Prim Care Companion CNS Disord 2021;23(6):21cr03074
To cite: Awake proning for COVID-19 in a state psychiatric hospital: a case series. Prim Care Companion CNS Disord. 2021;23(6):21cr03074.
To share: https://doi.org/10.4088/PCC.21cr03074
© Copyright 2021 Physicians Postgraduate Press, Inc.
aGeisel School of Medicine at Dartmouth, Concord, New Hampshire
bNew Hampshire Hospital, Concord, New Hampshire
*Corresponding author: Jeffrey C. Fetter, MD, Geisel School of Medicine at Dartmouth, New Hampshire Hospital, 36 Clinton St, Concord, NH 03301 ([email protected]).
The coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic has disproportionally affected patients with severe mental illness (SMI), who are more likely to contract severe acute respiratory coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection1 and to die from it if hospitalized.2 State psychiatric hospitals are congregate living settings that concentrate patients with SMI and are high-risk environments for COVID-19 outbreaks. When state psychiatric hospital patients develop symptomatic COVID-19, their acute medical treatment often occurs in a general medical hospital. They return to the state psychiatric hospital when they meet discharge criteria to the community. However, in our experience a population of patients discharged from the community hospital to our psychiatric facility continued to require oxygen after their emergency department (ED) visit or inpatient medical treatment. These patients required more intense nursing care than COVID patients without oxygen requirements and may constitute a group at higher risk for decompensation.
Early in the pandemic, critical care providers learned that prone positioning improved outcomes in intubated COVID patients by improving ventilation/perfusion matching.3,4 Later work demonstrated benefit to proning conscious patients in the ED.5–7
We report here a series of 3 involuntarily committed psychiatric patients with COVID-19 and hypoxia, who returned from the ED or inpatient medical care with ongoing oxygen requirements and were placed on an awake proning protocol.
Methods
Criteria for initiating the awake proning protocol included a diagnosis of COVID-19–induced hypoxia, returning from ED evaluation or inpatient medical hospitalization, requiring oxygen by nasal cannula, a history of bilateral changes on chest imaging not fully explained by cardiac failure, and ability to cooperate.
Patients were excluded and sent for medical evaluation if their respiratory rate was > 40 breaths/minute, obvious accessory muscle use was noted, their blood oxygen level was < 88%, or there was an unreliable pulse oximeter reading.
Protocol8–10
- Patients returning from the ED for suspected COVID-19–induced symptoms but who require oxygen within 24 hours of return will be evaluated for protocol.
- Assist to awake prone position with nurse and mental health worker present and monitor oxygen saturation every 5 minutes for 30 minutes while in prone position.
- If oxygen saturation worsens or requires in excess of 4 L per hour to maintain saturation over 90%, assist to supine position and call physician.
- If oxygen saturation remains the same or improves, continue prone position.
- At the bottom of every hour, the staff doing safety checks will verbally cue the patient to change to another position, either prone, left lateral decubitus, right lateral decubitus, or sitting upright for at least half an hour or as long as tolerated.
Nursing staff and patients were provided with an instruction sheet with a visual graphic guide.10
Case Series
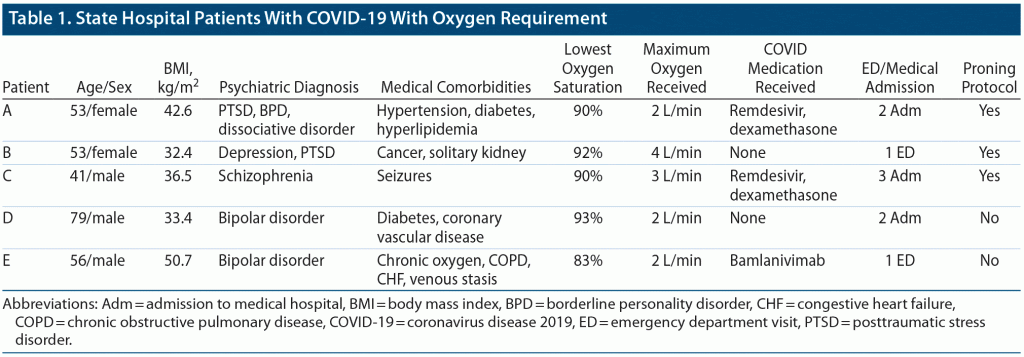
We utilized the awake proning protocol in 3 patients who had been evaluated in the medical hospital for COVID symptoms. For comparison, Table 1 includes these patients as well as 2 other patients who required transfer to the community hospital for COVID-19 care during the November 2020–January 2021 period and who received care in the state hospital COVID Care Unit (CCU). None of these patients required seclusion, restraint, or involuntary medications during their COVID-19–related illness. No patients were excluded for inability to cooperate.
