ABSTRACT
Objective: To assess children in the community for autism spectrum disorder (ASD) and associated risk factors.
Methods: In this 2-stage, cross-sectional study, children between 1.5 and 10 years of age were screened using the Chandigarh Autism Screening Instrument. Those with a score above the cutoff of 10 were assessed in detail using the Childhood Autism Rating Scale and the Autism Diagnostic Interview–Revised, and a detailed pediatric assessment was conducted. Risk factors were evaluated, and karyotype and fragile X genetic testing was done for those diagnosed with ASD. The study was conducted from July 2014 to December 2017.
Results: Compared to the control group, mothers of ASD children had more pregnancy-induced hypertension (PIH) and bleeding per vaginum (BPV) during the antenatal period. In the multivariate analysis, there was 6.3 times higher odds of having history of PIH (P = .02) and 7.7 times higher odds of BPV (P = .011) among children with ASD. There were much higher odds of having birth asphyxia (OR = 12.6), cardiorespiratory problems (OR = 10), metabolic abnormalities (hypoglycemia/ hypocalcemia) (OR = 12), and neonatal sepsis (OR = 16) in the ASD group compared to controls.
Conclusions: ASD patients experienced more antenatal and neonatal problems compared to controls.
Trial Registration: Clinical Trials Registry–India (CTRI/2017/02/007935)
Prim Care Companion CNS Disord 2023;25(2):22m03339
To cite: Arun P, Azad C, Kaur G, et al. A Community-based study of antenatal and neonatal risk factors in autism spectrum disorder. Prim Care Companion CNS Disord. 2023;25(2):22m03339.
To share: https://doi.org/10.4088/PCC.22m03339
© 2023 Physicians Postgraduate Press, Inc.
aDepartment of Psychiatry, Government Medical College and Hospital, Chandigarh, India
bDepartment of Pediatrics, Government Medical College and Hospital, Chandigarh, India
cDepartment of Physiology, Government Medical College and Hospital, Chandigarh, India
*Corresponding author: Priti Arun, MD, Department of Psychiatry, Government Medical College and Hospital, Sector 32, Chandigarh, India 160030 ([email protected]).
The ICD−10 describes autism spectrum disorder (ASD) as a pervasive developmental disorder (PDD) defined by the presence of abnormal and/or impaired development that manifests before the age of 3 years and by the characteristic type of abnormal functioning in all 3 areas of social interaction, communication, and restricted, repetitive behavior.1 Various studies have shown increasing prevalence of ASD, with a median of 62 per 10,000.2 A study by Poovathinal et al3 in a semiurban community of the south Indian state of Kerala found the prevalence of ASD to be 23.3 per 10,000. Various factors such as advanced parental age at birth, maternal prenatal medication use, bleeding, and gestational diabetes have been implicated in causation of ASD. The strongest evidence was found against previous fetal loss and maternal hypertension, preeclampsia, and proteinuria. Exact causality of ASD, however, remains elusive.4 There is a need to study antenatal and neonatal risk factors. Given reports of increasing prevalence of ASD and the public health implications, we conducted a community-based study to screen and evaluate antenatal and neonatal risk factors in children with ASD. The current study is part of a community-based survey, and a report on prevalence in the community has been published.5
METHODS
Study Design
This prospective, cross-sectional, single-center, community-based study was conducted by the Department of Psychiatry, Government Medical College and Hospital, Chandigarh, India. Children were recruited for the study after written informed consent was obtained from their parents. The study was conducted from July 2014 to December 2017. The study was conducted after approval from the institutional ethics committee and was registered with Clinical Trials Registry–India (CTRI/2017/02/007935).
Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
Children between the ages of 1.5 and 10 years5 were recruited after undergoing screening with the Chandigarh Autism Screening Instrument (CASI).6 A cutoff score of 10 on the CASI had a sensitivity of 89.16%, specificity of 89.13%, positive predictive value of 67.89%, and negative predictive value of 96.96%. Children with a CASI score > 10 were included as cases. Information regarding the antenatal and perinatal periods was obtained from hospital records made available by the parents.
Study Procedure and Data Collection
This cross-sectional 2-stage study was carried out in Chandigarh, Northern India. All children living in a defined area were screened for potential eligibility. The Union territory of Chandigarh was divided by urban, rural, or slum areas, and the proportionate population as per available census data was taken from each area. Sectors were randomly selected from the urban area.
