Prim Care Companion CNS Disord 2022;24(3):21cr03051
To cite: Roy C, Jaiswal S, B. P. J, et al. Haloperidol-induced acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis: a rare side effect. Prim Care Companion CNS Disord. 2022;24(3):21cr03051.
To share: https://doi.org/10.4088/PCC.21cr03051
© Copyright 2022 Physicians Postgraduate Press, Inc.
aDepartment of Psychiatry, Central Institute of Psychiatry, Kanke, Ranchi, Jharkhand, India
*Corresponding author: Varun Mehta, MD, DNB, Department of Psychiatry, Central Institute of Psychiatry, Kanke, Ranchi, Jharkhand, India, PIN- 834001 ([email protected]).
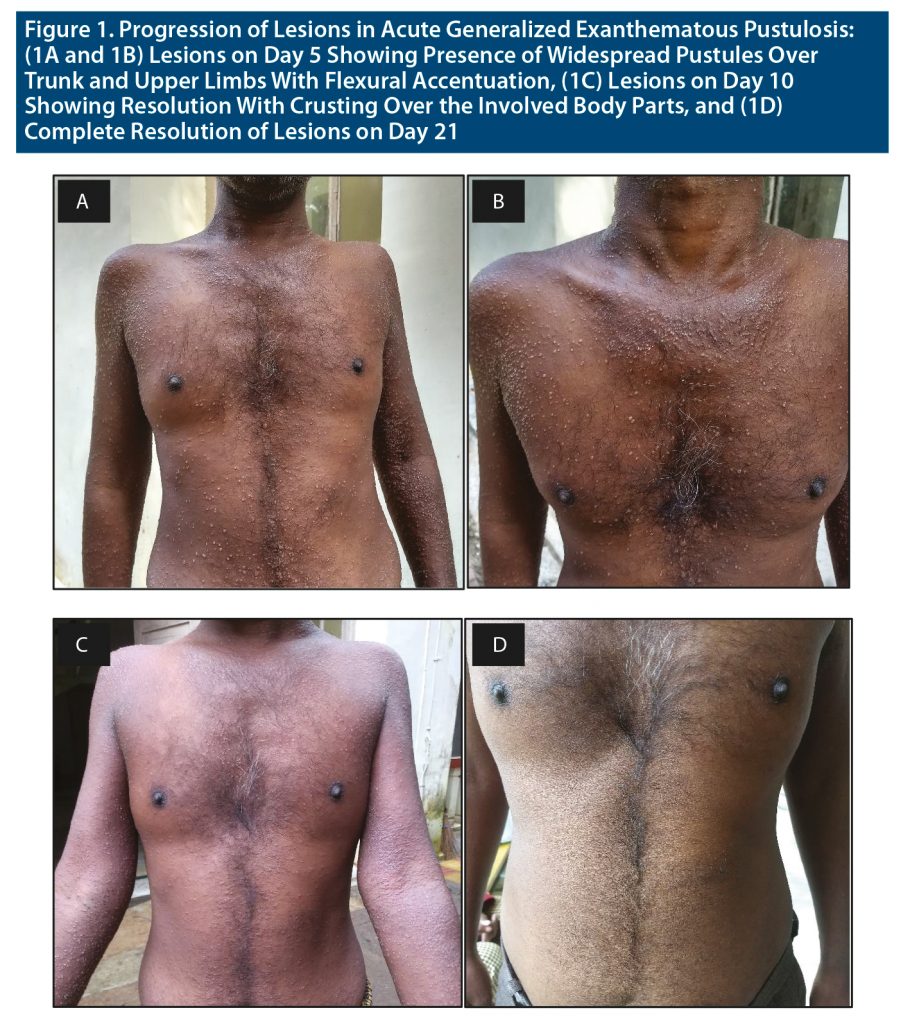
Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis (AGEP) is characterized by an acute onset formation of extensive nonfollicular sterile pustules on erythematous background combined with fever and peripheral blood leukocytosis.1 Characteristically, it starts in the main folds (axillary, inguinal, and submammary areas) and spreads quickly (within a few hours) on the trunk and limbs. AGEP is rare with incidence of 1 to 5 cases per million per year.2 The cause of AGEP in 90% percent of the cases is associated with ingestion of drugs like aminopenicillins, sulphonamides, quinolones, or hydroxychloroquine.3,4 Other causes include bacterial, viral, or parasitic infections; spider bites; herbal medications; lacquer; mercury; and even psoralen combined with ultraviolet A treatment.5 It follows a benign and self-limiting course, and treatment is mostly supportive. Here, we discuss a case wherein the patient had acute onset of pustules over the trunk and upper limbs after initiation of tablet haloperidol. He was diagnosed with AGEP, after which haloperidol was stopped and supportive treatment was provided.
