A Positive Association Between Homeostasis Model Assessment of Insulin Resistance Score and the Trp64Arg Polymorphism of the β3-Adrenergic Receptor Gene in Schizophrenia Patients in Taiwan
Objective: To investigate the possible association between the Trp64Arg polymorphism of the β3-adrenergic receptor gene and the homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance (HOMA-IR) index in schizophrenia patients in Taiwan.
Method: A total of 203 inpatients who met DSM-IV diagnostic criteria for schizophrenia were recruited from a psychiatry center in Taiwan from September 2002 to August 2003. All patients had been treated with antipsychotics for at least 6 months. The genotyping of the Trp64Arg polymorphism of the β3-adrenergic receptor gene was done by the polymerase chain reaction-restriction fragment length polymorphism method with the restriction enzyme MvaI. The HOMA-IR index was used to indicate the degree of insulin resistance.
Results: After adjusting for sex, age, and body mass index status, the association between the HOMA-IR index and the Trp64Arg polymorphism of the β3-adrenergic receptor gene was still positive (regression coefficient = −0.65, P = .033).
Conclusions: The polymorphism of the β3-adrenergic receptor gene may be related to the development of insulin resistance in chronic schizophrenia patients in Taiwan.
Prim Care Companion J Clin Psychiatry 2010;12(4);e1-e5
© Copyright 2010 Physicians Postgraduate Press, Inc.
Submitted: November 1, 2009; accepted November 30, 2009.
Published online: August 19, 2010 (doi:10.4088/PCC.09m00918yel).
Corresponding author: Tsuo-Hung Lan, MD, PhD, Department of Psychiatry, Taichung Veterans General Hospital, No. 200, Sec. 1, DongDa Rd, Taichung 407, Taiwan ([email protected]).
A growing body of evidence suggests a higher prevalence of metabolic abnormalities in schizophrenia patients, such as insulin resistance, hyperglycemia, and new-onset diabetes mellitus or dyslipidemia. For example, the prevalence rate of diabetes among patients with schizophrenia was estimated to be around 15% or an increased risk of 2- to 3-fold in previous reports.1 Perez-Iglesias et al2 followed 144 drug-naive schizophrenia patients for 1 year and found a statistically significant increase in the mean values of insulin levels and insulin resistance indexes. Kahn et al3 evaluated cases of first-episode schizophrenia after the first year of antipsychotic treatment in an open pragmatic randomized controlled trial and reported high rates of hyperglycemia (23.4%) and hypertriglycemia (35%). Green et al4 described a significant increase in total cholesterol but not in fasting glucose level in a cohort of 263 first-episode patients treated with haloperidol or olanzapine for 2 years. Although the aforementioned studies did not support the hypothesis that schizophrenia is associated with an underlying abnormality in glucose metabolism, there is evidence indicating that a high level of insulin resistance exists prior to the effects of treatment.5,6 Venkatasubramanian et al found a significantly higher mean insulin resistance score of antipsychotic-naive schizophrenia patients (n = 44) relative to healthy controls matched by age and sex.7 Identifying and treating insulin resistance in advance may help to prevent potential cardiovascular and diabetes risks of these patients in the future.8
Clinical Points
- The monitoring of insulin resistance is suggested to play an important role in schizophrenia patients exposed to antipsychotics.
- Current evidence supports the association between the ADRB3 gene and insulin resistance in schizophrenia.
- Clinicians might use genetic information as a reference to prescribe appropriate medications on an individual basis.
The β3-adrenergic receptor (ADRB3) is expressed predominantly in human visceral fat and is the principal mediator of catecholamine-stimulated thermogenesis and lipolysis. Therefore, ADRB3 dysfunction leads to visceral obesity, correlated with insulin resistance through its effect on energy expenditure of fat tissue.9 In 1995, a missense mutation in codon 64 of the ADRB3 gene with a replacement of tryptophan to arginine (Trp64Arg) was reported to be associated with insulin resistance or obesity.10 It was associated with an earlier onset of non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus in Pima,10 central obesity and hyperinsulinemia in Japanese,11 weight gain in French,12 and insulin resistance in Finnish populations.13 Later, in vitro studies on fat cells demonstrated that this Arg carrier did have a 10-fold decrease in ADRB3 receptor sensitivity.14 A consistent small effect of this ADRB3 mutation on body mass index (BMI) was replicated in 3 meta-analyses,15 but the association of Trp64Arg with insulin resistance was still controversial. Zhan et al16 used cross-sectional data from 128,052 individuals by meta-analyses and concluded that the association was only significant in the Asian population, albeit to a limited degree, increasing homeostasis model assessment (HOMA) by 0.55 in the Arg gene carriers.
