ABSTRACT
Objective: Major depressive disorder (MDD) is a chronic, debilitating mood disorder associated with poor medical outcomes. MDD has a multifactorial etiology with numerous biopsychosocial factors implicated as risk factors. Functional and psychiatric impairments have been evaluated in patients with liver cirrhosis; however, less is known about the prevalence and risk factors for the development of MDD in those patients. The objective of this study was to evaluate the risk of developing depression among adult patients with liver cirrhosis in the United States.
Methods: Data were collected using a commercial database, an aggregate of electronic health record data from 26 major integrated US health care systems consisting of 360 hospitals in the US from 1999 to 2019.
The study cohort was retrieved by searching the database for a Systematized Nomenclature of Medicine-Clinical Terms diagnosis of “cirrhosis of liver” during the designated period of the study.
The following factors were adjusted for in the analyses: age, sex, race, smoking, alcohol, substance abuse, underlying mental disorders, and comorbidities.
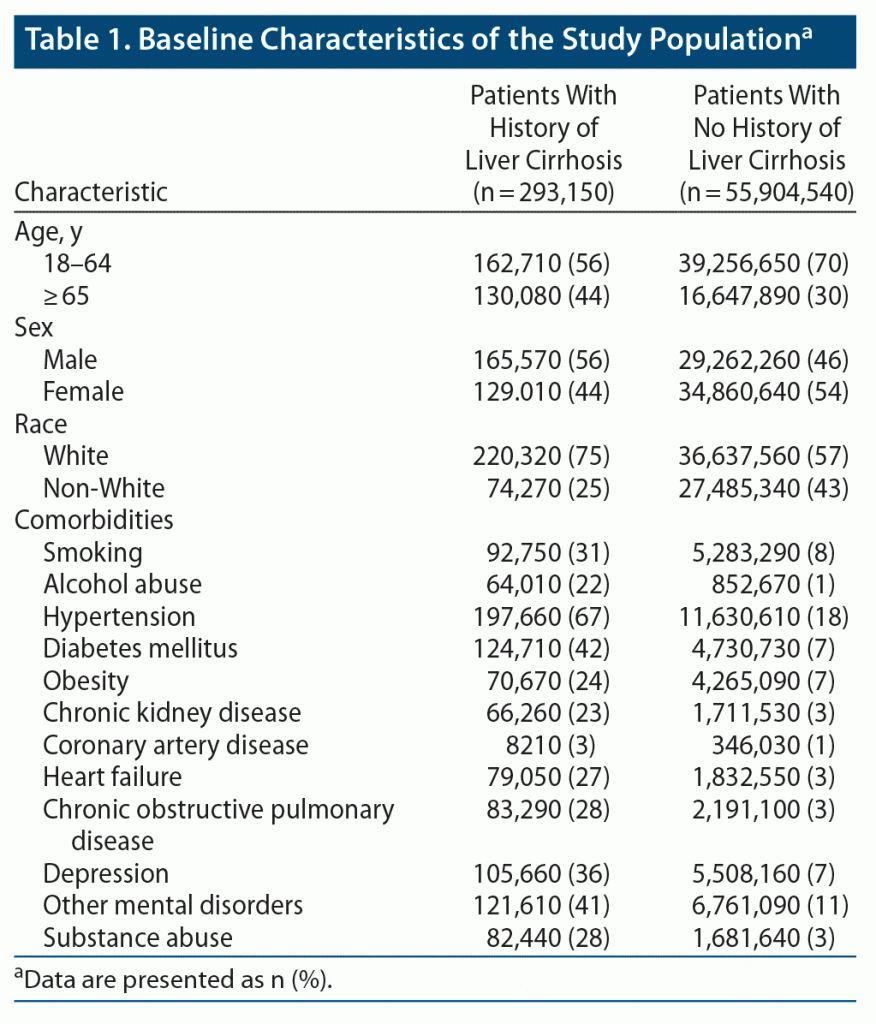
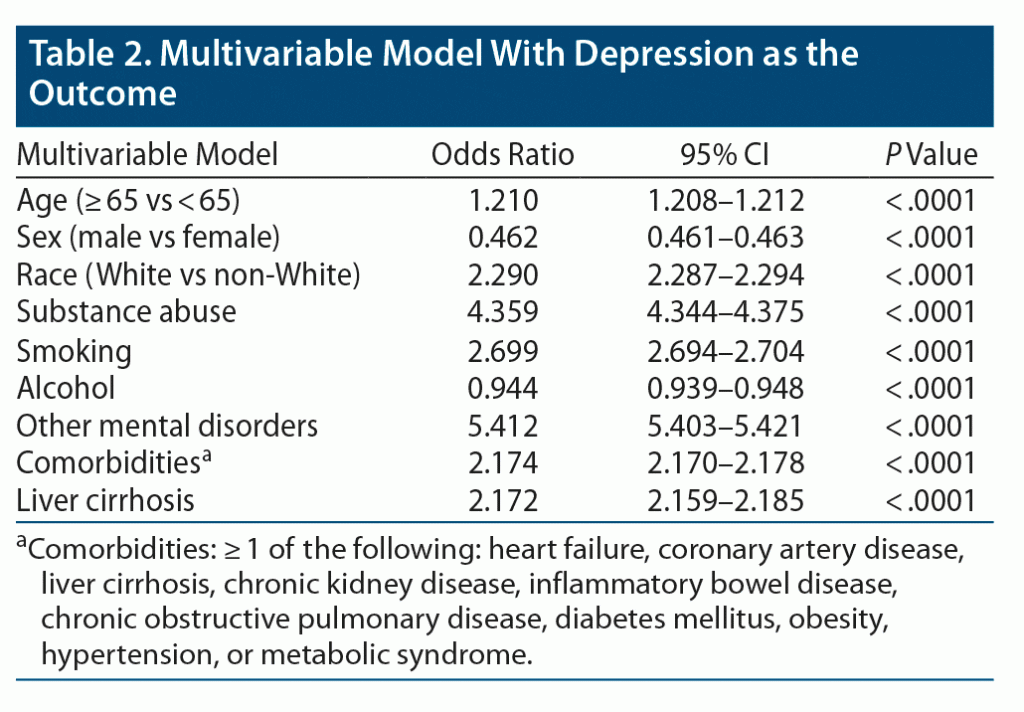
