Objective: To evaluate the efficacy, safety, and tolerability of an oral extended-release (ER) formulation of the nonstimulant metadoxine in the treatment of adult attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD).
Method: This was a 1:1 randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-design, phase 2 study of metadoxine ER 1,400 mg/d treatment for 6 weeks, following a 2-week baseline/screening period, involving 120 adults with DSM-IV-defined ADHD. A follow-up assessment occurred 2 weeks after the trial was completed. Efficacy measures included changes in Conners’ Adult ADHD Rating Scale-Investigator Rated (CAARS-INV) total ADHD symptoms score with adult ADHD prompts (primary measure), response rates (≥ 25% or 40% improvement in CAARS-INV total ADHD symptom score), Test of Variables of Attention (TOVA) performance, and Adult ADHD Quality of Life (AAQoL) total score. The study was conducted from March 15, 2011, to August 21, 2011.
Results: Intent-to-treat analysis revealed that subjects receiving metadoxine ER showed statistically significant improvement in CAARS-INV total ADHD symptoms score (P = .02), higher rate of response (≥ 25% [P = .03] or ≥ 40% [P = .04] improvement) on the CAARS-INV total ADHD symptoms score, and improvement in TOVA score (P = .02) and AAQoL score (P = .01) compared with the placebo group. Improvements in ADHD symptoms (scored by CAARS-INV) were significantly different in subjects treated with metadoxine ER versus placebo as early as 2 weeks following treatment initiation. Metadoxine ER was generally well tolerated, with nausea (17% [10/58] vs 0% [0/59]), fatigue (31% [18/58] vs 27% [16/59]), and headaches (29% [17/58] vs 39% [23/59]) being the most frequently reported adverse effects for the metadoxine ER and placebo groups, respectively.
Conclusions: Findings suggest that metadoxine ER is a well-tolerated and effective treatment for adults with ADHD.
Trial Registration: ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT01243242
J Clin Psychiatry 2012;73(12):1517-1523
© Copyright 2012 Physicians Postgraduate Press, Inc.
Submitted: March 7, 2012; accepted October 4, 2012(doi:10.4088/JCP.12m07767).
Corresponding author: Lenard A. Adler, MD, Psychiatry and Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, NYU School of Medicine, 650 First Ave, 7th Floor, New York, NY 10016 ([email protected]).
A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled,
Multicenter Study Evaluating the Efficacy, Safety,
and Tolerability of Extended-Release Metadoxine
in Adults With Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder
ABSTRACT
Objective: To evaluate the efficacy, safety, and tolerability of an oral extended-release (ER) formulation of the nonstimulant metadoxine in the treatment of adult attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD).
Method: This was a 1:1 randomized, double-blind,
placebo-controlled, parallel-design, phase 2 study
of metadoxine ER 1,400 mg/d treatment for 6 weeks, following a 2-week baseline/screening period, involving 120 adults with DSM-IV–defined ADHD. A follow-up assessment occurred 2 weeks after the trial was completed. Efficacy measures included changes in Conners’ Adult ADHD Rating Scale-Investigator Rated (CAARS-INV) total ADHD symptoms score with adult ADHD prompts (primary measure), response rates (≥ 25% or 40% improvement in CAARS-INV total ADHD symptom score), Test of Variables of Attention (TOVA) performance, and Adult ADHD Quality of Life (AAQoL) total score. The study was conducted from March 15, 2011, to August 21, 2011.
Results: Intent-to-treat analysis revealed that subjects receiving metadoxine ER showed statistically significant improvement in CAARS-INV total ADHD symptoms score (P = .02), higher rate of response (≥ 25% [P = .03] or ≥ 40% [P = .04] improvement) on the CAARS-INV total ADHD symptoms score, and improvement in TOVA score (P = .02) and AAQoL score (P = .01) compared with the placebo group. Improvements in ADHD symptoms (scored by CAARS-INV) were significantly different in subjects treated with metadoxine ER versus placebo as early as 2 weeks following treatment initiation. Metadoxine ER was generally well tolerated, with nausea (17% [10/58] vs 0% [0/59]), fatigue (31% [18/58] vs 27% [16/59]), and headaches (29% [17/58] vs 39% [23/59]) being the most frequently reported adverse effects for the metadoxine ER and placebo groups, respectively.
Conclusions: Findings suggest that metadoxine ER
is a well-tolerated and effective treatment for adults
with ADHD.
Trial Registration: ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT01243242
J Clin Psychiatry 2012;73(12):1517–1523
© Copyright 2012 Physicians Postgraduate Press, Inc.
Submitted: March 7, 2012; accepted October 4, 2012
(doi:10.4088/JCP.12m07767).
Corresponding author: Lenard A. Adler, MD, Psychiatry and Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, NYU School of Medicine, 650 First Ave, 7th Floor, New York, NY 10016 ([email protected]).
Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) is a common and morbid neuropsychiatric condition. Once believed to only affect children, ADHD is now known to persist into adolescence and adulthood in a sizeable number of cases.1–3 Approximately 4%–5% of adults worldwide are affected with ADHD.4
Adult ADHD is associated with increased health risks and health care costs, higher divorce rates, lower levels of socioeconomic attainment, lower academic achievement, unemployment and workplace deficits, increased risks for motor vehicle accidents, greater likelihood of additional psychiatric disorders, increased criminal activity and incarceration, and higher rates of substance use and abuse.5–7 Most adults with ADHD remain undiagnosed and untreated.4
While stimulants have been shown to be effective and safe for the treatment of ADHD, a significant percentage of adults with ADHD treated with stimulants either do not respond to or do not tolerate these treatments8; the utility of stimulants is hindered by the potential risk for abuse (stimulants are scheduled drugs9), and the magnitude of effect of nonstimulants in adult ADHD is less than that seen with stimulants.10 Consequently, it is important to develop safe and effective nonstimulant treatment alternatives.
MG01CI (hereafter referred to as metadoxine ER) is an extended-release oral nonstimulant formulation of metadoxine (pyridoxol l-2-pyrrolidone-5-carboxylate). Immediate-release metadoxine has been used in the treatment of acute alcohol intoxication and alcohol withdrawal syndrome for more than 30 years. Metadoxine ER demonstrated delayed time to maximum plasma concentration and extended half-life in a porcine model (data on file, Alcobra Ltd, 2012). The new extended-release metadoxine formulation prolongs the serum levels of metadoxine, increasing its clinical bioavailability, which may result in enhanced benefits.