Although a higher insulin resistance may endanger schizophrenia patients with more potential health-related risks, the association between this genetic variant and insulin resistance or obesity in schizophrenia patients is less investigated. Current evidence suggests that the effect of this ADRB3 mutation on insulin resistance is ethnically heterogeneous. Thus, we investigated the association of the ADRB3 Trp64Arg variant with insulin resistance and central obesity in schizophrenia patients of Taiwanese ethnic background.
METHOD
Patients
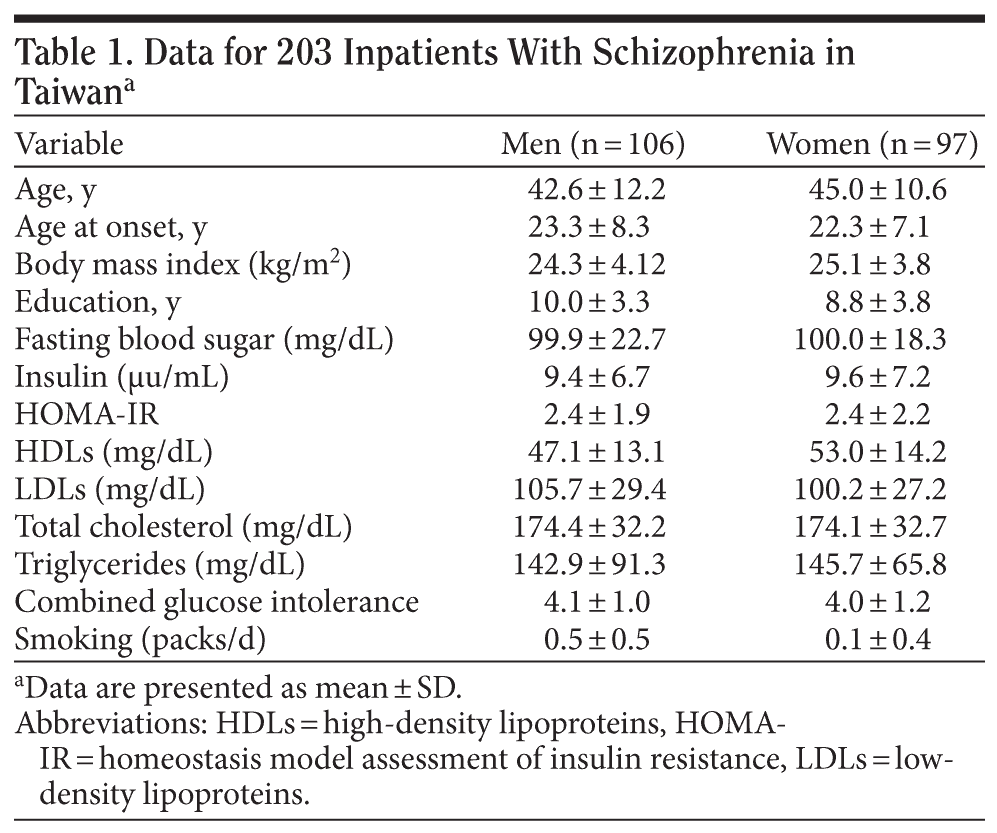
In this cross-sectional study, 203 inpatients who met DSM-IV criteria for schizophrenia were recruited from a psychiatry center in Taiwan from September 2002 to August 2003. All patients had been treated with antipsychotics for at least 6 months. The study protocol was approved by the Ethics Committee of the participating hospital (YLH-IRB-93001), and all participants completed the consent forms. A brief medical history, current psychopharmacotherapy, and daily activity level of each study subject were collected by a questionnaire administered by a trained interviewer or chart review. Advice on diet, exercise, and lifestyle was given to all patients. Anthropometrics measurement was done before breakfast. The body weight of each subject was checked again 1 month later. Body mass index (kg/m2) and waist-hip ratio were calculated for each individual.