Results: 56,197,690 adults were identified between 1999 and 2019. Of those, 293,150 had a diagnosis of liver cirrhosis. The prevalence of depression among those cirrhotic patients was 23.93% versus 7.61% in the noncirrhotic control group (95% CI, 16.1836%–16.4770%; P < .0001). By applying a multivariate analysis model, cirrhotic patients were found to be more likely to develop depression (odds ratio = 2.172; 95% CI, 2.159–2.185; P < .0001) compared to patients with no prior history of liver cirrhosis.
Conclusions: Liver cirrhosis is associated with increased risk of depression and is likely to be an independent risk factor in its development. Future efforts should focus on the identification and treatment of this debilitating condition in those with liver cirrhosis via an integrated care model.
Prim Care Companion CNS Disord 2022;24(1):20m02889
To cite: Abureesh M, Alkhayyat M, Abualnadi I, et al. Epidemiology of depressive disorders in patients with liver cirrhosis: a population-based study in the United States. Prim Care Companion CNS Disord. 2022;24(1):20m02889.
To share: https://doi.org/10.4088/PCC.20m02889
© Copyright 2022 Physicians Postgraduate Press, Inc.
aStaten Island University Hospital, Staten Island, New York
bCleveland Clinic Foundation, Cleveland, Ohio
cJFK University Medical Center, Edison, New Jersey
dRush University, Northshore University Health System, Evanston, Illinois
eBanner Behavioral Health Hospital, Scottsdale, Arizona
*Corresponding author: Liliane S. Deeb, MD, FACG, Staten Island University Hospital, 475 Seaview Ave, Staten Island, New York 10305 ([email protected]).