In stage 1, a door-to-door survey was conducted by research workers. Parents or guardians completed a demographic form and provided consent for the child to complete the CASI. Those with CASI scores above the cutoff were evaluated in the hospital or at their home if unable to come to the hospital.
In stage 2, children with a positive CASI score were assessed with the Childhood Autism Rating Scale7 and the Autism Diagnostic Interview–Revised.8 Diagnosis of ASD was made according to DSM-5 criteria. Detailed methodology is published elsewhere.5
Clinical and demographic details including risk factors associated with ASD such as birth defects and perinatal and neonatal insults were obtained. Details from the antenatal and neonatal period were obtained from the medical records made available by the parents. A detailed history was taken, and a physical examination was conducted at the hospital by a pediatrician well versed in neurodevelopmental disorders. Genetic evaluation in the form of karyotyping and fragile X testing was done in ASD patients after consent was received.
Age-and sex-matched controls who had scored below the CASI cutoff were evaluated at their homes by a medical graduate (MD in psychiatry) specifically trained for that purpose.
Sample Size Calculation
Sample size was calculated after the first stage of the community survey was nearing completion. Assuming Caesarean section rate as a major risk factor, the sample size was calculated based on a 90% confidence level, with an anticipated 20% Caesarean section rate among controls and 40% among the ASD group.9 With an anticipated odds ratio of 2.67, the optimum sample size was 27 cases with 660 controls and a case-control ratio of 1:25, which resulted in 80% power of the test. The number of cases of ASD was 27 based on the number of ASD cases detected at that time.
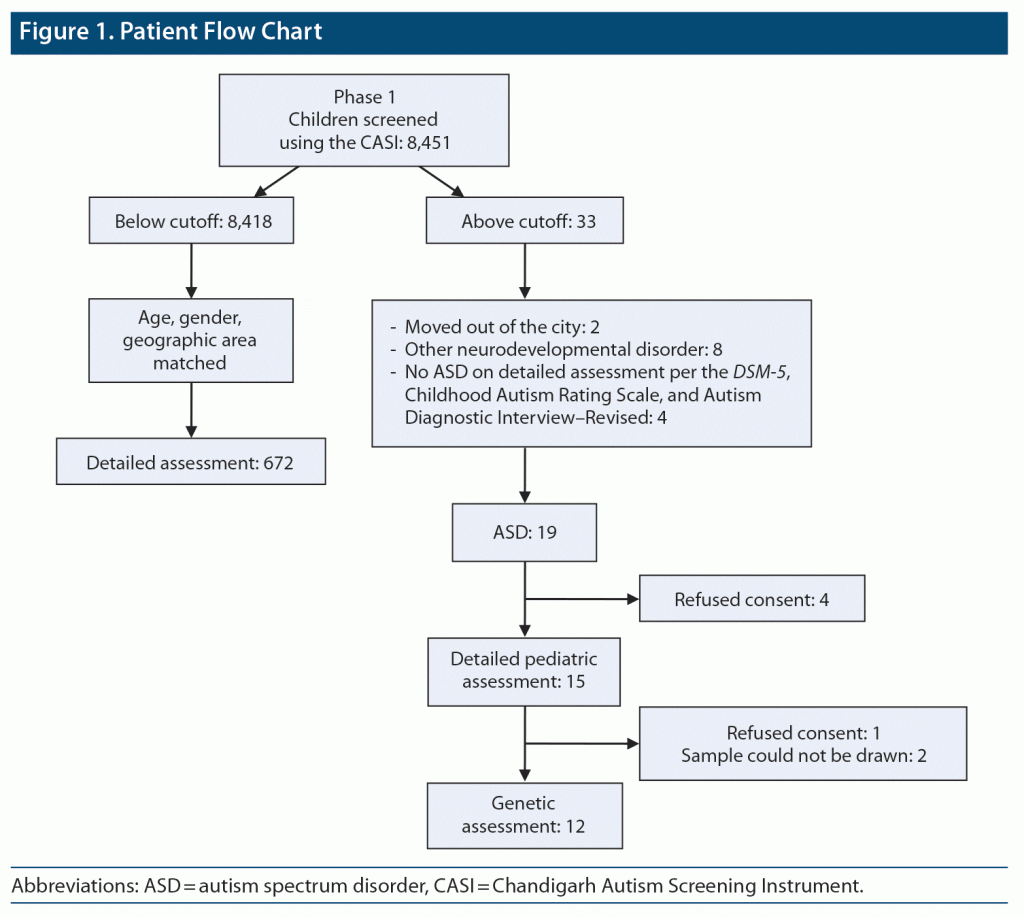
Among 19 cases diagnosed as having ASD, genetic evaluation was carried out to ascertain the underlying genetic cause. Fragile X testing using real-time PCR (molecular) method and karyotyping was done. Of 19 children, parents/guardians of 4 refused to provide consent for detailed pediatric assessment, hence pediatric assessment was done in only 15 cases. Genetic testing was not done in 5 cases due to refusal to provide consent and in 2 due to sampling issues. Thus, genetic testing was done in 12 children. In 2 children, no metaphases were available for karyotype despite repeat sampling (Figure 1).