Blood Assay and Genotyping
Venous blood samples were collected following routine procedure after an overnight fast. Blood glucose was measured by the hexokinase method, and the serum insulin concentration was assayed by routine chemiluminescent immunoassay in the laboratory of the participating hospital. Homeostasis model assessment was used to assess insulin resistance (HOMA-IR). The HOMA-IR index was calculated according to Matthews et al17 as follows: (fasting blood sugar in mg/dL) ח (serum insulin level in μu/mL) ׷ 405. In addition, we calculated the triglyceride/high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol ratio as a predictor of insulin resistance using the cutpoint of 3.5 described by McLaughlin et al.18 The DNA was isolated from peripheral leukocytes using a Puregene DNA isolation kit (Gentra Systems, Minneapolis, Minnesota). The genotyping of ADRB3 polymorphism was done by the polymerase chain reaction-restriction fragment length polymorphism method with the restriction enzyme MvaI as described previously.12
Statistical Analysis
The statistical analysis was performed with the SPSS for windows, version 12.0 (SPSS Inc, Chicago, Illinois). Data were expressed as mean ± SD. The t tests were used to compare genotypes for differences of continuous variables. Multiple linear regression analysis controlled for age, sex, BMI, and exercise level was performed to evaluate the effects of the ADRB3 gene polymorphism on the HOMA-IR index. The value P < .05 was accepted as statistically significant.
RESULTS
Basic Data
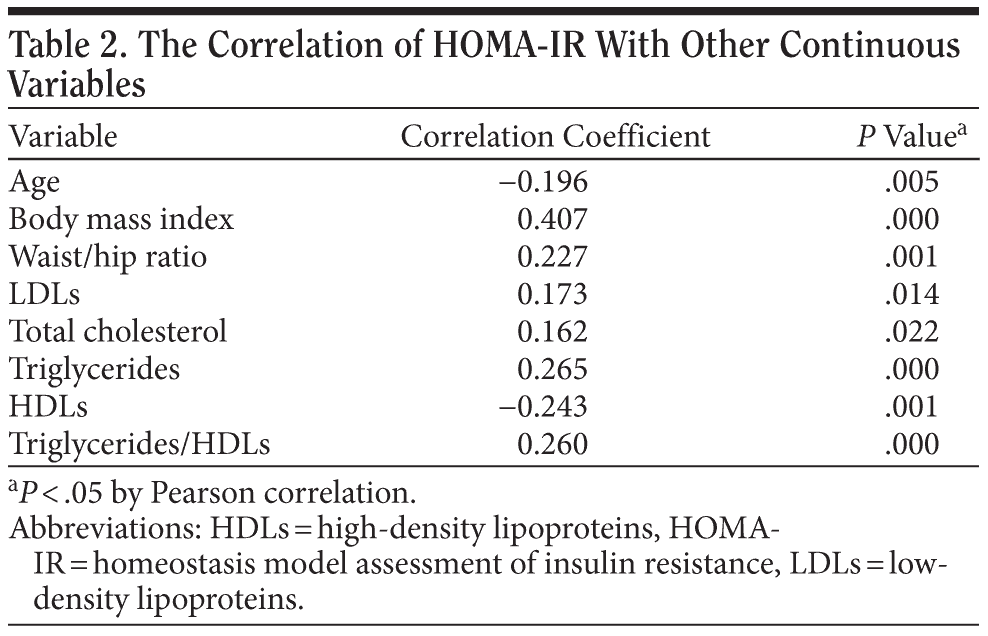
A total of 203 inpatients were recruited into the study. The basic data are shown in Table 1. About 30% of patients reached the definition of obesity (BMI ≥ 2719), 32.5% reached the definition of insulin resistance (HOMA-IR > 2.5),20 and 29.6% had triglyceride/HDL ratios > 3.5. Hypercholesterolemia and hypertriglyceridemia were defined as serum cholesterol level > 220 mg/dL and triglyceride levels > 150 mg/dL; 9.4% and 28.6% of our sample fulfilled the criteria of hypercholesterolemia and hypertriglyceridemia, respectively. Also, 15.8% of patients had fasting blood sugar levels over 110 mg/dL, and 14.3% had fasting insulin levels > 15.6 μu/mL. The waist-hip ratio (the circumference of the waist divided by that of the hips > 0.9 for men and > 0.85 for women) is used as a measure of central obesity. About 64.5% of our sample fulfilled the criteria of central obesity. The HOMA-IR index was found to be correlated with age, central obesity, and triglyceride/HDL ratio in our sample (Table 2).