Major depressive disorder (MDD), or clinical depression, is a psychiatric disorder characterized by 2 or more weeks of persistently depressed mood accompanied by symptoms such as feelings of worthlessness, guilt, hopelessness, helplessness, loss of self-esteem, sleep disturbance, changes in oral intake, anhedonia, loss of interest, and suicidality.1 Depression is highly prevalent globally and is a leading cause of disability.2–4 The Global Burden of Disease Study found depression to be a leading cause of disability among all illnesses.5 The lifetime prevalence of depression in the United States is estimated to be 17%.6 Depressive disorders not only commonly accompany chronic progressive medical conditions, such as coronary artery disease, diabetes mellitus, malignancy, stroke, neurodegenerative disease, and chronic liver diseases,7–10 but also serve as risk factors for their mortality, life burden, and cost.11–13
Liver cirrhosis is one of the diseases commonly associated with depression.14–16 It is characterized by progressive hepatic fibrosis, destruction of hepatic architecture, and formation of regenerative nodules. The most common causes of liver cirrhosis in the United States are hepatitis C, alcoholic liver disease, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, and iatrogenic insults.17,18 At the early stages of cirrhosis, termed compensated liver cirrhosis, patients may be asymptomatic or may report nonspecific neurovegetative symptoms such as anorexia, weight loss, weakness, and fatigue.19,20 If unidentified and untreated, these symptoms will progress to compensated liver cirrhosis, and symptoms of hepatic insufficiency such as jaundice, pruritus, hepatic encephalopathy, ascites, and variceal hemorrhage may develop.21 At this stage, the only treatment option available is liver transplantation. The progressive nature of this disease results in high rates of hospitalization, extensive exposure to medications, increased financial burden, frequent need for invasive procedures, changes in body image, and an increase in morbidity and mortality.20 All these factors contribute to the physical and psychological stress that mediates the development of depressive symptoms.
High rates of depression have been documented in patients with decompensated liver disease and in those anticipating liver transplantation.22,23 While on the transplant waiting list, cirrhotic patients who are depressed are more likely to have a terminal event compared to their counterparts who are not depressed.24 Studies have demonstrated high rates of disparity reflecting depression among patients with liver cirrhosis (point prevalence of 17%–57%)25,26 compared to the general population (point prevalence of 2%).27 Despite the relationship between depression and liver cirrhosis and its relevance to the clinical outcome, few studies in the literature have explored the prevalence of depression in cirrhotic patients. The aim of this study was to evaluate the risk of developing depression among adult patients with liver cirrhosis in the United States.
METHODS
Database
This retrospective study was performed using a large multi-institutional database (IBM Explorys Solutions, Armonk, New York) containing electronic health record (EHR) data from 26 health care systems, consisting of 360 US hospitals from 1999 to 2019.28 The data were collected from billing inquiries. Raw data of diagnoses, findings, and procedures were arranged in the Systematized Nomenclature of Medicine-Clinical Terms (SNOMED-CT) hierarchy. Prescription drug orders were mapped into SNOMED and RxNorm.28 The Explorys database, which is HIPAA compliant, generated multiple cohorts based on the presence or absence of SNOMED-CT diagnoses. These cohorts allow for further analysis to provide the temporal relationship between diagnoses and identification of sentinel diagnoses.28 To protect patient identity, cell counts in the database were rounded to the nearest 10.28 Explorys has been validated in multiple medical fields including gastroenterology and psychiatry.29–32
Patient Selection and Covariates
Active records of all adult patients aged ³ 18 years were identified between the years 1999 and 2019. The study cohort (liver cirrhosis) was then retrieved by searching the database for a SNOMED-CT diagnosis of “cirrhosis of liver” during the designated period of the study. Demographics such as age, sex, and race-based data were collected. Known risk factors of depression were identified by searching the database for their respective SNOMED-CT diagnoses including sex, race, age, smoking, substance abuse (including alcohol), other mental disorders, and comorbid conditions.