Metadoxine is an ion-pair salt of pyridoxine (vitamin B6) and 2-pyrrolidone-5-carboxylate (PCA). Pyridoxine is a precursor of coenzymes such as pyridoxal phosphate. Pyridoxal phosphate–dependent enzymes are necessary in the biosynthesis of 4 key neurotransmitters: serotonin, epinephrine, norepinephrine, and γ-aminobutyric acid.11 PCA is present in the diet and is produced endogenously by enzymatic conversion of γ-glutamyl amino acids to PCA and free amino acids. In its use for acute alcohol intoxication, metadoxine hastens the elimination of alcohol from the blood and tissues, helping to decrease hepatotoxicity and reestablish the functional structure of the liver.12 Although the exact mechanism of action of metadoxine ER is unknown, preclinical studies have posited that metadoxine can increase striatal dopamine levels13,14; this potential effect on dopaminergic function provides a further rationale for investigating metadoxine in ADHD.
The potential use of metadoxine in the treatment of ADHD was previously observed in a proof-of-concept phase 2a, single-site, open-label, single-arm study in 38 adult ADHD subjects (data on file, Alcobra Ltd, October 2010). That study showed that a single 1,400-mg dose of metadoxine ER improved cognitive performance, as assessed through the neuropsychological continuous performance Test of Variables of Attention (TOVA) and subtests of the Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale. In that initial phase 2a study, a significant and rapid response was observed within 90 minutes and was sustained for at least 7 hours.
On the basis of these preliminary data, we conducted a 6-week, randomized, placebo-controlled, parallel-design, double-blind study to evaluate the efficacy, safety, and tolerability of treatment with MG01CI in adults with ADHD. We hypothesized that metadoxine ER would be effective and well tolerated.
METHOD
Subjects
Subjects were adult men and women, 18–50 years of
age, diagnosed with ADHD based on Diagnostic and
Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fourth Edition (DSM-IV) criteria as assessed by Adult ADHD Clinical Diagnostic Scale version 1.2 (ACDS v1.2),15 the Structured Clinical Interview for DSM-IV (SCID),16 and a Clinical Global Impressions-Severity of Illness scale (CGI-S)17 score of ≥ 4.
Study Design
This study was a multisite randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 2 study of extended-release metadoxine (metadoxine ER) at a dose of 1,400 mg/d for 6 weeks compared with placebo in a 1:1 ratio of 120 adults with ADHD (ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT01243242). Metadoxine ER is a 1:1 organic salt of pyridoxine and l-PCA that contains metadoxine 490 mg immediate release and 910 mg sustained release. The study consisted of 3 periods: (1) a screening period of up to 2 weeks, (2) a 6-week double-blind treatment period, and (3) a safety follow-up period 2 weeks after cessation of treatment, described as follows. The study was conducted from March 15, 2011, to August 21, 2011. Ethics committee approvals were obtained from Geha Mental Health Center, Petach Tikva, Israel, and Rambam Health Care Campus, Haifa, Israel, as well as from the Israeli Ministry of Health.
Screening Period—Visit 1 (days –14 to 0)
After informed consent was obtained, screening procedures were performed, including a battery of rating scales
for confirmation of ADHD diagnosis (ACDS v1.2), exclusion of other significant psychiatric comorbidities as assessed through the SCID, Beck Depression Inventory,18 and State-Trait Anxiety Inventory.19 Additional assessments included a continuous performance test—the TOVA,20 CGI-S, Adult ADHD Quality of Life Scale (AAQoL),21 Conners’ Adult ADHD Rating Scale-Investigator Rated total ADHD symptoms score (CAARS-INV) with NYU/MGH adult ADHD prompts,15,22,23 and Columbia-Suicide Severity Rating Scale (C-SSRS).24 Assessments included inclusion/exclusion criteria, demographic data, medical history, prior medications, neurologic examination, physical examination,
height and weight, vital signs, 12-lead electrocardiogram (ECG), laboratory evaluations including hematology (complete blood count), chemistry, urinalysis, and a urine pregnancy test for women of childbearing potential. All raters of these assessments received thorough training before and during the study for ACDS v1.2, CGI-S, and CAARS-INV with prompts. The plan for a successful training of study personnel for ADHD diagnostic and symptom assessment was based on established principles.25
Treatment Period—Visit 2 (day 0), Visit 3 (day 7),
Visit 4 (day 14), Visit 5 (day 28), and Visit 6 (day 42)
At visit 2 (day 0), eligible and consenting subjects were randomized in a 1:1 ratio to metadoxine ER 1,400 mg/d or placebo. Subjects were instructed to take the medication once daily at the start of their day until the next scheduled visit. There was no titration period; metadoxine ER dosing was 1,400 mg throughout the study. At study visits 3 (day 7), 4 (day 14), 5 (day 28), and 6 (day 42), subjects underwent evaluations using the CAARS-INV, TOVA, and AAQoL to assess treatment response.
At each visit, subjects also underwent safety assessments including recording of adverse events (AEs) (by patient report) and concomitant medications, laboratory evaluations, neurologic examination, physical examination, vital signs, 12-lead ECG, and C-SSRS. Study drug (used and unused) was collected at each of these visits for accountability purposes. Subjects meeting 85% treatment adherence were included in the efficacy per-protocol analysis.
Follow-Up Period—Visit 7 (day 56)
Two weeks after end of treatment, subjects underwent safety assessments including laboratory evaluations, physical examination, neurologic examination, vital signs, and 12-lead ECG, C-SSRS, and documentation of AEs, if any, that occurred during this period. After an amendment to
the study, most subjects were also evaluated at this point using CAARS-INV, TOVA, and AAQoL.
Primary Efficacy Measure
The primary efficacy measure was the change in CAARS-INV total ADHD symptoms score between the study groups from baseline/screening to treatment termination.
Secondary Efficacy and Functional Outcome Measures
Secondary measures compared differences between the baseline/screening visit and end of treatment with respect to (1) response rates as measured by percent of patients achieving predefined decreases (≥ 25% and > 40%) in CAARS-INV total ADHD symptoms score, (2) change in performance on TOVA ADHD score, and (3) change in the AAQoL total score.