RESULTS
The total number of children screened in the community survey was 8,451. Of those, 19 were diagnosed with ASD. The prevalence rate was 2.25 per 1,000. Eight children above the cutoff on the CASI were found to not have ASD but had other neurodevelopmental disorders. Of 8,418 children who scored below the cutoff on the CASI, 672 were assessed for antenatal and neonatal history using a specifically designed proforma.
Demographic Profile
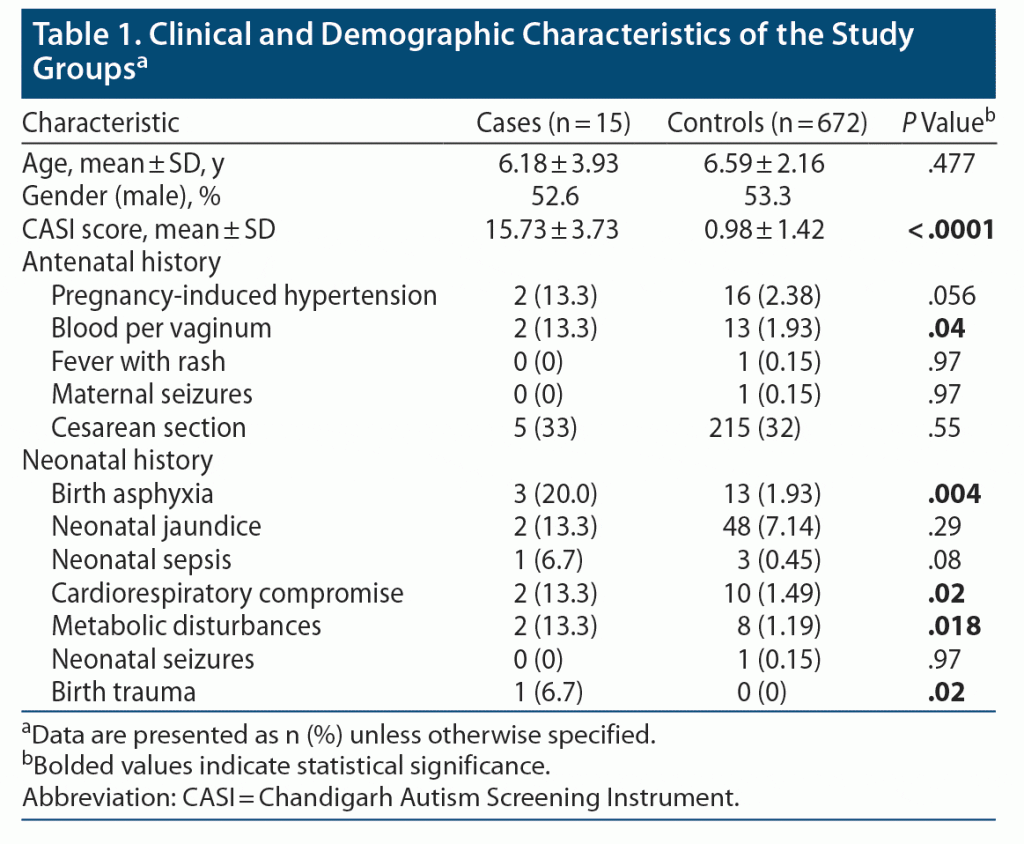
Antenatal history. Two of 15 (13.3%) children with ASD had antenatal history of pregnancy-induced hypertension (PIH) and bleeding per vaginum (BPV); however, only BPV was significantly higher in the ASD group. For all other factors, such as fever with rash, maternal seizures, and Caesarean section, there was no statistically significant difference between the groups (Table 1).
