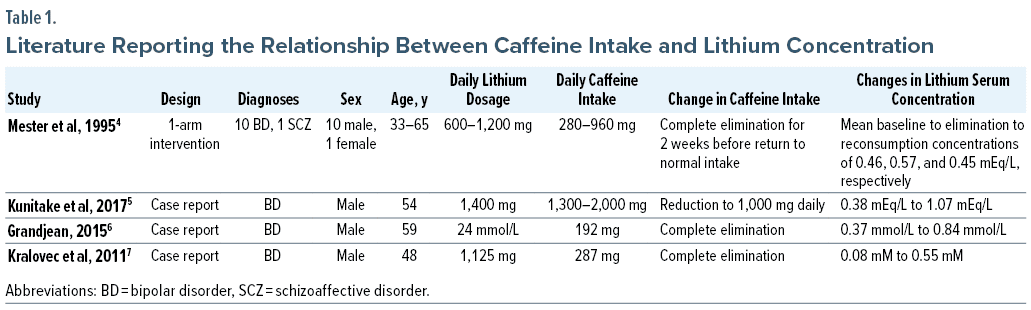
Caffeine is one of the most commonly used stimulants in the United States, with some studies reporting up to 85% of the population consuming at least 1 caffeinated beverage daily.1,2 Caffeine is a methylxanthine alkaloid that directly acts in the central nervous system. While lithium is often used as a first-line treatment for mood stabilization in bipolar disorder, the effect of caffeine on lithium is poorly understood, and available literature is predominantly restricted to case reports of patients with bipolar disorder (Table 1).3–7 Lithium is exclusively excreted by the kidneys, so caffeine may potentiate lithium excretion through its diuretic effect at the kidneys by increasing renal blood flow, glomerular filtration, and sodium excretion.8,9
Here, we present a case of a male patient with schizoaffective disorder found to have supratherapeutic lithium serum concentrations following sudden caffeine reduction, thereby managed with lithium dosage reduction that precipitated exacerbation of psychiatric symptomatology.
Case Report
A 59-year-old man with a psychiatric history of schizoaffective disorder, bipolar type presented to the emergency department (ED) for evaluation of auditory hallucinations and manic symptoms. For 2 years, his standard daily caffeine intake was estimated to be 1,027 mg, derived from 4 servings of Monster Energy drink (160 mg caffeine/serving), 3 servings of Coca-Cola (34 mg caffeine/serving), and 3 servings of coffee (95 mg of caffeine/serving). During this period, his psychiatric symptoms were well-controlled with daily lithium carbonate 900 mg SA, sertraline 200 mg, and risperidone 5 mg. Outpatient lithium serum concentrations measured at 0.6–1.1 mmol/L (reference range, 0.5–1.2 mmol/L) for a year. Given significant dental work planned for the upcoming year, he reduced his daily caffeine intake overnight by 87.4% (898 mg) to 129 mg, derived from 1 coffee and 1 soda. Two months later, still consuming 129 mg of caffeine daily, his lithium serum concentration was incidentally measured at 2.1 mmol/L. At this time, the patient was still asymptomatic, and lithium carbonate 900 mg SA was changed to lithium carbonate 300 mg daily.
Over the next 3 weeks, he reported decreased need for sleep, racing thoughts, severe paranoia, rapid speech, anhedonia, and increased irritability with no changes to his caffeine intake. He eventually presented to the ED for auditory command hallucinations. In the ED, lithium and creatinine serum concentrations were measured at 0.1 mmol/L and 1.17 mg/dL, respectively. During his 1-week hospital course with a caffeine-free diet, daily lithium carbonate SA 600 mg was initiated, and his lithium serum concentration was measured at 1.3 mmol/L. Thus, the lithium dosage was reduced to 450 mg daily, and his lithium serum concentration was 0.4 mmol/L at discharge. His psychiatric symptoms resolved, and his creatinine serum concentration normalized to 1.1 mg/dL. The patient was discharged with lithium carbonate 450 mg SA daily and home medications with instructions to minimize his caffeine intake. Two weeks later, the patient had increased his daily caffeine intake to 640 mg, and his lithium serum concentration was measured at 0.2 mmol/L. The patient again exhibited exacerbation of psychiatric symptoms 2 weeks later, resulting in readmission.