Statistical Analyses
Efficacy analyses were conducted on the intent-to-treat population. The efficacy analyses used 2-sample t test and nonparametric Wilcoxon-Mann-Whitney rank sum test and the median test for independent samples for testing the statistical significance of the difference in changes in CAARS-INV total ADHD symptoms score from screening (visit 1) to end of treatment (visit 6) between groups. More stringent nonparametric statistics were used to ensure stability and increase confidence in the analysis and to rule out possibility of extreme (outlier) data points affecting outcome in a small population (eg, the median test). We have therefore prespecified both t test and nonparametric tests for analysis of the primary endpoint. Analysis of covariance (ANCOVA) was used to compare group differences in changes from visit 1 to visit 6 in both the primary endpoint and secondary endpoint scales with adjustment for confounders (baseline score, site, age, and gender). t Tests were applied for testing differences between the groups in changes in efficacy parameters (CAARS, AAQoL, and TOVA scores) from visit 6 to visit 7. Paired t test was applied for testing within-group changes in efficacy parameters (CAARS, AAQoL, and TOVA scores) from visit 6 to visit 7. Chi-square test was applied for testing the statistical significance of the difference between the study groups in the rates of responders. All tests applied were 2-tailed, and P value of 5% or less was considered statistically significant. Effect size was calculated as a standardized mean difference26 (Cohen d: [mean change metadoxine – mean change placebo]/pooled SD).
Secondary Analyses
Treatment response rates were calculated based on a priori determinations of ≥ 25% or 40% improvement in CAARS-INV total ADHD symptoms score from baseline (visit 1) to termination (visit 6), as done previously in an adult ADHD treatment (atomoxetine) trial.27 Use of these cutoffs is also supported by a study comparing linkage of changes in ADHD symptom ratings versus ratings of clinical global improvement in children and adults treated with lisdexamfetamine.28 Safety analyses were descriptive and based on the frequency of spontaneously reported AEs and on the observation of clinically significant abnormal laboratory values including vital signs and ECG.
RESULTS
Demographics
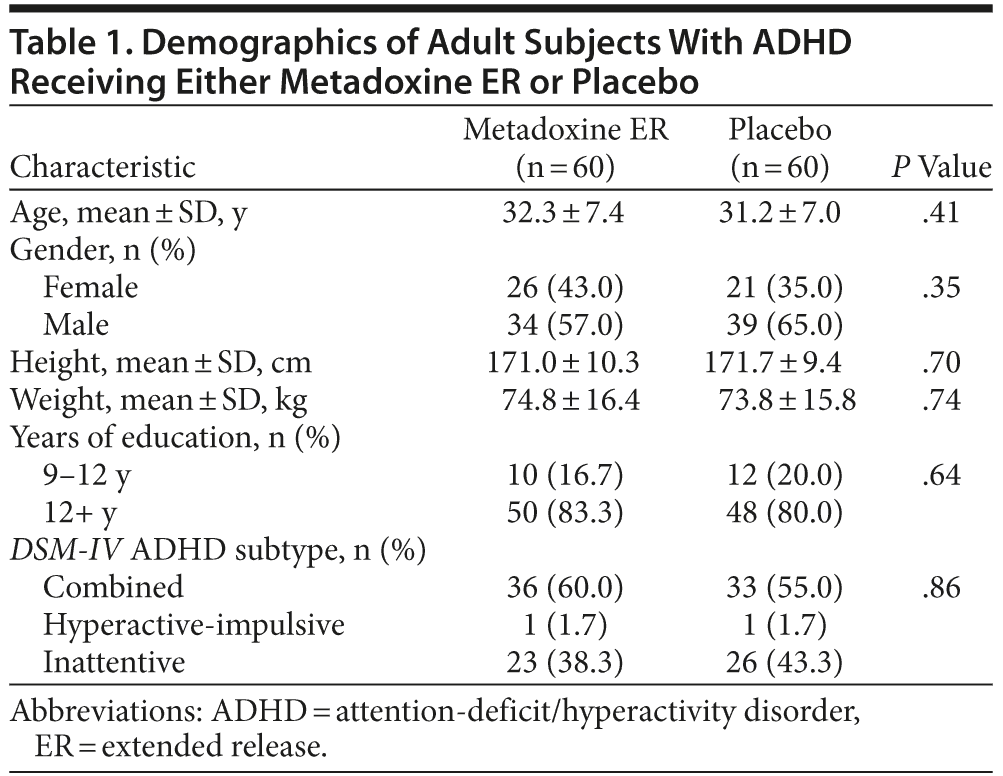
One hundred seventy-four patients were screened, and 54 patients were excluded, primarily because of exclusionary psychiatric comorbidity (Figure 1). Thus, 120 subjects who satisfied all inclusion and exclusion criteria were randomized; 60 to metadoxine ER and 60 to placebo. The age, sex distribution, and educational background of the sample were similar for the metadoxine ER and placebo groups (Table 1). All randomized subjects had a childhood onset of ADHD (prior to 7 years of age) and persistence of symptoms into adulthood. Most subjects (69/120; 57.5%) had combined type ADHD, while the remaining patients had predominantly inattentive type (49/120; 40.8%). Only 2 subjects, 1 in each arm, had hyperactive-impulsive type.