Statistical Analysis
Patients with liver cirrhosis (study group) were compared with noncirrhotic patients (control group). The overall period prevalence was calculated by dividing the total number of individuals with the diagnosis of depression by the total number of individuals in Explorys. The prevalence rates of depression in the study group (cirrhotic patients) and in the control group (noncirrhotic patients) were calculated by dividing the total number of individuals with depression by the total number of individuals with and without liver cirrhosis, respectively. Cases of depression were included in this analysis only if the diagnosis of cirrhosis preceded diagnosis of depression. The odds ratio (OR) for univariable analysis and its standard error and 95% confidence interval were calculated using MedCalc Statistical Software (Ostend, Belgium). To adjust for possible confounding from the covariates listed previously, multivariate regression model was constructed using binary logistic regression with liver cirrhosis as the dependent variable. Statistical analysis for the multivariable multivariate model was performed using SPSS version 25 (IBM Corp, Armonk, New York). For all analyses, a 2-sided P value < .05 was considered statistically significant.
RESULTS
Of the 56,197,690 patients identified between 1999 and 2019, 293,150 carried a diagnosis of liver cirrhosis, while 55,904,540 had no history of liver disease. Basic demographic characteristics in both groups are shown in Table 1.
Based on our study, the documented prevalence of depression among people with liver cirrhosis is 23.93%. This rate is significantly higher than the prevalence of 7.61% we found in noncirrhotic patients (P < .0001). After adjusting for age, sex, race, smoking, substance abuse including alcohol, other mental disorders, and comorbid conditions, we found that patients with liver cirrhosis were more likely to develop depression (OR = 2.172; 95% CI, 2.159–2.185; P < .0001) compared to patients with no prior history of liver cirrhosis. When looking at the development of depression, having other mental disorders was the strongest predicting factor by a decided margin; other predictors were age ³ 65 years, female sex, history of polysubstance abuse, nicotine use, and the presence of more than 1 comorbidity or chronic disease. ORs and 95% confidence intervals for these factors are presented in Table 2.
DISCUSSION
Our findings suggest a strong association between liver cirrhosis and depression. The cause of this association is likely multifactorial, involving biological, social, and psychological factors. Substance abuse and nonadherence with medications are behaviors common in both chronic liver disease and MDD, which can create an environment of nonresponsiveness to standard treatments.33,34 Biologically, the inflammatory component of depression is increasingly recognized, making it reasonable to assume that there may be a physiologic mechanism linking liver cirrhosis and depressive symptoms. Loftis et al35 showed that higher levels of proinflammatory cytokines detected in patients with chronic liver disease correlated positively to the severity of depression in some subgroups. Increased levels of CD8+ T cells (also known as “killer T cells”) have been shown to correlate with severity of depressive symptoms in cirrhotic patients. These findings, among many, suggest that specific inflammatory and immune reactions in cirrhotic patients may by mechanistically linked to the development of depressive symptoms.36–38
A variety of point prevalence of depression in cirrhotic patients as well as in the general population has been reported in the literature.34,39 This variation in the prevalence of depression is consistent with the complexity of diagnosing MDD, inaccuracies in chart documentations, and increasing mental health literacy among physicians. Across these studies, the prevalence of depression was noted to be higher in cirrhotic patients,34,40 and it has been noted that the severity of liver disease correlates with the severity of depressive symptoms.41 Similar to the general population, female sex was associated with higher risk of depression in those with cirrhosis.42
Cirrhosis is associated with impaired functionality and recurrent hospitalizations. When other morbidities are present, our study showed that people with cirrhosis have a higher likelihood of developing depression. These findings are consistent with a meta-analysis by Read et al.43 In a thematic analysis performed by Stanners et al,44 patients with multiple comorbidities attributed their depression to subjective changes in their internal and external environment related to their suboptimal physical health. Our finding that nicotine use is a significant risk factor in the development of depression in cirrhotic patients is consistent with a meta-analysis by Fluharty et al,45 showing that depression was reported prior to nicotine use in over half of the subjects. The association between psychiatric disorders, polysubstance abuse, and depression is prevalent in the literature, is well known to clinicians,39,46 and is consistent with our findings that substance abuse is a predictive factor in the development of depressive symptoms. The strong association between polysubstance abuse and liver cirrhosis warrants the need for perception and early recognition of depression along with robust screening and treatment protocols in the hepatic care setting.
