Background: There is a paucity of studies on treatment of childhood-onset bipolar disorder and its associated comorbidities, which leads to a wide diversity of opinion on choice and sequencing of treatment options.
Methods: From December 2018 to January 2019, a graphic depiction of medications and weekly ratings of symptoms of mania, depression, anxiety, attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), and oppositional behavior that parents had rated on their 9-year-old child over a period of several years was sent to experts in child and adult bipolar disorder. These responding medical doctors (MDs, 8 child and 18 adult psychiatrists) rated a comprehensive list of medications that they would choose (and with what priority) to treat the child’s now improved mood (mania and depression) but continued mild to moderate symptoms of anxiety, ADHD, and oppositional behavior.
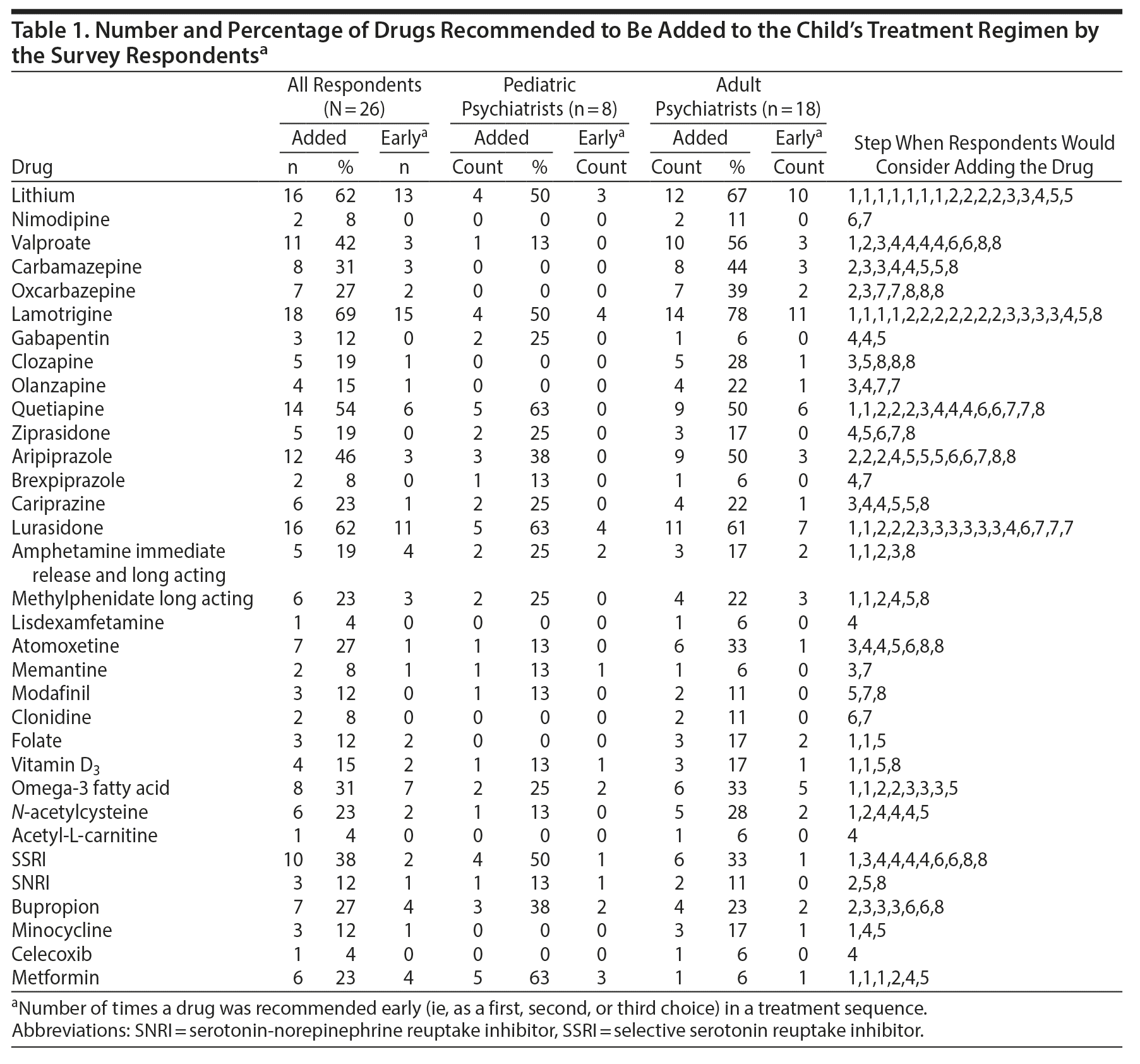
Results: In the whole group, the drugs most highly endorsed were lamotrigine: 69%, lithium: 62%, lurasidone: 62%, quetiapine: 54%, aripiprazole: 46%, and valproate: 42%. Among the antidepressants, 38% endorsed a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor, 12% a serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor, and 27% bupropion. Of the child MDs, 75% suggested increasing the 1-mg dose of risperidone, while few adult MDs suggested this. Conversely, 56% of the adult MDs suggested using valproate, while only 1 child MD did so. There was little consensus on how to manage ADHD symptoms unresponsive to methylphenidate 36 mg/d. How these treatment options were sequenced also varied widely.