Patient A
This was a 53-year-old woman admitted to the state psychiatric hospital with psychiatric diagnoses of bipolar disorder with suicidal ideation, posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD), depression, anxiety, borderline personality disorder, and dissociative disorder. Her medical comorbidities included hypertension, hypercholesterolemia, and diabetes mellitus type 2. Initially presenting to the CCU with a temperature of 101.6°F, cough, malaise, and bilateral diminished breath sounds, she had 2 medical admissions 1 week apart of 3 and 2 days, respectively. On the second admission, she received remdesivir, dexamethasone, and intravenous antibiotics. Upon return to the CCU, she continued to have fatigue with exertion and shortness of breath, but was able to maintain an oxygen saturation of 92%–93% on room air and above 95% on 1 L/min. On the proning protocol for the first 30 minutes, her oxygen saturation on 1 L/min of oxygen ranged between 94% and 96%. She reported that the left decubitus side-lying position with the head of bed at 30% was difficult to sleep in but otherwise had no reported complaints with any part of the protocol. The nurse observed that during bed moves the patient sometimes appeared dissociative. On the second day of the protocol, her oxygen saturation ranged from 93% to 97% on 0–1 L/min, and the protocol was stopped when fully weaned from oxygen.
Patient B
This was a 53-year-old woman admitted to the state hospital with psychiatric diagnoses of major depressive disorder and PTSD. She also had a nonpulmonary multicancer history and a solitary kidney. She first presented with fatigue, decreased appetite, low-grade fever, headache, body aches, and a nonproductive cough. She had clear lung auscultation but a positive BinaxNOW test. She initially had some difficulty with word retrieval and became frustrated. Over the first night, she had extensive coughing, an oxygen saturation of 92% on room air, and diminished lung sounds especially in the right lower lobe. She was evaluated in the ED for dyspnea but returned to the CCU without supplemental oxygen. She continued to have a headache, cough, fatigue, coryza, coarse crackles in bilateral lower lobes, and diminished sounds in the right lung base and midlung. She intermittently needed oxygen at 3 to 4 L/min to maintain an oxygen saturation above 95%. A chest x-ray showed worsening patchy bilateral basilar airspace disease and probable small bilateral effusions. She used an incentive spirometer regularly. She participated in the proning protocol for 3 consecutive days. On the second day, she was on 2 L oxygen during the process with oxygen saturations between 95% and 98%. She stated that the proning was subjectively helpful with dyspnea and mucus congestion. Her oxygen saturation during the first hour of proning ranged from 95% to 97% on 2 L/min. She attributed concurrent increased back pain to coughing. Ten days after her COVID test, she was transferred out of the CCU with no dyspnea on room air.