Frequency of the Trp64Arg Allele
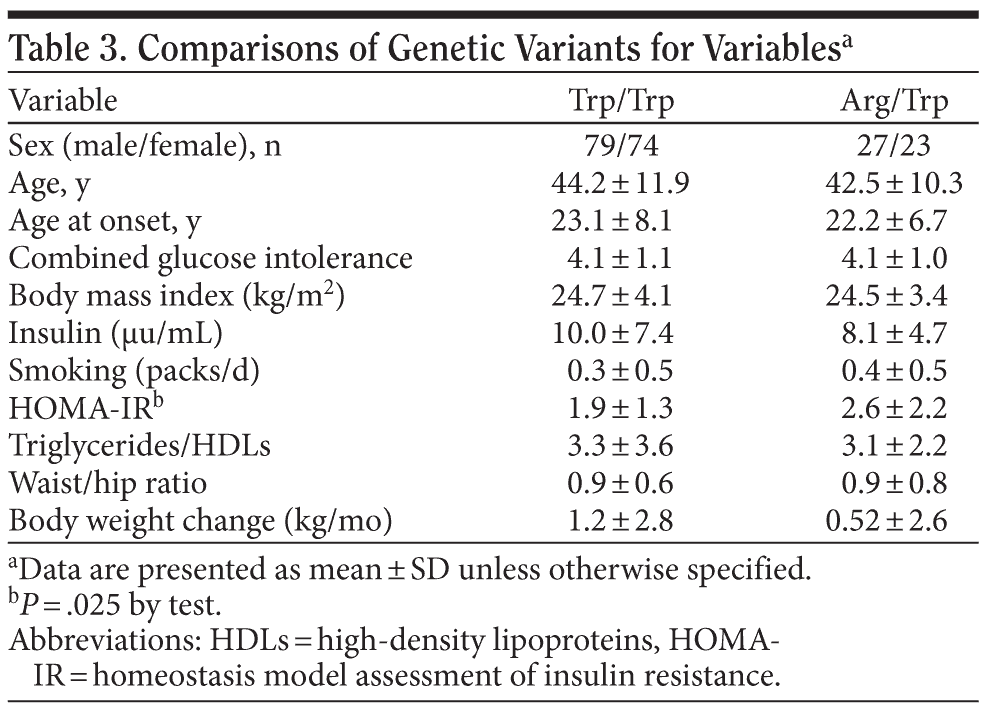
The overall frequency of the 64Arg allele was 12.3%. None were Arg/Arg homozygous, 24.6% were heterozygous, and 75.4% were Trp/Trp homozygous.
The Association Between Genetic Polymorphism, HOMA-IR, and Obesity
There was no significant difference of age, age at onset, combined glucose intolerance, gender distribution, or BMI among different genotypes as shown in Table 3. However, there was a statistically significant difference of HOMA-IR index among different genotypes. After adjusting for each participant’s sex, age, and BMI status, the association between HOMA-IR index and the Trp64Arg polymorphism of the β3-adrenergic receptor gene was still positive (regression coefficient = −0.65, P = .033). Using BMI ≥ 27 as the criteria of obesity, we found that the Trp64Arg variant was associated with insulin resistance in the obese group (P = .004 by t test), while no significant association was observed in the nonobese group.
DISCUSSION
The frequency of the Arg carrier of the ADRB3 gene in our sample was 12.3%. This rate is lower than those reported in Pima Indian and Japanese subjects but is similar to previous reports of 13.9% in other Taiwanese populations.21,22 In our sample, the 64Arg variant of the ADRB3 gene was not associated with age at onset of schizophrenia or combined glucose intolerance.