This is the largest study, to our knowledge, to evaluate the association between liver cirrhosis and depression in a US population, and the large sample size is a significant strength of our study. The sizable number of patients provided also functions to eliminate the effect of minor confounders and improves the ability to identify relatively uncommon associations.
In addition to the retrospective design of our study, other limitations include the inability to determine social history and life events, which have shown positive associations with depression. However, given that Explorys aggregates data from 50 states throughout the United States, this partially limits the effect of geographic and socioeconomic confounders as well as improves generalizability of the results. A major hindrance in all studies based primarily on chart data is that it is not possible to verify the validity of diagnosis. This weakness of our study is partially mitigated by the large number of clinicians who were involved in making the diagnosis in our large sample. Another limitation is the overlap between constitutional symptoms of chronic liver disease and neurovegetative symptoms of MDD, likely creating significant diagnostic ambiguity when screening for depression.
This study confirms an association between liver cirrhosis and depression and points to the significant need for integrated psychiatric care in the treatment of cirrhotic patients. Our findings may also influence the type of psychiatric care recommended. Based on our findings, we recommend that physicians of cirrhotic patients formally screen for depressive symptoms, routinely test for substance abuse, screen for common psychiatric disorders, and address comorbid medical problems. Adjunct use of psychiatric referral is warranted in patients with decompensating psychiatric disorders, and treatment of depressive symptoms will likely improve their medical and biopsychosocial outcomes.
Submitted: December 4, 2020; accepted April 1, 2021.
Published online: January 13, 2022.
Potential conflicts of interest: None.
Funding/support: None.
Clinical Points
- It is postulated that the propensity for patients with liver cirrhosis to develop depression is higher than for those without cirrhosis.
- A holistic approach should be initiated, including referral to a psychiatrist, to possibly improve morbidity and quality of life in patients with cirrhosis.
- Physicians treating patients with cirrhosis should screen for mental disorders including depression and substance use disorders.
References (46)

- Vahia VN. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders 5: a quick glance. Indian J Psychiatry. 2013;55(3):220–223. PubMed CrossRef
- Kessler RC, Berglund P, Demler O, et al; National Comorbidity Survey Replication. The epidemiology of major depressive disorder: results from the National Comorbidity Survey Replication (NCS-R). JAMA. 2003;289(23):3095–3105. PubMed CrossRef
- Goldberg D. The detection and treatment of depression in the physically ill. World Psychiatry. 2010;9(1):16–20. PubMed CrossRef
- Friedrich MJ. Depression is the leading cause of disability around the world. JAMA. 2017;317(15):1517. PubMed CrossRef
- Murray CJL, Lopez AD, eds. The Global Burden of Disease: A Comprehensive Assessment of Mortality and Disability From Diseases, Injuries, and Risk Factors in 1990 and Projected to 2020. Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press; 1996.
