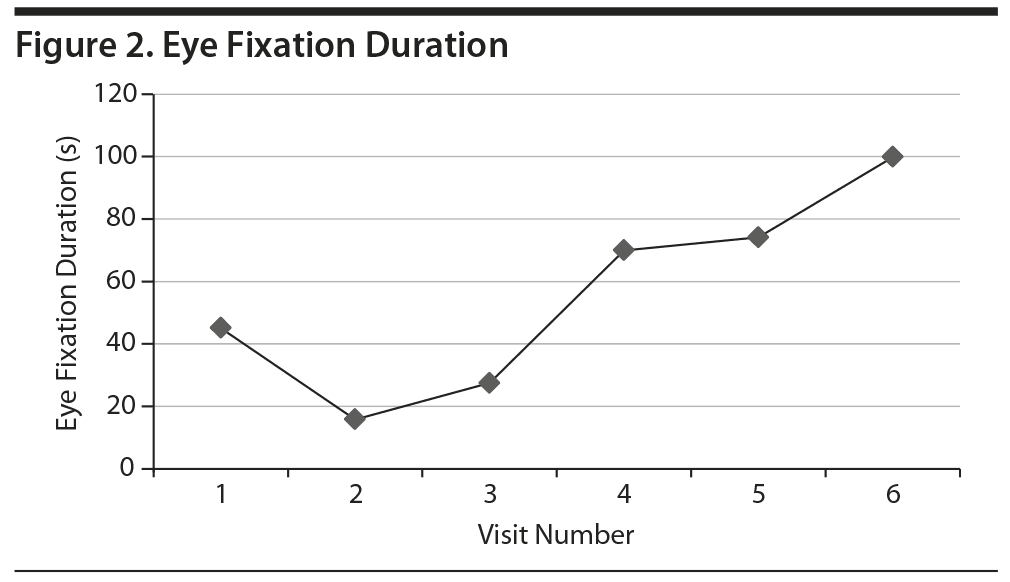
Within 24 hours following each self-administered intranasal dose of ketamine, Ms A reported significant improvement in mood and had dramatically improved Beck Depression Inventory and Montgomery-Asberg Depression Rating Scale scores (dose escalation as follows: 20 mg on day 1; 40 mg on days 7, 14, 17, 21, 24, and 27; 60 mg on days 30, 33, 37, 40, and 42) (Figure 1). The patient also reported increased ease of interacting with others, reduced urge to purge, more flexibility and tolerance of routine change, increased motivation, improved concentration, decreased suicidal thoughts, and feeling more connected to others. Eye tracking data employing the NimStim Stimulus Set3 were clinically measured prior to doses 1-6 of ketamine in an effort to track change in social interest. This tool measures the length of gaze fixation on the eye region of fearful, happy, or calm facial expressions. The length of the patient’s gaze fixation increased over the course of treatment (Figure 2). Intranasal ketamine was generally well tolerated, with adverse effects including only transient sedation, dizziness, numbness of limbs and face, blurred vision lasting approximately 90 minutes postdose, and headache lasting 6-10 hours postdose. Vital signs were monitored closely following each administration, and there was no notable change in heart rate, blood pressure, or body temperature.
This preliminary case report describes broad clinical improvement in mood in an adult with ASD and multiple comorbid psychiatric diagnoses via intranasal ketamine treatment. The significant change noted on the eye tracking paradigm may be reflective of several factors including desensitization to the eye tracking stimuli or improvement in depressed mood, or it may suggest improved social interest with treatment in this patient. This work is limited due to the single and complicated patient. However, the overall tolerability of intranasal ketamine coupled with broad clinical improvement suggests need for future study in the ASD population.
References
1. Zarate CA Jr, Singh JB, Carlson PJ, et al. A randomized trial of an N-methyl-d-aspartate antagonist in treatment-resistant major depression. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2006;63(8):856-864. PubMed doi:10.1001/archpsyc.63.8.856
2. Papolos DF, Teicher MH, Faedda GL, et al. Clinical experience using intranasal ketamine in the treatment of pediatric bipolar disorder/fear of harm phenotype. J Affect Disord. 2013;147(1-3):431-436. PubMed doi:10.1016/j.jad.2012.08.040
3. Tottenham N, Borscheid A, Ellertsen K, et al. Categorization of facial expressions in children and adults: establishing a larger stimulus set. Presented at: 9th Annual Meeting of the Cognitive Neuroscience Society; April 14-16, 2002; San Francisco, CA.
Corresponding author: Logan K. Wink, MD, Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center, 3333 Burnet Ave MLC 4002, Cincinnati, OH 45229 ([email protected]).
Author affiliations: Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center (Drs Wink, Shaffer, Pedapati, Schaefer, and Erickson and Ms Friedmann); and University of Cincinnati (Dr O’ Melia), Cincinnati, Ohio.
Submitted: December 2, 2013; accepted April 28, 2014.
Potential conflicts of interest: Dr Wink has been a consultant for Otsuka and has received grant/research support from Simons Foundation, John Merck Fund, US Department of Defense, Autism Speaks, SynapDx, and Cures Within Reach. Dr Shaffer has received grant/research support from Autism Speaks. Dr Erickson has been a consultant for Alcobra, Roche Group, and Confluence Pharmaceuticals; has received grant/research support from Simons Foundation, Angelman Syndrome Foundation, John Merck Fund, US Department of Defense, and Autism Speaks; and is a stock shareholder in Confluence Pharmaceuticals. Drs O’ Melia, Pedapati, and Schaefer and Ms Friedmann report no potential conflict of interest.
Funding/support: None reported.
J Clin Psychiatry 2014;75(8):835-836 (doi:10.4088/JCP.13cr08917).
© Copyright 2014 Physicians Postgraduate Press, Inc.