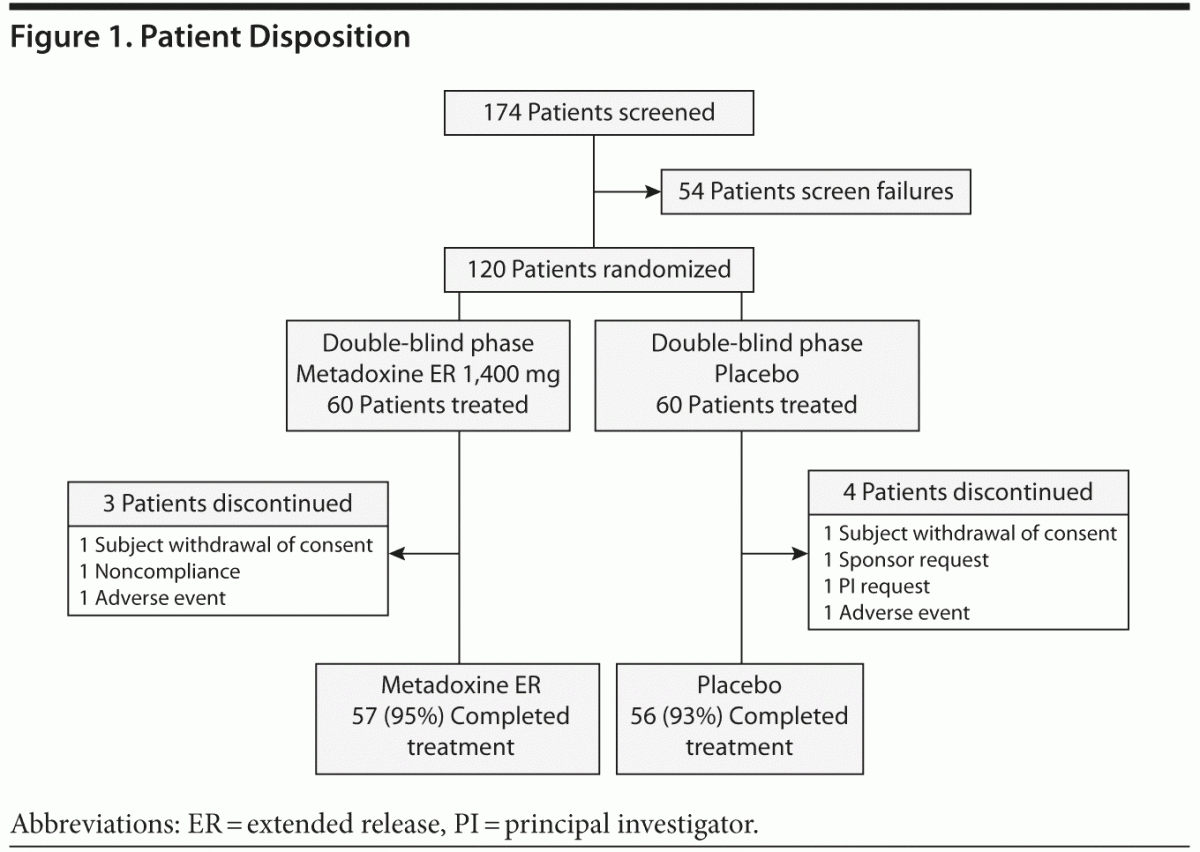
Seven (5.8%) of 120 subjects terminated the study prematurely (3 in the metadoxine ER group [5.0%], 4 in the placebo group [6.7%]). Of these, 1 subject (1.7%) in each study group discontinued due to AEs. Other reasons for premature discontinuation included withdrawal of consent (2 subjects, 1 in each group), noncompliance (1 subject in metadoxine ER group), investigator’s request (1 subject in placebo group; request due to patient account of extreme impulsivity and recklessness following medication), and sponsor’s request (1 subject in placebo group; request due to report of coexisting sleep apnea following randomization). A total of 113 subjects completed treatment: 57 (95%) of those in the metadoxine ER group and 56 (93%) of those in the placebo group.
Primary Efficacy Evaluation
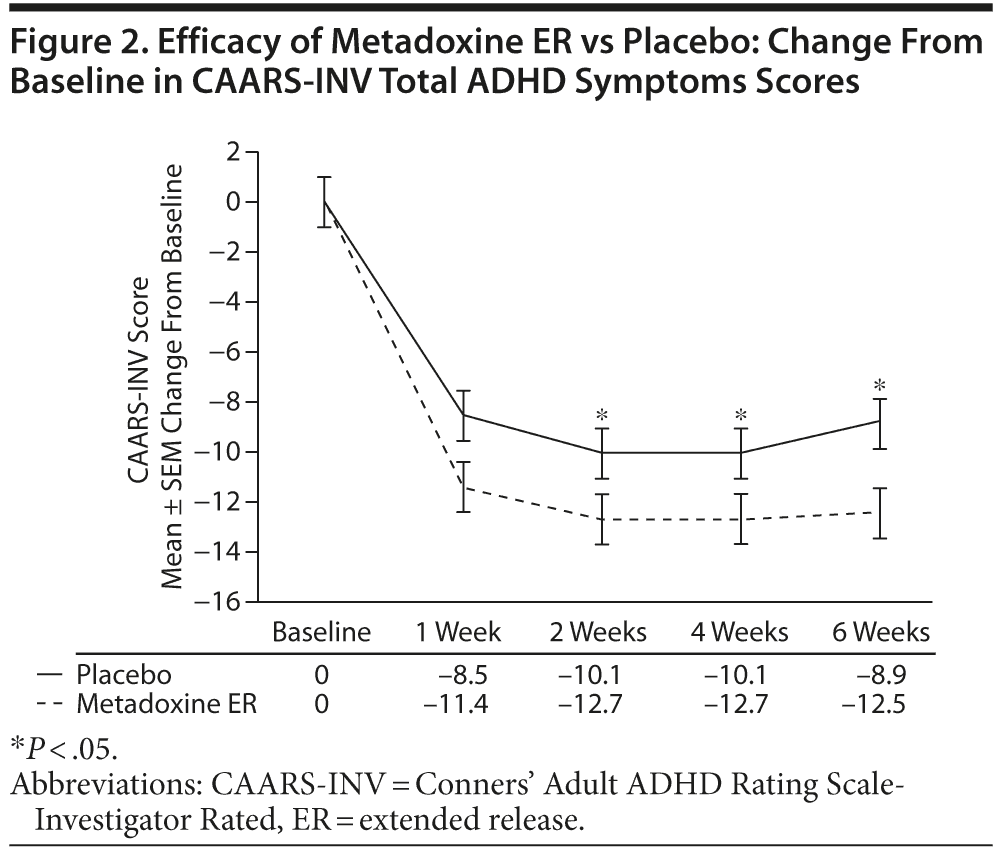
The mean ± SD CAARS-INV total ADHD symptoms score was 37.1 ± 8.4 in both study groups at screening. As shown in Figure 2, at the end of treatment, a mean decrease of 12.5 ± 8.8 points in CAARS-INV score was observed in the metadoxine ER group, versus a decrease of 8.9 ± 9.2 points in the placebo group (all calculated P values significant: by median test for independent samples, P = .02; by Wilcoxon, P = .02; by ANCOVA adjusted for baseline score, gender, site, and age, P = .03; and by t test, P = .04). The effect was observed as early week 1/visit 3 (P = .04, ANCOVA adjusted for baseline score, gender, site, and age). The effect size of metadoxine ER versus placebo on CAARS-INV total ADHD symptoms score was 0.4.