Neonatal history. History of birth asphyxia was found in a significantly higher number of ASD patients (n = 3, 20%), whereas only around 2% of controls had birth asphyxia (P = .004). Similarly, history of birth trauma, cardiorespiratory problems, and metabolic disturbances (hypoglycemia/hypocalcemia) during the neonatal period was seen in a higher proportion of children with ASD (P = .02, .018, and .02, respectively). Birth trauma was defined as mechanical injury sustained by a newborn during delivery. T-test (parametric test) was applied for age and CASI score, and Fisher exact test (nonparametric test) was used for the remaining variables.
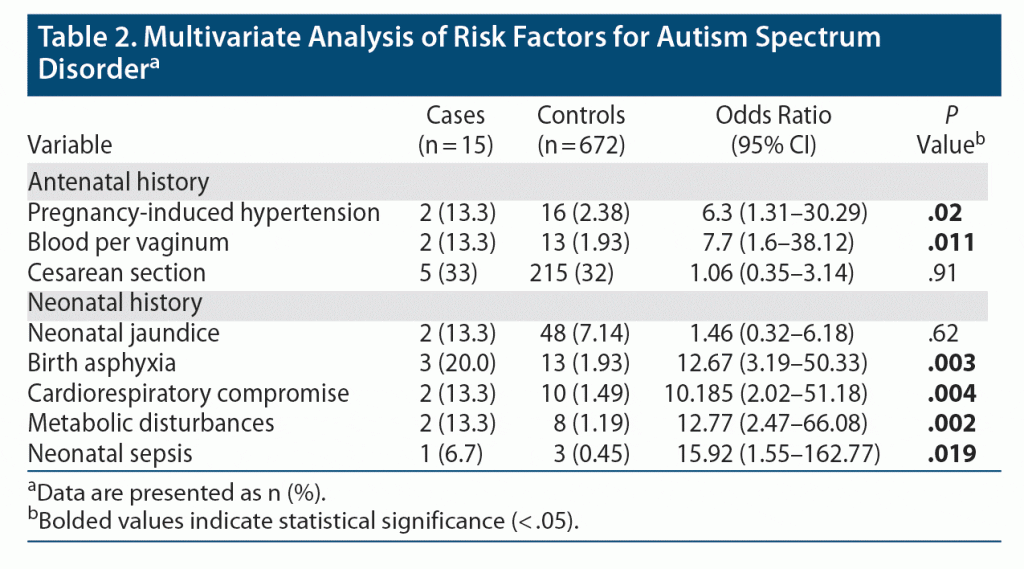
The multivariate analysis showed that ASD patients had 6.3 times higher odds of having history of PIH (P = .02) and 7.7 times higher odds of BPV (P = .011). Among the neonatal history, birth asphyxia, cardiorespiratory problems, neonatal sepsis, and metabolic problems were statistically significant factors. There was a 12.6 times higher chance of having birth asphyxia (P = .003) in the ASD group. Compared to controls, ASD patients had a 10 times higher chance of cardiorespiratory problems, 12 times higher chance of metabolic abnormalities, and 16 times higher chance of neonatal sepsis. Thus, ASD patients had higher chances of eventful neonatal problems compared to controls (Table 2).
Genetic testing showed that 1 child (10%) had fragile X syndrome and 1 child (10%) had a marker chromosome as seen in the karyotype. The child with the marker chromosome had profound intellectual disability (IQ = 8). Genetic etiology was found in 16.67% of children with ASD (2 of 12). The parents of the child with the marker chromosome refused to consent to provide another sample for microarray analysis, hence the location of the chromosome could not be ascertained. For 2 children, no metaphases were available for karyotype analysis.
DISCUSSION
In this study, PIH and BPV were found to be higher in mothers of children with ASD. Birth asphyxia, cardiorespiratory compromise, birth trauma, and hypoglycemia were significantly higher in children with ASD.