The Arg carrier of the ADRB3 gene was not associated with any surrogate indicator of obesity such as BMI or waist-hip ratio in our sample. Tsai et al23 found no significant association of this ADRB3 variant with clozapine-induced weight gain in 87 schizophrenia patients in Taiwan. However, a consistent small effect of the ADRB3 variant on BMI was demonstrated in at least 3 meta-analyses.15 Obesity is a complex phenotype that involves multiple genetic variants interacting with environmental and behavior factors. There are many other putative candidate genes of obesity that were not considered in our sample, and this may offer an explanation of inconsistency. Ujike et al24 identified genetic variants of serotonin-2A (5-HT2A) receptors, 5-HT2C receptors, the G-protein β3 subunit, and the ADRB3 gene as possible genetic risk factors for olanzapine-induced weight gain in 164 schizophrenia patients, and these genetic variants showed additive genetic effects on weight gain.
The ADRB3 Trp64Arg variant was associated with insulin resistance in our sample. After adjusting for sex, age, and BMI status, the Arg carrier of the ADRB3 gene was still associated with higher insulin resistance (regression coefficient = −0.65, P = .033). Using BMI ≥ 27 as the criteria of obesity, we found that the association of the Trp64Arg variant and insulin resistance existed only in the obese group (P = .004 by t test) and not in the nonobese group. This is inconsistent with Tsai et al,21 who surveyed 299 pregnant women and concluded that the ADRB3 Trp64Arg variant has no effect on obesity but might be a possible determinant of insulin resistance in the Taiwanese population. Nagano et al25 analyzed 89 Japanese patients with schizophrenia and concluded that the 64Arg allele, with a frequency of 22%, was not associated with obesity, type 2 diabetes mellitus, dyslipidemia, hypertension, or plasma insulin.
Our observation is consistent with the “insulin hypothesis” of obesity-associated insulin resistance.26 In this regard, insulin resistance is believed to be a result of lipotoxicity. This hypothesis is supported by the well-established role of free fatty acids in the promotion of insulin secretion in pancreatic β cells and findings about GPR40 in the signal translation of free fatty acids in β cells. More important, it is the combination of insulin and free fatty acids that represents a promising mechanism for the initiation of obesity-associated insulin resistance. Under this concept, several hypotheses, including inflammation, diacylglycerol-protein kinase C, and endoplasmic reticulum and oxidative stress, have been developed to specify the cellular and molecular mechanism of lipotoxicity.26 In fact, Trp64Arg variants of the ADRB3 gene have already been reported to be associated with increased fasting free fatty acid concentration.27 However, we did not check free fatty acid levels in our sample.
The Trp64Arg variant was not associated with insulin level in our sample. In the 50 patients who fulfilled the definition of BMI ≥ 27, the Trp64Arg variant was associated with lower fasting insulin levels (P = .007). There are reports that the ADRB3 variant affected insulin secretion directly.28 Hojlund et al29 also found that twins heterozygous for the Trp64Arg polymorphism showed significantly lower fasting insulin and glucose concentration compared with their homozygous wild-type cotwins.
There are limitations in our study. First, the effect of antipsychotic drug was not controlled. However, since polypharmacy was prevalent in our sample, it was almost impossible to control the effect of psychopharmacotherapy. We also found that the BMI difference for patients who took first- and second-generation antipsychotics was insignificant statistically (data not listed here).
Also, the number of patients enrolled was small. A larger sample size may be required to test the relationship between obesity and the ADRB3 gene in schizophrenia patients. Finally, there are many other important molecules such as free fatty acid and insulin-like growth factor-17 to be surveyed along with insulin level to clarify the complex association between insulin resistance and the ADRB3 variant.
Insulin resistance is believed to develop long before other associated diseases, such as diabetes, hypertension, or cardiovascular diseases. Thus, identifying and treating insulin resistance in advance has great preventive value.8 There is evidence suggesting that interventions such as weight loss, exercise, and increased dietary fiber intake may be beneficial to improve insulin sensitivity or even diabetes progression.8 Through early detection, these effective interventions can be initiated as soon as possible in genetically susceptible patients to achieve better preventive effects.
Drug names: clozapine (Clozaril, FazaClo, and others), haloperidol (Haldol and others), olanzapine (Zyprexa).