Case Report
A 35-year-old patient from urban India with no significant past, personal, or family history of psychiatric, autoimmune, or allergic disorder presented with chief complaints of aggressive assaultive behavior, suspiciousness, remaining aloof, and wandering tendency for the past year. The mental status examination revealed a cooperative patient with increased motor activity with an irritable affect, delusion of grandiosity, and delusion of persecution along with third-person auditory hallucinations. The diagnosis was kept as schizophrenia. After receiving a 3-day course of psychotropic injections, he was switched to tablet haloperidol 10 mg. Five days after initiation of treatment, the patient developed acute-onset pustular lesions mainly over the trunk and upper limbs associated with pruritis (Figure 1). There was flexural accentuation and no mucosal involvement. Investigations showed the total leukocyte count as 15,900 mm3 and the neutrophils as 78%. The liver function tests, renal function tests, serologic tests, and routine stool examination were unremarkable. Tzanck smear revealed inflammatory cells, and skin biopsy revealed superficial and deep perivascular and periappendageal infiltrate of lymphocytes and numerous eosinophils (Supplementary Appendix 1). The papillary dermis showed edema. AGEP validation score of the EuroSCAR study group was 8.4 The patient was diagnosed with AGEP, and haloperidol was stopped, as it was considered the offending drug. Tablet prednisolone 30 mg was started in tapering doses along with tablet fexofenadine 120 mg for 10 days. Topical calamine and fluocinolone acetate lotion were also continued for 14 days. The lesions completely resolved after 12 days on the above medication. Post recovery, the patient was started on second-generation antipsychotic tablet aripiprazole 5 mg, which was optimized to 20 mg/d. The patient was discharged approximately 6 weeks after admission, and at outpatient follow-up a month later, he showed good tolerance to tablet aripiprazole and reported no incidence of drug rashes.
Discussion
This is the first case, to the best of our knowledge, reporting psychotropics to be the offending drug causing AGEP. Haloperidol is a first-generation antipsychotic used in the treatment of various psychiatric disorders. During the onset of the lesion, the patient was only on tablet haloperidol 10 mg with no other concomitant medication. We were unable to link the causation to the existing mechanism of action or the chemical structure of haloperidol. However, AGEP is believed to be a delayed type of hypersensitivity characterized by activation of drug-specific CD4 and CD8 T cells. After migration to the skin, these T cells use perforin/granzyme B and Fas ligand to cause keratinocytes apoptosis, resulting in epidermal vesicle formation.1 Drug-specific T cells along with other inflammatory cells also produce various cytokines and chemokines, mainly CXCL8 (IL-8),5 a potent neutrophil-attracting chemokine, which lead to neutrophil accumulation within the vesicles and subsequent formation of pustules. A correlation between mutations in the IL-36RN gene, encoding the interleukine-36 receptor antagonist (IL-36Ra), and the development of generalized pustular eruptions after drug intake has also been found.6
Several diagnostic criteria have been proposed along with a well-recognized scoring system elaborated by the EuroSCAR project.4,7 The differential diagnoses include generalized pustular psoriasis, pustular vasculitis, autoimmune blistering disease, pustular eruption from infections, Behcet’s disease, and others.8 Although most can be excluded without difficulty, some may be a diagnostic challenge, especially differentiating between AGEP and generalized pustular psoriasis. Our case adds to the existing literature of offending agents behind AGEP and dermatologic reaction to haloperidol.
Published online: June 7, 2022.
Relevant financial relationships: None.
Funding/support: None.
Patient consent: Consent was received from the patient to publish the case report, and information has been de-identified to protect anonymity.
Supplementary material: See accompanying pages.
References (8)

- Thienvibul C, Vachiramon V, Chanprapaph K. Five-year retrospective review of acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis. Dermatol Res Pract. 2015;2015:260928. PubMed CrossRef
- Sidoroff A. Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis. Chem Immunol Allergy. 2012;97:139–148. PubMed CrossRef
- Chang SL, Huang YH, Yang CH, et al. Clinical manifestations and characteristics of patients with acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis in Asia. Acta Derm Venereol. 2008;88(4):363–365. PubMed
- Sidoroff A, Dunant A, Viboud C, et al. Risk factors for acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis (AGEP): results of a multinational case-control study (EuroSCAR). Br J Dermatol. 2007;157(5):989–996. PubMed CrossRef
- Feldmeyer L, Heidemeyer K, Yawalkar N. Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis: pathogenesis, genetic background, clinical variants and therapy. Int J Mol Sci. 2016;17(8):1214. PubMed CrossRef
- Gabay C, Towne JE. Regulation and function of interleukin-36 cytokines in homeostasis and pathological conditions. J Leukoc Biol. 2015;97(4):645–652. PubMed CrossRef
- Duckworth L, Maheshwari MB, Thomson MA. A diagnostic challenge: acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis or pustular psoriasis due to terbinafine. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2012;37(1):24–27. PubMed CrossRef
- Sidoroff A, Halevy S, Bavinck JN, et al. Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis (AGEP): a clinical reaction pattern. J Cutan Pathol. 2001;28(3):113–119. PubMed CrossRef
Enjoy this premium PDF as part of your membership benefits!