Patient C
This was a 41-year-old man who had a prior psychiatric diagnosis of schizophrenia and medical diagnosis of seizures. Initially, he complained of a throbbing headache with an oxygen saturation of 95%, but his BinaxNow test returned negative. Two days later, he had chills, a severe headache, a nonproductive cough, and vomiting, and the BinaxNOW was positive. He was placed on oxygen 2 L/min for dyspnea. During isolation, he remained psychotic with no unsafe behaviors. He was transferred to the community hospital for worsening mental status, temperature of 102° F, a productive cough, and an oxygen requirement up to 3 L/min. He was diagnosed with metabolic encephalopathy with acute hypoxemic respiratory failure and received remdesivir and dexamethasone. He was transferred back to the CCU with an oxygen saturation of 97% on room air. Three days later, he was readmitted to the community hospital for respiratory failure, sepsis, and acute encephalopathy with an oxygen saturation of 90%–91% on room air. He received intravenous ceftriaxone and azithromycin. Two days after discharge, he was admitted to the community hospital a third time for pneumonia and dyspnea and treated with intravenous doxycycline and ceftriaxone for 3 days. He was discharged with a plan to complete his antibiotics and a prednisone taper. He initially had an oxygen saturation of 93% on room air, but the following day his saturation decreased to 91%, and he required 3 L/min. He consented to the proning protocol and was progressively weaned off supplemental oxygen over the next 2 days. There were no complaints of discomfort or side effects of proning.
Discussion
Prone positioning has been hypothesized to improve outcomes in particular COVID patients because it enhances gas exchange and removal of secretions, both of which lead to better oxygenation through several mechanisms. First, the prone position increases lung tissue compliance by creating a more even distribution of total stress and strain on lung tissue. Second, prone positioning recruits more alveoli. Physical suppression of the alveolar opening is greater in the dependent portion of the lung due to gravity. Therefore, placement of the greater dorsal lung mass in the nondependent position with prone positioning improves overall recruitment of alveolar units. Prone positioning also recruits alveoli in the posterior and peri-abdominal lung by reducing pressure from the heart and abdomen.11,12
Awake prone positioning was recommended as an international standard of care for a subset of COVID inpatients as early as April 12, 2020 by the Intensive Care Society.13 Despite this, as far as the authors are aware, this is the first case series report of a prone positioning trial in acutely ill psychiatric inpatients with COVID-19. People with symptoms of active mental illness are less likely to be offered standard of care medical treatments because of the assumption or perception that their symptoms would interfere with cooperation,14 leading to considerable inequalities in the provision of their physical health care.14–16 People with SMI comprise the very population that should be offered the standard of care, as patients hospitalized for psychiatric disorders are at increased risk of contracting and transmitting COVID-1917,18 and are 1.5 times as likely to die from COVID-19 as their hospitalized peers without SMI.19 It has been proposed that inpatient psychiatric facilities have an increased risk of COVID infection and institutional outbreaks because of the presence of shared dining areas, bathrooms, and other common areas with limited space for social distancing. This is a major impediment to psychiatric hospitals providing a safe environment in which patients may recover.17,18
Psychiatric inpatients often carry an additional burden of multiple medical comorbidities, including respiratory compromise from tobacco use14 and metabolic syndrome,14 putting them at even higher risk of morbidity and mortality from COVID-19. What we show is that providing a standard of care medical treatment for COVID-19 to patients with SMI at a state hospital is both feasible to do and acceptable to patients.
Our study has several limitations. It is retrospective, and the number of cases is small. As an initial feasibility and acceptability study, our study was not designed to assess outcome, and it is well known that improvements in oxygenation do not necessarily translate into decreased mortality. However, we show that involuntarily committed psychiatric inpatients, members of a population that does not always receive standard of care due to the assumption that they cannot cooperate because of cognitive impairment or disorganized behavior or thinking were able to cooperate with the protocol and found it acceptable. While we consider this to be an initial important observation, further research is necessary to determine the best respiratory management strategies for acutely ill psychiatric patients in state hospitals settings.
Received: July 13, 2021.
Published online: October 28, 2021.
Potential conflicts of interest: No authors have conflicts of interest or ethical disclosures. Drugs with an emergency use authorization for COVID-19 are mentioned (bamlanivimab, remdesivir), as is the use of dexamethasone for COVID-19, which is an off-label use.
Funding/support: None.
Patient consent: Consent was received from the patients to report in a case series, and the information was de-identified. Body mass index was also rounded to the nearest multiple of 5 to protect their identities.