Discussion
The present case, to our knowledge, represents the only reported case in the setting of schizoaffective disorder, bipolar type and the largest reported reduction in caffeine intake correlated with supratherapeutic lithium serum concentration. Subsequent intervention with rapid reduction of lithium dosage likely resulted in both subtherapeutic lithium concentration and unopposed sertraline activity, precipitating his manic state. The present case highlights the possible role of caffeine in the alteration of lithium pharmacokinetics. As such, providers should closely monitor caffeine intake and lithium concentrations for careful titration. Additionally, dosage adjustment in the setting of asymptomatic lithium toxicity should be done judiciously in small increments. These considerations are especially important for patients who are reducing caffeine intake after stabilization of psychiatric symptomatology with lithium.
Article Information
Published Online: April 9, 2024.
https://doi.org/10.4088/PCC.23cr03642
© 2024 Physicians Postgraduate Press, Inc.
Prim Care Companion CNS Disord 2024;26(2):23cr03642
Submitted: August 24, 2023; accepted: November 15, 2023.
To Cite: Song JJ, Eyabi JC, Awatramani PD, et al. Sudden reduction in caffeine intake increases serum lithium concentration to supratherapeutic level: a case report. Prim Care Companion CNS Disord. 2024;26(2):23cr03642.
Author Affiliations: Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, Texas (Song); Menninger Department of Psychiatry and Behavioral Sciences, Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, Texas (Eyabi, Awatramani, Mitchell, Nene); Mental Health Care Line Michael E. DeBakey Veterans Affairs Medical Center, Houston, Texas (Awatramani, Nene).
Corresponding Author: Sudhanshu Y. Nene, MD, MPH, Michael E, Debakey Veterans Affairs Medical Center, Mental Health Care Line, 2002 Holcombe Blvd, Houston, TX 77030 ([email protected]).
Funding/Support: None.
Relevant Financial Relationships: None.
Patient Consent: Verbal consent was received from the patient to publish the case report, and information has been de-identified to protect anonymity.
ORCID: Jeffrey Song: 0000-0003-0902-6779); Jorgen Eyabi: 0000-0002-3820-8494; Brian Mitchell: 0000-0003-1735-5601
References (9)

- Mitchell DC, Knight CA, Hockenberry J, et al. Beverage caffeine intakes in the US Food Chem Toxicol. 2014;63:136–142. PubMed CrossRef
- Sweeney MM, Weaver DC, Vincent KB, et al. Prevalence and correlates of caffeine use disorder symptoms among a United States sample. J Caffeine Adenosine Res. 2020;10(1):4–11. PubMed CrossRef
- Frigerio S, Strawbridge R, Young AH. The impact of caffeine consumption on clinical symptoms in patients with bipolar disorder: a systematic review. Bipolar Disord. 2021;23(3):241–251. PubMed CrossRef
- Mester R, Toren P, Mizrachi I, et al. Caffeine withdrawal increases lithium blood levels. Biol Psychiatry. 1995;37(5):348–350. PubMed CrossRef
- Kunitake Y, Mizoguchi Y, Sogawa R, et al. Effect of excessive coffee consumption on the clinical course of a patient with bipolar disorder: a case report and literature review. Clin Neuropharmacol. 2017;40(4):160–162. PubMed CrossRef
- Grandjean E. Lithium/Coca Cola interaction decreased lithium serum concentration: case report. React Wkly. 2015;(1568):184.
- Kralovec K, Fartacek R, Plöderl M, et al. Low serum lithium associated with immoderate use of Coca-Cola Zero. J Clin Psychopharmacol. 2011;31(4):534–544. PubMed CrossRef
- Ott M, Stegmayr B, Salander Renberg E, et al. Lithium intoxication: incidence, clinical course and renal function—a population-based retrospective cohort study. J Psychopharmacol. 2016;30(10):1008–1019. PubMed CrossRef
- Evans J, Richards J, Battisi A. Caffeine. StatPearls Internet. Published online January 2023. Accessed July 1, 2023. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK519490/
Enjoy this premium PDF as part of your membership benefits!