The results showed that PIH among mothers was higher but not statistically significant (at the .056 level, autistic group: 13.3%, control group: 2.38%). This finding is consistent with a study by Guinchat et al.10 The finding of higher PIH in the autistic group was reported in earlier studies,11 wherein the prevalence of PIH along with other comorbidities was higher (9.6%) in the ASD group compared to that of the controls (6.8%), but the differences were not statistically significant.
BPV among mothers was also significantly (at the .05 level) higher in the autism group (13.3%) compared to the control group (1.93%). This finding is in accordance with early studies (during the 1970s) showing the relationship between uterine bleeding in mothers and their subsequently delivered children who developed the syndromes of autism and childhood psychosis.12 Glasson et al13 also reported higher incidence of postpartum hemorrhage in mothers of ASD cases.
Regarding prenatal and postnatal factors, birth asphyxia was found in 20% of the autism group, which was significantly higher compared to the control group (P = .004). The OR was 12.6 (95% CI, 3.19–50.33) in the multivariate analysis. Fetal distress was rated as a primary predictor of ASD by Glasson et al.13 Cardiorespiratory compromise among the autism group (13.3%) was significantly (at the .05 level) higher compared to the control group (1.49%). This finding is supported by other studies14,15 in which the association between perinatal asphyxia and the development of ASD was reported. A study by Fezer et al14 reported that prevalence of prematurity, low birth weight, and perinatal asphyxia among children with ASD was higher than the general prevalence of these conditions among all live births in their country, region, and state.
Birth complications like trauma or ischemia have been found to be strongly linked to ASD.16 In our sample population, birth trauma was not reported in in the control group; however, 6.7% of the autism group suffered from birth trauma, which is significant at the .01 level. Our study thus confirms that birth trauma or injury was a factor associated with autism risk as was also found in a meta-analysis conducted by Modabbernia et al.15 Similar observations about PIH, maternal bleeding, and birth asphyxia have also been made in southeast Asian studies.17,18
Metabolic disturbance was significantly (at the .05 level) higher in the autism group (13.3%) compared to the control group (1.19%) (OR: 12.77; 95% CI, 2.47–66.08). Previous studies have also reported higher rates of metabolic disturbances. The metabolic disturbance reported in our study was hypoglycemia. Hypoglycemia in the neonatal period is a recognized risk factor for brain damage.19
We studied other factors such as x-ray exposure, drug intake, and trauma during the antenatal period, which were not reported in either of the groups. Fever with rash and seizure during pregnancy were reported in the control group (1 case each) but not in the autism group.
Findings of the present study regarding karyotype abnormalities are consistent with that of Çöp et al20 in which karyotype abnormalities were found in 9.7% of cases. The finding of fragile X in 16.6% of children is also consistent with another study wherein fragile X syndrome was found in 6% of children with autism.21 However, in an earlier study a much lower prevalence (1.6%) of fragile X syndrome was found in children.22 A similar rate of 1.5% was found in the study by Çöp et al.20 Fragile X syndrome is the most commonly known single gene cause of ASD. In the present study, the number was too low to comment on percentage.
Strengths and Limitations
The strength of our study is that it was based in the community, noting information from medical records of a community sample. A limitation is the small number of ASD cases, which reduces the power of the study. Inability to assess all the cases for detailed pediatric assessment and genetic testing is another limitation However there is enough evidence to point toward multifactorial causation of ASD.
CONCLUSION
ASD patients experienced more antenatal and neonatal problems compared to controls. This study contributes to knowledge regarding the role of antenatal and postnatal factors in causation of ASD, as it supports the accumulating evidence.
Submitted: June 19, 2022; accepted September 21, 2022.
Published online: March 28, 2023.
Relevant financial relationships: None.
Funding/support: The study received funding from the Department of Health Research, Government of India.
Role of the sponsor: The funding agency approved the research proposal but had no role in analysis, interpretation, writing, or publication of the manuscript.
Clinical Points
- Children with autism spectrum disorder (ASD) have higher chances of having had antenatal and neonatal complications.
- A higher proportion of mothers of children with ASD had pregnancy-induced hypertension and bleeding per vaginum during the antenatal period.
- Birth asphyxia, history of birth trauma, cardiorespiratory problems, and metabolic disturbances (hypoglycemia/hypocalcemia) during the neonatal period were more common in children with ASD.