- Kessler RC, Berglund P, Demler O, et al. Lifetime prevalence and age-of-onset distributions of DSM-IV disorders in the National Comorbidity Survey Replication. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2005;62(6):593–602. PubMed CrossRef
- Frasure-Smith N, Lespérance F, Talajic M. Depression following myocardial infarction: impact on 6-month survival. JAMA. 1993;270(15):1819–1825. PubMed CrossRef
- Rocha NS, Fleck MP. Evaluation of quality of life in adults with chronic health conditions: the role of depressive symptoms. Br J Psychiatry. 2010;32(2):119–124. PubMed CrossRef
- Shekelle RB, Raynor WJ Jr, Ostfeld AM, et al. Psychological depression and 17-year risk of death from cancer. Psychosom Med. 1981;43(2):117–125. PubMed CrossRef
- Gutteling JJ, de Man RA, van der Plas SM, et al. Determinants of quality of life in chronic liver patients. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2006;23(11):1629–1635. PubMed CrossRef
- Spitzer RL, Kroenke K, Linzer M, et al. Health-related quality of life in primary care patients with mental disorders: results from the PRIME-MD 1000 Study. JAMA. 1995;274(19):1511–1517. PubMed CrossRef
- Simon GE, VonKorff M, Barlow W. Health care costs of primary care patients with recognized depression. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1995;52(10):850–856. PubMed CrossRef
- Diez-Quevedo C, Lupón J, González B, et al. Depression, antidepressants, and long-term mortality in heart failure. Int J Cardiol. 2013;167(4):1217–1225. PubMed CrossRef
- Younossi ZM, Boparai N, McCormick M, et al. Assessment of utilities and health-related quality of life in patients with chronic liver disease. Am J Gastroenterol. 2001;96(2):579–583. PubMed CrossRef
- Bianchi G, Marchesini G, Nicolino F, et al. Psychological status and depression in patients with liver cirrhosis. Dig Liver Dis. 2005;37(8):593–600. PubMed CrossRef
- Kanwal F, Hays RD, Kilbourne AM, et al. Are physician-derived disease severity indices associated with health-related quality of life in patients with end-stage liver disease? Am J Gastroenterol. 2004;99(9):1726–1732. PubMed CrossRef
- Zhou WC, Zhang QB, Qiao L. Pathogenesis of liver cirrhosis. World J Gastroenterol. 2014;20(23):7312–7324. PubMed CrossRef
- Wong RJ, Aguilar M, Cheung R, et al. Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis is the second leading etiology of liver disease among adults awaiting liver transplantation in the United States. Gastroenterology. 2015;148(3):547–555. PubMed CrossRef
- Sargent S, ed. Liver Diseases: An Essential Guide for Nurses and Health Care Professionals. Wiley-Blackwell; 2009.
- D’Amico G, Garcia-Tsao G, Pagliaro L. Natural history and prognostic indicators of survival in cirrhosis: a systematic review of 118 studies. J Hepatol. 2006;44(1):217–231. PubMed CrossRef
- Planas R, Ballesté B, Alvarez MA, et al. Natural history of decompensated hepatitis C virus-related cirrhosis: a study of 200 patients. J Hepatol. 2004;40(5):823–830. PubMed CrossRef
- Rodrigue JR, Davis GL, Howard RJ, et al. Psychological adjustment of liver transplant candidates. Clin Transplant. 1993;7(3):228–229. PubMed
- Bonsel GJ, Essink-Bot ML, Klompmaker IJ, et al. Assessment of the quality of life before and following liver transplantation: first results. Transplantation. 1992;53(4):796–800. PubMed CrossRef
- Singh N, Gayowski T, Wagener MM, et al. Depression in patients with cirrhosis. impact on outcome. Dig Dis Sci. 1997;42(7):1421–1427. PubMed CrossRef
- Mullish BH, Kabir MS, Thursz MR, et al. Review article: depression and the use of antidepressants in patients with chronic liver disease or liver transplantation. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2014;40(8):880–892. PubMed CrossRef
- Nardelli S, Pentassuglio I, Pasquale C, et al. Depression, anxiety and alexithymia symptoms are major determinants of health-related quality of life (HRQoL) in cirrhotic patients. Metab Brain Dis. 2013;28(2):239–243. PubMed CrossRef