Secondary Outcomes: CAARS-INV Total ADHD Symptoms Score—Response Rates
A ≥ 25% improvement in CAARS-INV total ADHD symptoms score was shown at treatment endpoint in 55% (32/58) of the metadoxine ER subjects, compared with 34% (20/59) of those in the placebo group (Yates χ2: χ21 = 4.53, P = .03), while a > 40% improvement in CAARS-INV total ADHD symptoms score was shown at treatment endpoint in 43% (25/58) of the metadoxine ER subjects, compared with 24% (14/59) of those in the placebo group (Yates χ2: χ21 = 4.11, P = .04).
TOVA ADHD Scores
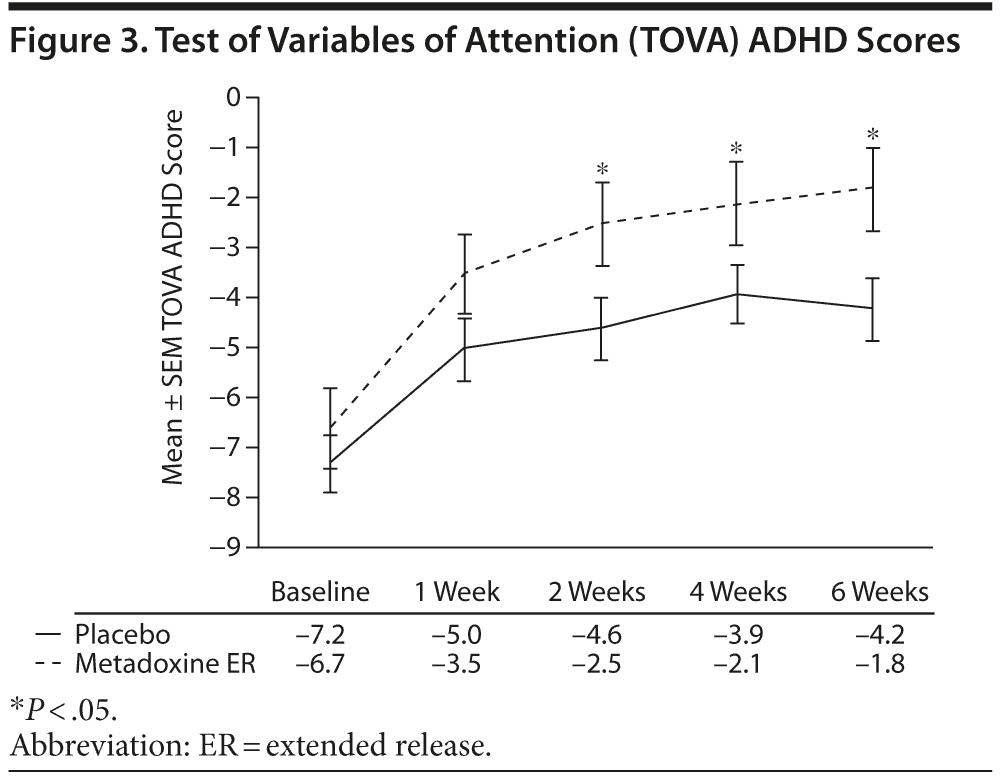
At screening, the mean ± SD TOVA ADHD score was −6.6 ± 8.5 in the metadoxine ER group compared with −7.3 ± 7.2 in the placebo group (Figure 3). From screening to end of treatment, a mean increase of 5.0 ± 8.9 points was observed in the ADHD scores of the metadoxine ER group compared to 3.0 ± 6.4 points in the placebo group (P = .02, adjusted for baseline score, gender, site, and age). A significant difference in change between groups was observed starting at week 2/visit 4 (P < .04 adjusted for baseline score, gender, site, and age). At the end of treatment, the mean ADHD score in the metadoxine ER group reached −1.8 ± 4.9, while the mean score in the placebo group was −4.2 ± 5.6, indicating significant clinical improvement in performance with metadoxine ER treatment.
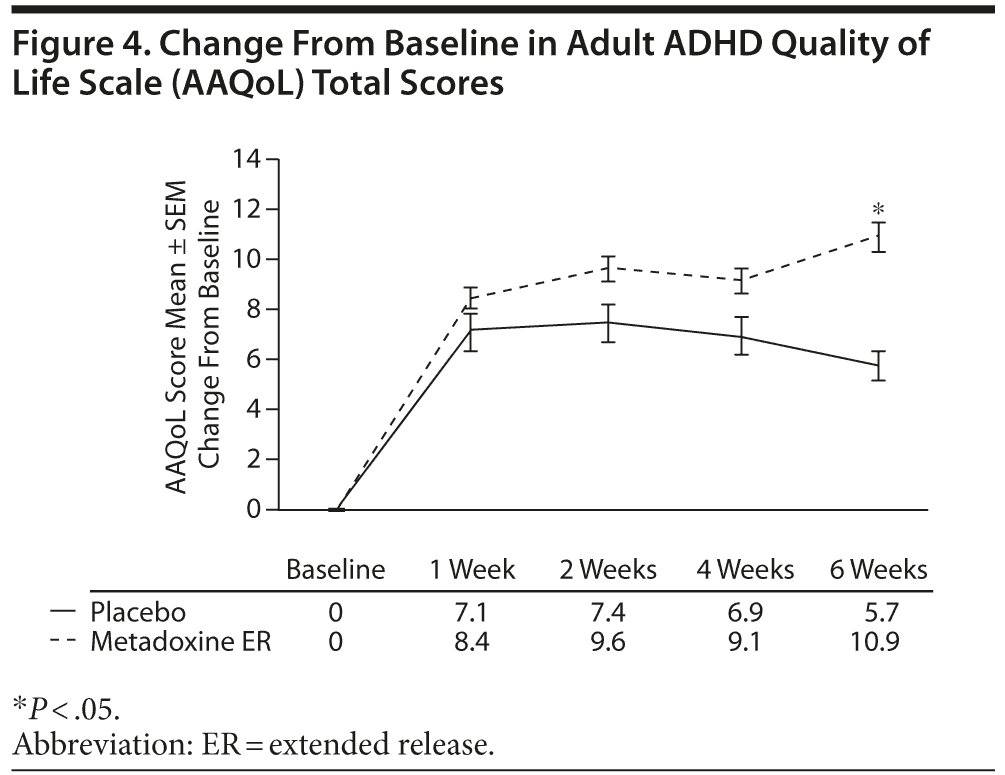
AAQoL Scores
At screening, the respective mean ± SD AAQoL total scores were 58.4 ± 14.7 and 56.3 ± 13.3 in the metadoxine
ER and placebo groups. A mean increase of 10.9 ± 11.2 points was observed in the metadoxine ER group between screening and end of treatment, compared with 5.7 ± 15.8 in the placebo group (P = .01, adjusted for baseline score, gender, site, and age) (Figure 4).