Author affiliations: Department of Psychiatry, National Yang-Ming University (Drs Chiu, Wang, and T-H Lan); Department of Health, Jianan Mental Hospital (Dr Chiu); Department of Psychiatry, National Yang-Ming University Hospital (Drs Lee and T-H Lan); Institute of Population Health Sciences, National Health Research Institutes (Drs T-Y Lan, Loh, and T-H Lan); Department of Psychiatry, Taichung Veterans General Hospital (Dr T-H Lan); and Institute of Public Health, China Medical University (Dr T-Y Lan), Taiwan.
Potential conflicts of interest: None reported.
Funding/support: This study was supported by a grant from the Taiwan Department of Health (93033) in 2002 for the establishment of the Evidence-Based Medicine Center, Yu-Li Hospital, Taiwan.
REFERENCES
1. Holt RI, Peveler RC. Association between antipsychotic drugs and diabetes. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2006;8(2):125-135. PubMed doi:10.1111/j.1463-1326.2005.00495.x
2. Perez-Iglesias R, Mata I, Pelayo-Teran JM, et al. Glucose and lipid disturbances after 1 year of antipsychotic treatment in a drug-naׯve population. Schizophr Res. 2009;107(2-3):115-121. PubMed doi:10.1016/j.schres.2008.09.028
3. Kahn RS, Fleischhacker WW, Boter H, et al; EUFEST Study Group. Effectiveness of antipsychotic drugs in first-episode schizophrenia and schizophreniform disorder: an open randomised clinical trial. Lancet. 2008;371(9618):1085-1097. PubMed doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(08)60486-9
4. Green AI, Lieberman JA, Hamer RM, et al; HGDH Study Group. Olanzapine and haloperidol in first episode psychosis: two-year data. Schizophr Res. 2006;86(1-3):234-243. PubMed doi:10.1016/j.schres.2006.06.021
5. Spelman LM, Walsh PI, Sharifi N, et al. Impaired glucose tolerance in first-episode drug-naׯve patients with schizophrenia. Diabet Med. 2007;24(5):481-485. PubMed doi:10.1111/j.1464-5491.2007.02092.x
6. Van Nimegen LJM, Storosum JG, Blumer RME, et al. Hepatic insulin resistance in antipsychotic naׯve patients with schizophrenia: stable isotopes studies of glucose metabolism. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2008;93(2):572-577. PubMed doi:10.1210/jc.2007-1167
7. Venkatasubramanian G, Chittiprol S, Neelakantachar N, et al. Insulin and insulin-like growth factor-1 abnormalities in antipsychotic-naive schizophrenia. Am J Psychiatry. 2007;164(10):1557-1560. PubMed doi:10.1176/appi.ajp.2007.07020233
8. Rao G. Insulin resistance syndrome. Am Fam Physician. 2001;63(6):1159-1163, 1165-1166. PubMed
9. Emorine L, Blin N, Strosberg AD. The human beta3-adrenoceptor: the search for a physiological function. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1994;15(1):3-7. PubMed doi:10.1016/0165-6147(94)90118-X
10. Walston J, Silver K, Bogardus C, et al. Time of onset of non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus and genetic variation in the beta3-adrenergic-receptor gene. N Engl J Med. 1995;333(6):343-347. PubMed doi:10.1056/NEJM199508103330603
11. Kadowaki H, Yasuda K, Iwamoto K, et al. A mutation in the beta3-adrenergic receptor gene is associated with obesity and hyperinsulinemia in Japanese subjects. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1995;215(2):555-560. PubMed doi:10.1006/bbrc.1995.2500
12. Clément K, Vaisse C, Manning BSJ, et al. Genetic variation in the beta3-adrenergic receptor and an increased capacity to gain weight in patients with morbid obesity. N Engl J Med. 1995;333(6):352-354. PubMed doi:10.1056/NEJM199508103330605
13. Widén E, Lehto M, Kanninen T, et al. Association of a polymorphism in the beta 3-adrenergic-receptor gene with features of the insulin resistance syndrome in Finns. N Engl J Med. 1995;333(6):348-351. PubMed doi:10.1056/NEJM199508103330604
14. Hoffstedt J, Poirier O, Thörne A, et al. Polymorphism of the human beta3-adrenoceptor gene forms a well-conserved haplotype that is associated with moderate obesity and altered receptor function. Diabetes. 1999;48(1):203-205. PubMed doi:10.2337/diabetes.48.1.203
15. Shuldiner AR, Sabra M. Trp64Arg beta3-adrenoceptor: when does a candidate gene become a disease-susceptibility gene? Obes Res. 2001;9(12):806-809. PubMed doi:10.1038/oby.2001.109
16. Zhan S, Ho SC. Meta-analysis of the association of the Trp64Arg polymorphism in the beta3 adrenergic receptor with insulin resistance. Obes Res. 2005;13(10):1709-1719. PubMed doi:10.1038/oby.2005.209
17. Matthews DR, Hosker JP, Rudenski AS, et al. Homeostasis model assessment: insulin resistance and beta-cell function from fasting plasma glucose and insulin concentrations in man. Diabetologia. 1985;28(7):412-419. PubMed doi:10.1007/BF00280883
18. McLaughlin T, Reaven G, Abbasi F, et al. Is there a simple way to identify insulin-resistant individuals at increased risk of cardiovascular disease? Am J Cardiol. 2005;96(3):399-404. PubMed doi:10.1016/j.amjcard.2005.03.085