References (22)

- International Classification of Diseases. 10th ed. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2010.
- Elsabbagh M, Divan G, Koh YJ, et al. Global prevalence of autism and other pervasive developmental disorders. Autism Res. 2012;5(3):160–179. PubMed CrossRef
- Poovathinal SA, Anitha A, Thomas R, et al. Prevalence of autism spectrum disorders in a semiurban community in south India. Ann Epidemiol. 2016;26(9):663–665.e8. PubMed CrossRef
- Gardener H, Spiegelman D, Buka SL. Prenatal risk factors for autism: comprehensive meta-analysis. Br J Psychiatry. 2009;195(1):7–14. PubMed CrossRef
- Arun P, Chavan BS. Survey of autism spectrum disorder in Chandigarh, India. Indian J Med Res. 2021;154(3):476–482. PubMed CrossRef
- Arun P, Chavan BS. Development of a screening instrument for autism spectrum disorder: Chandigarh Autism Screening Instrument. Indian J Med Res. 2018;147(4):369–375. PubMed CrossRef
- Rutter M, LeCouteur A. Autism Diagnostic Interview – Revised. Torrance, CA: Western Psychological Corporation; 2003.
- Schopler E, Van Bourgondien ME, Wellman GJ, et al. Childhood Autism Rating Scale. 2nd ed. Torrance: Western Psychological Services; 2010.
- Silva VBD, Maia FA, Oliveira AJS, et al. Association between autism spectrum disorder and peripartum events: a case-control study. Rev Paul Pediatr. 2022;41:e2021220. PubMed CrossRef
- Guinchat V, Thorsen P, Laurent C, et al. Pre-, peri- and neonatal risk factors for autism. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 2012;91(3):287–300. PubMed CrossRef
- Chandradasa M, Rohanachandra Y, Dahanayake D, et al. A Comparative study on medical comorbidities among children with autism spectrum disorder and controls in a children’s hospital. Sri Lanka J Child Health. 2017;46(3):262–266. CrossRef
- Torrey EF, Hersh SP, McCabe KD. Early childhood psychosis and bleeding during pregnancy: a prospective study of gravid women and their offspring. J Autism Child Schizophr. 1975;5(4):287–297. PubMed CrossRef
- Glasson EJ, Bower C, Petterson B, et al. Perinatal factors and the development of autism: a population study. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2004;61(6):618–627. PubMed CrossRef
- Fezer GF, Matos MB, Nau AL, et al. Perinatal features of children with autism spectrum disorder. Rev Paul Pediatr. 2017;35(2):130–135. PubMed CrossRef
- Modabbernia A, Mollon J, Boffetta P, et al. Impaired gas exchange at birth and risk of intellectual disability and autism: a meta-analysis. J Autism Dev Disord. 2016;46(5):1847–1859. PubMed CrossRef
- Modabbernia A, Velthorst E, Reichenberg A. Environmental risk factors for autism: an evidence-based review of systematic reviews and meta-analyses. Mol Autism. 2017;8(1):13. PubMed CrossRef
- Nath S, Roy R, Mukherjee S. Perinatal complications associated with autism–a case control study in a neurodevelopment and early intervention clinic. J Indian Med Assoc. 2012;110(8):526–529. PubMed
- Malla A, Pathak J, Shrestha S, et al. A study on parental age, pregnancy events and autism spectrum disorders. J Kathmandu Med Coll. 2017;6(1):14–21. CrossRef
- De Angelis LC, Brigati G, Polleri G, et al. Neonatal hypoglycemia and brain vulnerability. front endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021;16;12:634305.
- Çöp E, Yurtbaşi P, Öner Ö, et al. Genetic testing in children with autism spectrum disorders. Anadolu Psikiyatri Derg. 2015;16(6):426–432. PubMed CrossRef
- García-Nonell C, Ratera ER, Harris S, et al. Secondary medical diagnosis in fragile X syndrome with and without autism spectrum disorder. Am J Med Genet A. 2008;146A(15):1911–1916. PubMed CrossRef
- Bailey DB Jr, Mesibov GB, Hatton DD, et al. Autistic behavior in young boys with fragile X syndrome. J Autism Dev Disord. 1998;28(6):499–508. PubMed CrossRef
Enjoy this premium PDF as part of your membership benefits!