Visit 7 (2 weeks after treatment termination)
In the metadoxine ER group, CAARS-INV total ADHD symptoms scores decreased from a mean ± SD of 37.1 ± 8.4 at visit 1 (screening) to 25.0 ± 11.2 at visit 6 (end of treatment). However, a significant worsening of ADHD symptoms was observed at visit 7 (follow-up) relative to visit 6 (mean 2.9-point increase; P = .01). The same trend toward reversal of efficacy was noted in AAQoL score, which increased from a mean of 58.4 ± 14.7 at visit 1 to 69.6 ± 14.3 at visit 6, whereas an erosion of quality-of-life ratings was seen by visit 7 (follow-up) (3.7-point decrease; P = .002). Likewise, mean TOVA ADHD scores improved from visit 1 to visit 6 (−6.6 ± 8.5 to −1.8 ± 4.9, respectively). Yet, from visit 6 to visit 7 (follow-up), the mean score decreased 2.4 ± 5.8 points (P = .01). Ultimately, P values for change from visit 1 to visit 7 (follow-up) between treatment groups were not statistically significant: CAARS-INV total ADHD symptoms score, P = .50, NS; AAQoL, P = .20, NS; TOVA ADHD score, P = .86, NS. In the placebo group, no significant changes were seen in CAARS-INV total ADHD symptoms, AAQoL, or TOVA ADHD scores, indicating that scores nearly returned to baseline after washout between visits 6 and 7.
Safety Evaluations
A total of 293 AEs occurred in 85/117 subjects (72.6%), with slightly fewer AEs in the metadoxine ER group (142 AEs in 44/58, 75.9% subjects) compared with the placebo group (151 AEs in 41/59, 69.5% subjects); this difference was not statistically significant (P = .44, NS). The majority (98.6%) of AEs were treatment-emergent (289 treatment-emergent AEs/293 total AEs). A total of 224 AEs were considered treatment-related, occurring at comparable rates in the 2 study groups (metadoxine ER: 110 events vs placebo: 114 events; P = .38, NS). The majority of AEs were rated “mild” in intensity. Two “severe” AEs (5.2%) were observed in the metadoxine ER group, both deemed unrelated to study drug (appendicitis and neuroendocrine tumor).
The most common AE was nausea, which occurred exclusively in the metadoxine ER group (13 AEs in 10/58 subjects [17.2%]); all such events were considered to be related to study treatment. Fatigue occurred in similar numbers regardless of group (metadoxine ER: 20 AEs in 18/58 [31.0%] vs placebo: 18 AEs in 16/59 [27.1%]), with all fatigue AEs in the metadoxine ER group considered related to treatment. Notably, headache occurred less frequently in the metadoxine ER group (22 AEs in 17/58 [29.3%] vs 24 AEs in 23/59 [39.0%] in placebo), with the majority of all headache AEs considered related to treatment. Other AEs that occurred in the 5%–10% range within the respective metadoxine ER and placebo groups were upper abdominal pain (8.6% vs 5.1%), oropharyngeal pain (8.6% vs 6.8%), back pain (6.9% vs 5.1%), dizziness (5.2% vs 1.7%), and initial insomnias (5.3% vs 1.7%). Side effects occurred mostly at the initiation of medication and generally spontaneously resolved without treatment or clinical intervention. Two subjects, 1 in each group, discontinued the study early due to AEs; the subject in the metadoxine ER group discontinued due to an escalation of possibly related AEs, including headache, nausea, dizziness, stomachache, decreased appetite, difficulty to concentrate, and memory impairment. The subject in the placebo group discontinued study drug due to low back pain and headache.
There were no reported abnormalities of cardiac rhythm. C-SSRS showed similar resolution from screening to end of treatment in the metadoxine ER and placebo groups. The majority of neurologic examination parameters were normal among subjects in both treatment groups, with all observed abnormalities considered not clinically significant. Physical examination, laboratory parameters, vital signs, and ECG showed no consistent differences between treatment groups or cumulative changes over time.
DISCUSSION
The present 6-week phase 2b randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study extends previous pilot results showing that subjects receiving treatment with metadoxine ER experienced significantly larger improvements in ADHD symptoms, neuropsychological test performance, and quality of life compared with those receiving placebo. Treatment with metadoxine ER was generally well tolerated.
There was a signal indicating relatively rapid response to metadoxine ER, which separated from placebo at 1 week on the CAARS-INV and 2 weeks on the TOVA. The magnitude of this response was maintained or increased throughout the 6 weeks of treatment. The time to onset of response with metadoxine ER may be somewhat more rapid than that observed with the other approved nonstimulant for adults, atomoxetine, which may require up to 6 weeks or more to obtain the full effect.29 These findings of relatively rapid onset of effect are consistent with findings from an earlier phase 2a study in which TOVA ADHD scores improved 2 hours after the first dose was given (data on file, Alcobra Ltd, October 2010). Systematic study of time to onset of effect with metadoxine ER would therefore seem to be a fruitful area for future research.
There were also significant positive effects of metadoxine ER on total AAQoL scores; the time course of this response was somewhat later (between weeks 4 and 6) as compared to improvements in CAARS-INV total ADHD symptoms score (improvement was seen at week 2 and was maintained through week 6 of treatment). A prior study30 that examined quality-of-life ratings in ADHD found a lag in improvement in quality-of-life ratings (Global Assessment of Functioning) versus earlier improvement noted in ADHD ratings, based on the need for time for symptomatic improvement to translate into changes in quality of life. However, a more recent study31 did not find a temporal dissociation between quality-of-life measures and ADHD symptom scores.