References (19)

- Taquet M, Luciano S, Geddes J, et al. Bidirectional associations between COVID-19 and psychiatric disorder: retrospective cohort studies of 62,354 COVID-19 cases in the USA. Lancet Psychiatry. 2021;8(2):130–140. PubMed CrossRef
- Wang Q, Rong X, Volkow N. World J Psych prepub. Wiley Online Library website. Accessed October 12, 2021. https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/wps.20806
- Ding L, Wang L, Ma W, et al. Efficacy and safety of early prone positioning combined with HFNC or NIV in moderate to severe ARDS: a multi-center prospective cohort study. Crit Care. 2020;24(1):28. PubMed CrossRef
- Carsetti A, Damia Paciarini A, Marini B, et al. Prolonged prone position ventilation for SARS-CoV-2 patients is feasible and effective. Crit Care. 2020;24(1):225. PubMed CrossRef
- Xu Q, Wang T, Qin X, et al. Early awake prone position combined with high-flow nasal oxygen therapy in severe COVID-19: a case series. Crit Care. 2020;24(1):250. PubMed CrossRef
- Caputo ND, Strayer RJ, Levitan R. Early self-proning in awake, non-intubated patients in the emergency department: a single ED’s experience during the COVID-19 pandemic. Acad Emerg Med. 2020;27(5):375–378. PubMed CrossRef
- Sartini C, Tresoldi M, Scarpellini P, et al. Respiratory parameters in patients with COVID-19 after using noninvasive ventilation in the prone position outside the intensive care unit. JAMA. 2020;323(22):2338–2340. PubMed CrossRef
- Bower G, He H. Protocol for awake prone positioning in COVID-19 patients: to do it earlier, easier, and longer. Crit Care. 2020;24(1):371. PubMed CrossRef
- Bentley SK, Iavicoli L, Cherkas D, et al. Guidance and patient instructions for proning and repositioning of awake, nonintubated COVID-19 patients. Acad Emerg Med. 2020;27(8):787–791. PubMed CrossRef
- Jiang LG, LeBaron J, Bodnar D, et al. Conscious proning: an introduction of a proning protocol for non-intubed, awake, hypoxic emergency department COVID-19 patients. Acad Emerg Med. 2020;27(7):566–569. PubMed CrossRef
- Guérin C, Albert RK, Beitler J, et al. Prone position in ARDS patients: why, when, how and for whom. Intensive Care Med. 2020;46(12):2385–2396. PubMed CrossRef
- Kallet RH. A comprehensive review of prone position in ARDS. Respir Care. 2015;60(11):1660–1687. PubMed CrossRef
- Bamford P, Bentley A, Dean J, et al. ICS Guidance for Prone Positioning of the Conscious COVID Patient 2020. United Kingdom: Intensive Care Society; 2020.
- DE Hert M, Correll CU, Bobes J, et al. Physical illness in patients with severe mental disorders, I: prevalence, impact of medications and disparities in health care. World Psychiatry. 2011;10(1):52–77. PubMed CrossRef
- Viron MJ, Stern TA. The impact of serious mental illness on health and healthcare. Psychosomatics. 2010;51(6):458–465. PubMed CrossRef
- Lawrence D, Kisely S. Inequalities in healthcare provision for people with severe mental illness. J Psychopharmacol. 2010;24(suppl):61–68. PubMed CrossRef
- Ji H, Liu L, Huang T, et al. Nosocomial infections in psychiatric hospitals during the COVID-19 outbreak. Eur J Psychiatry. 2020;34(3):177–179. PubMed CrossRef
- Shao Y, Shao Y, Fei JM. Psychiatry hospital management facing COVID-19: from medical staff to patients. Brain Behav Immun. 2020;88:947. PubMed
- Li L, Li F, Fortunati F, et al. Association of a prior psychiatric diagnosis with mortality among hospitalized patients with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) infection. JAMA Netw Open. 2020;3(9):e2023282. PubMed CrossRef
Enjoy this premium PDF as part of your membership benefits!