Conclusions: There was wide variation in suggestions on to how to treat persistent symptoms of anxiety, ADHD, and oppositional behavior in a child whose mania and depression had been brought under good control. We surmise that this great diversity in recommendations among experts in child and adult bipolar disorder stems at least partially from inadequate literature on treatment and that a new emphasis on funding and conducting studies on efficacy and effectiveness is needed.
Little Agreement on Treating Residual Bipolar Disorder Symptoms in a Child
ABSTRACT
Background: There is a paucity of studies on treatment of childhood-onset bipolar disorder and its associated comorbidities, which leads to a wide diversity of opinion on choice and sequencing of treatment options.
Methods: From December 2018 to January 2019, a graphic depiction of medications and weekly ratings of symptoms of mania, depression, anxiety, attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), and oppositional behavior that parents had rated on their 9-year-old child over a period of several years was sent to experts in child and adult bipolar disorder. These responding medical doctors (MDs, 8 child and 18 adult psychiatrists) rated a comprehensive list of medications that they would choose (and with what priority) to treat the child’s now improved mood (mania and depression) but continued mild to moderate symptoms of anxiety, ADHD, and oppositional behavior.
Results: In the whole group, the drugs most highly endorsed were lamotrigine: 69%, lithium: 62%, lurasidone: 62%, quetiapine: 54%, aripiprazole: 46%, and valproate: 42%. Among the antidepressants, 38% endorsed a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor, 12% a serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor, and 27% bupropion. Of the child MDs, 75% suggested increasing the 1-mg dose of risperidone, while few adult MDs suggested this. Conversely, 56% of the adult MDs suggested using valproate, while only 1 child MD did so. There was little consensus on how to manage ADHD symptoms unresponsive to methylphenidate 36 mg/d. How these treatment options were sequenced also varied widely.
Conclusions: There was wide variation in suggestions on to how to treat persistent symptoms of anxiety, ADHD, and oppositional behavior in a child whose mania and depression had been brought under good control. We surmise that this great diversity in recommendations among experts in child and adult bipolar disorder stems at least partially from inadequate literature on treatment and that a new emphasis on funding and conducting studies on efficacy and effectiveness is needed.
Prim Care Companion CNS Disord 2020;22(5):19m02574
To cite: Post RM, Rowe M, Findling R. Little agreement on treating residual bipolar disorder symptoms in a child. Prim Care Companion CNS Disord. 2020;22(5):19m02574.
To share: https://doi.org/10.4088/PCC.19m02574
© Copyright 2020 Physicians Postgraduate Press, Inc.
aDepartment of Psychiatry, George Washington University School of Medicine, Bipolar Collaborative Network, Bethesda, Maryland
bDepartment of Psychiatry, Virginia Commonwealth University, Richmond, Virginia
*Corresponding author: Robert M. Post, MD, Department of Psychiatry, George Washington University School of Medicine, Bipolar Collaborative Network, 5415 W Cedar Lane, Ste 201-B, Bethesda, MD 20814 ([email protected]).