Treatment with metadoxine ER was relatively well tolerated. There were no statistically significant cardiovascular effects associated with metadoxine ER treatment on blood pressure, pulse, or ECG; this is potentially important given the increases in blood pressure and pulse seen with current concerns around other therapeutic alternatives (extended release stimulants and atomoxetine) for adults.32,33
There were no serious adverse effects, and although some study subjects experienced nausea, fatigue, and headache, 95% of the subjects in the metadoxine ER group completed the study. Also, although cases of peripheral neuropathy using megadoses of vitamin B6 have been reported following chronic use,34 no such cases have been reported regarding metadoxine despite its use for chronic treatment of alcoholic liver disease in several countries. It is possible that the different metabolic properties of metadoxine result in better tolerability of the drug.35
This study has several limitations. Adults with comorbid psychiatric diseases were excluded from the current study; this potentially limits extrapolation of these results to the broader adult population with ADHD. Although this trial was placebo-controlled, we used only a single dose of metadoxine ER. While no undue cardiovascular problems were revealed in this study, additional, larger studies are needed to confirm this safety aspect. Also, it is possible that AEs were somewhat underestimated, as these were not recorded via a structured assessment, but rather by investigator inquiry of subject report; however, structured assessments of AEs have the potential to overestimate reports of AEs.
This study provides initial evidence that metadoxine ER has demonstrable efficacy in the treatment of adults with ADHD with a relatively short time to onset of clinical effect and a favorable safety profile.
Drug names: atomoxetine (Strattera), lisdexamfetamine (Vyvanse).
Author affiliations: Geha Mental Health Center, Petach Tikva (Drs Manor, Salomy, and Weizman); Sackler Faculty of Medicine, Tel Aviv University, Tel Aviv (Drs Manor and Weizman); Rambam Health Care Campus, Haifa (Drs Ben-Hayun and Aharon-Peretz); and Alcobra Ltd, Tel Aviv (Drs Daniely and Megiddo), Israel; Mount Sinai Medical Center (Dr Newcorn) and Departments of Psychiatry and Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, New York University Medical Center; and Psychiatry Service, New York VA Harbor Healthcare System (Dr Adler), New York, New York; and Massachusetts General Hospital and Harvard Medical
School, Boston (Dr Biederman).
Potential conflicts of interest: Dr Manor has been a consultant to Enzymotec, Janssen-Cilag, Teva, and Novartis; has received research support from Alcobra; and has been on a speakers/advisory board for Janssen-Cilag. Dr Weizman has been a consultant to Eli Lilly, Sanofi-Aventis, Pfizer, Lundbeck, and Teva and has been on a speakers/
advisory board for AstraZeneca, Eli Lilly, Pfizer, Teva, Lundbeck, and Sanofi-Aventis. Dr Daniely is an employee of Alcobra. Dr Megiddo
is an employee of, consultant to, and stock shareholder in Alcobra.
Dr Newcorn has been a consultant to Alcobra, Eli Lilly, Biobehavioral Diagnostics, Shire, Neos, and Otsuka and has received honoraria from and been on the advisory boards of Eli Lilly, Ortho-McNeil-Janssen, and Shire. Dr Biederman is currently receiving research support from ElMindA, Janssen, McNeil, and Shire; in 2012, he received an honorarium from the Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) Psychiatry Academy and the Children’s Hospital of Southwest Florida/Lee Memorial Health System for tuition-funded CME courses; in 2011, he gave a single unpaid talk for Juste Pharmaceutical Spain, received honoraria from the MGH Psychiatry Academy for a tuition-funded CME course, received an honorarium for presenting at an international scientific conference on ADHD, received an honorarium from Cambridge University Press for a chapter publication, and received departmental royalties from a copyrighted rating scale used for ADHD diagnoses, paid by Eli Lilly, Shire, and AstraZeneca; these royalties were paid to the Department of Psychiatry at MGH. Dr Adler has been a consultant to Alcobra, Otsuka, Shire, Theravance, National Football League, and Major League Baseball; has received grant/research support from National Institute on Drug Abuse, Shire, Chelsea Therapeutics, Theravance, Eli Lilly, and Bristol-Myers Squibb; has received an options grant from Alcobra; has received honoraria from Alcobra, Otsuka, Shire, Theravance, National Football League, and Major League Baseball; and has received royalty payments (as inventor) from New York University for license of adult ADHD scales and training materials since 2004. Drs Ben-Hayun, Aharon-Peretz, and Salomy report no potential conflict of interest.
Funding/support: This study was funded by Alcobra Ltd, Tel Aviv, Israel.
Role of sponsor: Alcobra was involved in the design, the choice of clinical sites and investigators, the conduct of the trial, the collection
and monitoring of data using a contract research organization, the analysis and interpretation, and the writing and approval of this manuscript. The authors have had full control of all primary data.
Acknowledgments: The authors thank Aviva Galili Taiber, MSc, and Daphna Reich, MSc, of Alcobra for assistance in trial operations; Ron Gasbarro, PharmD, for assistance in manuscript writing and editing;
and Gil Harari, PhD, and Medistat Ltd for statistical support. The authors also acknowledge Kimberly Kovacs, MA, for her editorial assistance.
The acknowledged individuals report no additional potential conflict
of interest.