- Patten SB, Wang JL, Beck CA, et al. Measurement issues related to the evaluation and monitoring of major depression prevalence in Canada. Chronic Dis Can. 2005;26(4):100–106. PubMed
- IBM Explorys Solutions. Accessed December 1, 2021. https://www.ibm.com/watson-health/about/explorys
- Alkhayyat M, Qapaja T, Aggarwal M, et al. Epidemiology and risk of psychiatric disorders among celiac disease patients: a population-based national study. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021;36(8):2165–2170. PubMed CrossRef
- Alkhayyat M, Saleh MA, Abureesh M, et al. The risk of acute and chronic pancreatitis in celiac disease. Dig Dis Sci. 2021;66(8):2691–2699. PubMed CrossRef
- Alkhayyat M, Abureesh M, Gill A, et al. Lower rates of colorectal cancer in patients with inflammatory bowel disease using anti-TNF therapy. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2021;27(7):1052–1060. PubMed CrossRef
- Khan D, Abureesh M, Alkhayyat M, et al. Prevalence of myocardial infarction in patients with chronic pancreatitis. Pancreas. 2021;50(1):99–103. PubMed CrossRef
- DiMatteo MR, Lepper HS, Croghan TW. Depression is a risk factor for noncompliance with medical treatment: meta-analysis of the effects of anxiety and depression on patient adherence. Arch Intern Med. 2000;160(14):2101–2107. PubMed CrossRef
- Buganza-Torio E, Mitchell N, Abraldes JG, et al. Depression in cirrhosis: a prospective evaluation of the prevalence, predictors and development of a screening nomogram. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2019;49(2):194–201. PubMed CrossRef
- Loftis JM, Huckans M, Ruimy S, et al. Depressive symptoms in patients with chronic hepatitis C are correlated with elevated plasma levels of interleukin-1beta and tumor necrosis factor-alpha. Neurosci Lett. 2008;430(3):264–268. PubMed CrossRef
- Ko FY, Tsai SJ, Yang AC, et al. Association of CD8 T cells with depression and anxiety in patients with liver cirrhosis. Int J Psychiatry Med. 2013;45(1):15–29. PubMed CrossRef
- Dantzer R, O’Connor JC, Freund GG, et al. From inflammation to sickness and depression: when the immune system subjugates the brain. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2008;9(1):46–56. PubMed CrossRef
- Laso FJ, Madruga JI, López A, et al. Distribution of peripheral blood lymphoid subsets in alcoholic liver cirrhosis: influence of ethanol intake. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 1996;20(9):1564–1568. PubMed CrossRef
- Kessler RC, Ormel J, Petukhova M, et al. Development of lifetime comorbidity in the World Health Organization world mental health surveys. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2011;68(1):90–100. PubMed CrossRef
- Zhang AZ, Wang QC, Huang KM, et al. Prevalence of depression and anxiety in patients with chronic digestive system diseases: a multicenter epidemiological study. World J Gastroenterol. 2016;22(42):9437–9444. PubMed CrossRef
- Zhu HP, Gu YR, Zhang GL, et al. Depression in patients with chronic hepatitis B and cirrhosis is closely associated with the severity of liver cirrhosis. Exp Ther Med. 2016;12(1):405–409. PubMed CrossRef
- Pedersen CB, Mors O, Bertelsen A, et al. A comprehensive nationwide study of the incidence rate and lifetime risk for treated mental disorders. JAMA Psychiatry. 2014;71(5):573–581. PubMed CrossRef
- Read JR, Sharpe L, Modini M, et al. Multimorbidity and depression: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Affect Disord. 2017;221:36–46. PubMed CrossRef
- Stanners MN, Barton CA, Shakib S, et al. Depression diagnosis and treatment amongst multimorbid patients: a thematic analysis. BMC Fam Pract. 2014;15(1):124. PubMed CrossRef
- Fluharty M, Taylor AE, Grabski M, et al. The association of cigarette smoking with depression and anxiety: a systematic review. Nicotine Tob Res. 2017;19(1):3–13. PubMed CrossRef
- Hybels CF, Blazer DG. Epidemiology of late-life mental disorders. Clin Geriatr Med. 2003;19(4):663–696. PubMed CrossRef
Enjoy this premium PDF as part of your membership benefits!