19. Department of Health, Taiwan, ROC. http://www.doh.gov.tw/cht2006/index_populace.aspx. Accessed June 25, 2010.
20. Taniguchi A, Fukushima M, Sakai M, et al. The role of the body mass index and triglyceride levels in identifying insulin-sensitive and insulin-resistant variants in Japanese non-insulin-dependent diabetic patients. Metabolism. 2000;49(8):1001-1005. PubMed doi:10.1053/meta.2000.7735
21. Tsai PJ, Ho SC, Tsai LP, et al. Lack of relationship between beta3-adrenergic receptor gene polymorphism and gestational diabetes mellitus in a Taiwanese population. Metabolism. 2004;53(9):1136-1139. PubMed doi:10.1016/j.metabol.2004.04.006
22. Sheu WHH, Lee WJ, Yao YE, et al. Lack of association between genetic variation in the beta3-adrenergic receptor gene and insulin resistance in patients with coronary heart disease. Metabolism. 1999;48(5):651-654. PubMed doi:10.1016/S0026-0495(99)90066-5
23. Tsai SJ, Yu YW, Lin CH, et al. Association study of adrenergic beta3 receptor (Trp64Arg) and G-protein beta3 subunit gene (C825T) polymorphisms and weight change during clozapine treatment. Neuropsychobiology. 2004;50(1):37-40. PubMed doi:10.1159/000077939
24. Ujike H, Nomura A, Morita Y, et al. Multiple genetic factors in olanzapine-induced weight gain in schizophrenia patients: a cohort study. J Clin Psychiatry. 2008;69(9):1416-1422. PubMed doi:10.4088/JCP.v69n0909
25. Nagano T, Matsuda Y, Tanioka T, et al. No association of the Trp 64 Arg mutation of the beta3-adrenergic receptor gene with obesity, type 2 diabetes mellitus, hyperlipidemia, and hypertension in Japanese patients with schizophrenia. J Med Invest. 2005;52(1-2):57-64. PubMed doi:10.2152/jmi.52.57
26. Ye J. Role of insulin in the pathogenesis of free fatty acid-induced insulin resistance in skeletal muscle. Endocr Metab Immune Disord Drug Targets. 2007;7(1):65-74. PubMed
27. Carlsson M, Orho-Melander M, Hedenbro J, et al. Common variants in the beta2-Gln27Glu and beta3-Trp64Arg: adrenoceptor genes are associated with elevated serum NEFA concentrations and type II diabetes. Diabetologia. 2001;44(5):629-636. PubMed doi:10.1007/s001250051670
28. Christiansen C, Poulsen P, Beck-Nielsen H. The Trp64Arg mutation of the adrenergic beta3 receptor gene impairs insulin secretion: a twin study. Diabet Med. 1999;16(10):835-840. PubMed doi:10.1046/j.1464-5491.1999.00130.x
29. H׸jlund K, Christiansen C, Bj׸rnsbo KS, et al. Energy expenditure, body composition and insulin response to glucose in male twins discordant for the Trp64Arg polymorphism of the beta3-adrenergic receptor gene. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2006;8(3):322-330. PubMed doi:10.1111/j.1463-1326.2005.00509.x