REFERENCES
1. Biederman J, Petty CR, Clarke A, et al. Predictors of persistent
ADHD: an 11-year follow-up study. J Psychiatr Res. 2011;45(2):
150–155. doi:10.1016/j.jpsychires.2010.06.009 PubMed
2. Biederman J, Petty CR, Evans M, et al. How persistent is ADHD? a controlled 10-year follow-up study of boys with ADHD. Psychiatry
Res. 2010;177(3):299–304. doi:10.1016/j.psychres.2009.12.010 PubMed
3. Kessler RC, Adler LA, Barkley R, et al. Patterns and predictors of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder persistence into adulthood: results from the National Comorbidity Survey Replication. Biol Psychiatry. 2005;57(11):1442–1451. doi:10.1016/j.biopsych.2005.04.001 PubMed
4. Kessler RC, Adler L, Barkley R, et al. The prevalence and correlates
of adult ADHD in the United States: results from the National Comorbidity Survey Replication. Am J Psychiatry. 2006;163(4):
716–723. PubMed
5. Rösler M, Retz W, Retz-Junginger P, et al. Prevalence of attention
deficit-/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and comorbid disorders in young male prison inmates. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2004;254(6):365–371. doi:10.1007/s00406-004-0516-z PubMed
6. Biederman J, Faraone SV, Spencer TJ, et al. Functional impairments in adults with self-reports of diagnosed ADHD: a controlled study of 1001 adults in the community. J Clin Psychiatry. 2006;67(4):524–540. doi:10.4088/JCP.v67n0403 PubMed
7. Reimer B, Mehler B, D’Ambrosio LA, et al. The impact of distractions on young adult drivers with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). Accid Anal Prev. 2010;42(3):842–851. doi:10.1016/j.aap.2009.06.021 PubMed
8. Biederman J, Arnsten AF, Faraone SV, et al. New developments in the treatment of ADHD. J Clin Psychiatry. 2006;67(1):148–159. doi:10.4088/JCP.v67n0121 PubMed
9. Wilens TE, Adler LA, Adams J, et al. Misuse and diversion of stimulants prescribed for ADHD: a systematic review of the literature. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2008;47(1):21–31. doi:10.1097/chi.0b013e31815a56f1 PubMed
10. Faraone SV, Glatt SJ. A comparison of the efficacy of medications for adult attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder using meta-analysis of
effect sizes. J Clin Psychiatry. 2010;71(6):754–763. doi:10.4088/JCP.08m04902pur PubMed
11. Vitamin B6 (pyridoxine and pyridoxal 5′-phosphate). Altern Med Rev. 2001;6(1):87–92. PubMed
12. Díaz Martínez MC, Díaz Martínez A, Villamil Salcedo V, et al. Efficacy of metadoxine in the management of acute alcohol intoxication. J Int Med Res. 2002;30(1):44–51. PubMed
13. Fornai F, Grazia Alessandrì M, Bonuccelli U, et al. Effect of metadoxine on striatal dopamine levels in C57 black mice. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1993;45(5):476–478. doi:10.1111/j.2042-7158.1993.tb05579.x PubMed
14. Guilarte TR, Wagner HN Jr, Frost JJ. Effects of perinatal vitamin B6 deficiency on dopaminergic neurochemistry. J Neurochem. 1987;48(2):
432–439. doi:10.1111/j.1471-4159.1987.tb04111.x PubMed
15. Adler L, Cohen J. Diagnosis and evaluation of adults with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Psychiatr Clin North Am. 2004;27(2):
187–201. doi:10.1016/j.psc.2003.12.003 PubMed
16. First MB, Spitzer RL, Gibbon M, et al. Structured Clinical Interview for DSM-IV-TR Axis I Disorders-Patient Edition (SCID-I/P). New York, NY: Biometrics Research Department, New York State Psychiatric Institute; 2002.
17. Guy W. Clinical global impressions. In: Guy W, ed. ECDEU Assessment Manual for Psychopharmacology (revised). US Department of Health, Education and Welfare publication (ADM) 76-338. Rockville, MD: National Institute of Mental Health; 1976:217–221.
18. Beck AT, Ward CH, Mendelson M, et al. An inventory for measuring depression. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1961;4(6):561–571. doi:10.1001/archpsyc.1961.01710120031004 PubMed
19. Spielberger CD. State-Trait Anxiety Inventory (STAI: Form Y). Palo Alto, CA: Consulting Psychologists Press; 1983.
20. Greenberg LM, Waldman ID. Developmental normative data on the
Test of Variables of Attention (TOVA). J Child Psychol Psychiatry. 1993;
34(6):1019–1030. PubMed
21. Brod M, Johnston J, Able S, et al. Validation of the Adult Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder Quality-of-Life Scale (AAQoL):
a disease-specific quality-of-life measure. Qual Life Res. 2006;15(1):
117–129. doi:10.1007/s11136-005-8325-z PubMed
22. Conners CK, Erhardt D, Sparrow E. Conners’ Adult ADHD Rating Scales. North Tonawanda, NY: Multi-Health Systems, Inc; 1999.
23. Van Voorhees EE, Hardy KK, Kollins SH. Reliability and validity of self- and other-ratings of symptoms of ADHD in adults. J Atten Disord. 2011;
15(3):224–234. doi:10.1177/1087054709356163 PubMed
24. Posner K, Brown GK, Stanley B, et al. The Columbia-Suicide Severity Rating Scale: initial validity and internal consistency findings from three multisite studies with adolescents and adults. Am J Psychiatry. 2011;
168(12):1266–1277. doi:10.1176/appi.ajp.2011.10111704 PubMed
25. Adler LA, Spencer T, Faraone SV, et al. Training raters to assess
adult ADHD: reliability of ratings. J Atten Disord. 2005;8(3):121–126. doi:10.1177/1087054705277168 PubMed
26. Cohen J. Statistical Power Analysis for the Behavioral Sciences. 2nd ed. Hillsdale, NJ: Erlbaum; 1988.
27. Durell T, Adler L, Wilens T, et al. Atomoxetine treatment for ADHD: younger adults compared with older adults. J Atten Disord. 2010;13(4):
401–406. doi:10.1177/1087054709342203 PubMed
28. Goodman D, Faraone SV, Adler LA, et al. Interpreting ADHD Rating Scale scores: linking ADHD Rating Scale scores and CGI levels in two randomized controlled trials of lisdexamfetamine dimesylate in ADHD. Prim Psychiatry. 2010;17(3):44–52.
29. Adler LA, Spencer T, Brown TE, et al. Once-daily atomoxetine for adult attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: a 6-month, double-blind trial. J Clin Psychopharmacol. 2009;29(1):44–50. doi:10.1097/JCP.0b013e318192e4a0 PubMed
30. Spencer T, Biederman J, Wilens T, et al. A large, double-blind, randomized clinical trial of methylphenidate in the treatment of adults with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Biol Psychiatry. 2005;57(5):
456–463. doi:10.1016/j.biopsych.2004.11.043 PubMed
31. Weiss MD, Gibbins C, Goodman DW, et al. Moderators and mediators
of symptoms and quality of life outcomes in an open-label study of adults treated for attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. J Clin Psychiatry. 2010;71(4):381–390. Published online Feb 23, 2010. doi:10.4088/JCP.08m04709pur PubMed
32. Wilens TE, Hammerness PG, Biederman J, et al. Blood pressure
changes associated with medication treatment of adults with
attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. J Clin Psychiatry. 2005;66(2):253–259. doi:10.4088/JCP.v66n0215 PubMed
33. Hammerness PG, Surman CB, Chilton A. Adult attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder treatment and cardiovascular implications.
Curr Psychiatry Rep. 2011;13(5):357–363. doi:10.1007/s11920-011-0213-3 PubMed
34. Cohen M, Bendich A. Safety of pyridoxine: a review of human and animal studies. Toxicol Lett. 1986;34(2–3):129–139. doi:10.1016/0378-4274(86)90202-X PubMed
35. Addolorato G, Ancona C, Capristo E, et al. Metadoxine in the treatment of acute and chronic alcoholism: a review. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 2003;16(3):207–214. PubMed
This PDF is free for all visitors!