We started a Child Network to allow parents of children aged 2-12 years to rate symptoms of depression, anxiety, attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), oppositional behavior, and mania weekly on a secure website.1-3 These longitudinal ratings could then be printed out and taken to physicians and clinicians involved in the child’s treatment so that symptom evolution and response to any treatment could be easily visualized graphically. One such 9-year-old girl was rated by her parents for about 1 year but remained highly symptomatic in all domains.3 After informed consent was obtained, we illustrated this child’s course of illness and the current attempts at pharmacologic treatment that had been utilized. A variety of suggestions for more effective treatment of the child’s mania and depression were included in the case presentation and discussion of this first article.3
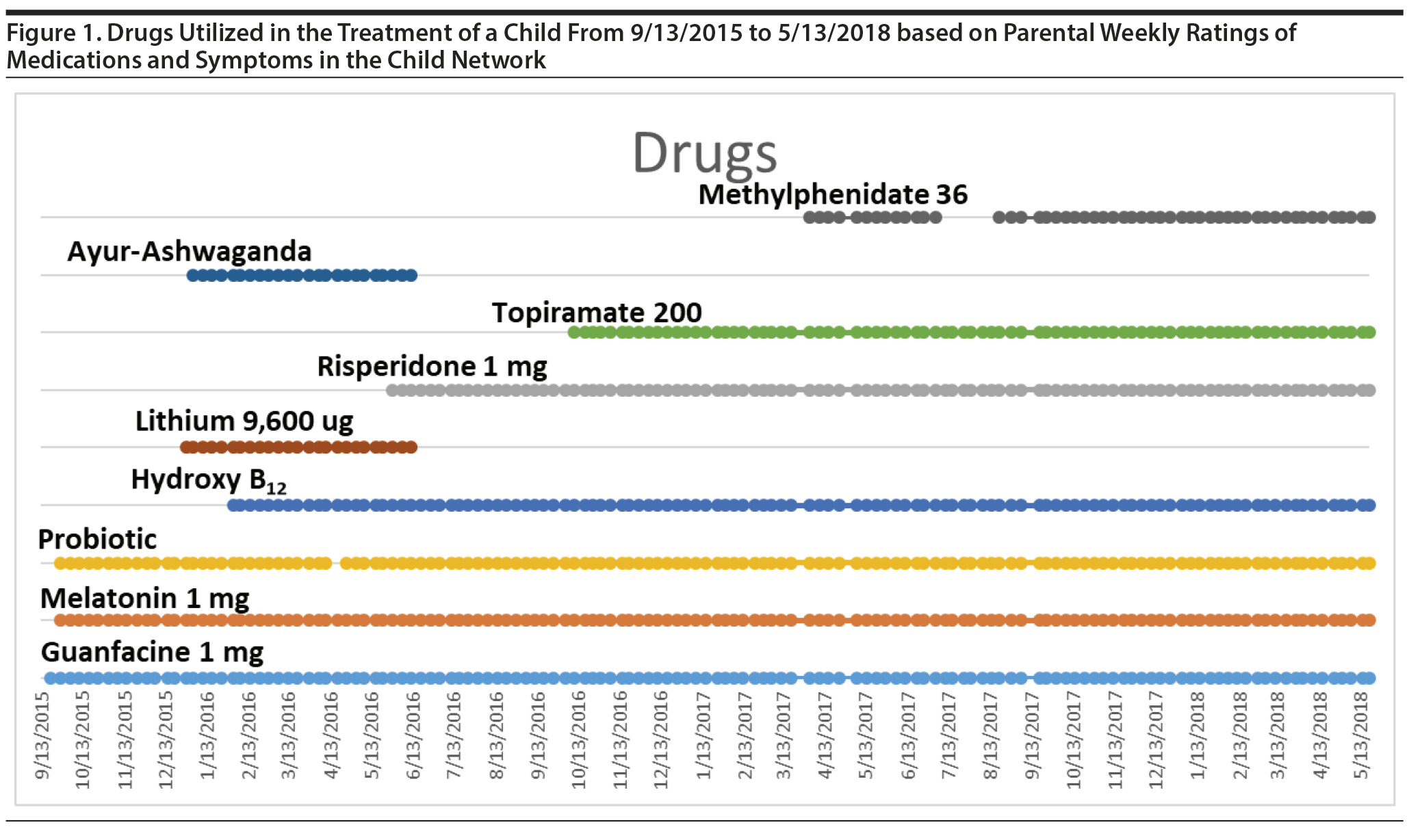
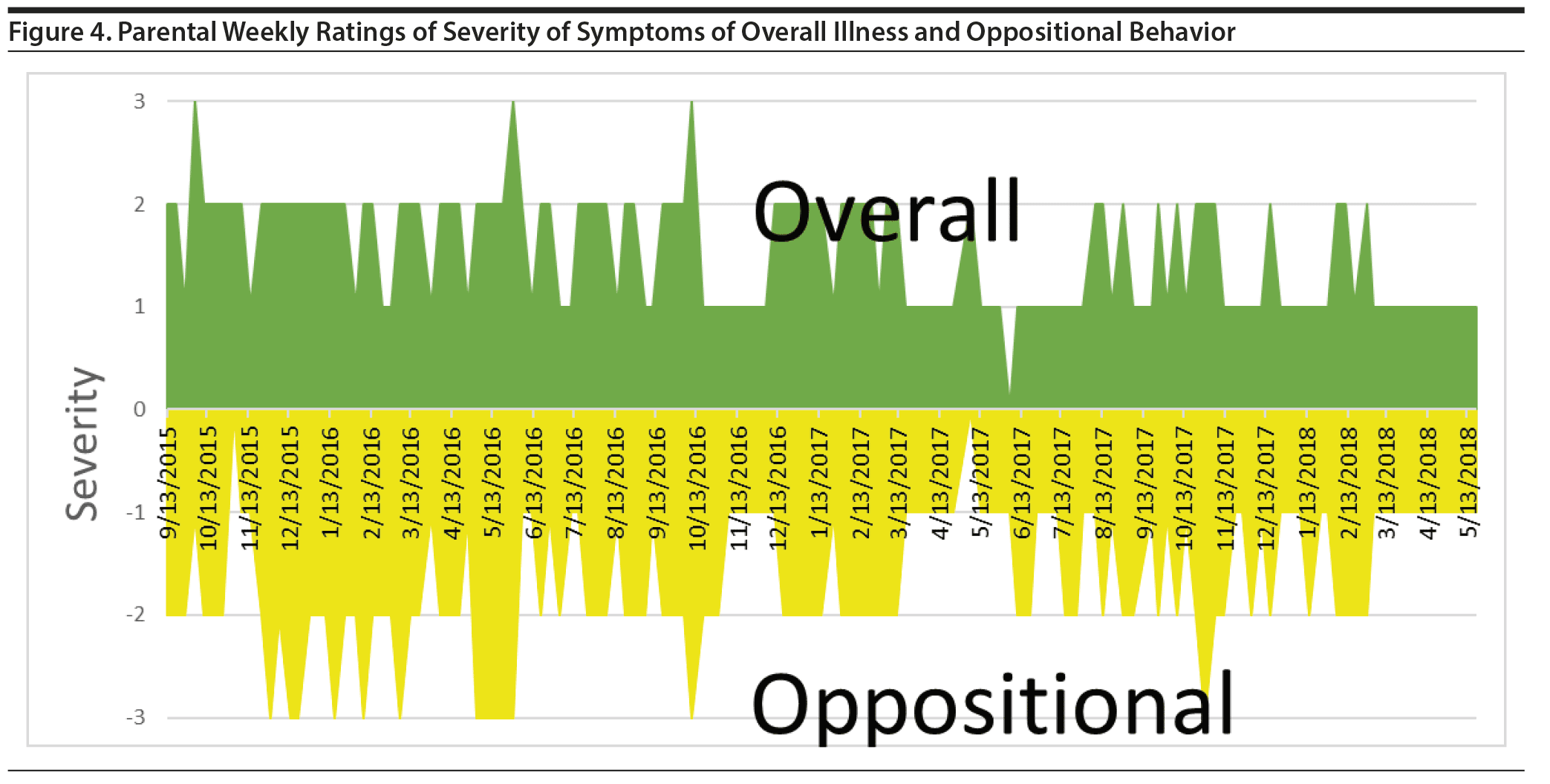
The child’s parents continued to rate their daughter weekly for approximately another 1.5 years. This entire course of illness is depicted in Figure 1. The figure shows that the child finally had a good antimanic and antidepressant response to treatment, but she was left with considerable residual symptoms of anxiety, ADHD, and oppositional behavior. Given the paucity of a systematic treatment literature in such a child,4-7 we thought it timely to see what other experts in the field would recommend, rather than making further suggestions on our own as we had done previously.3
We thus mailed the graphic to experts in child and adult psychiatry along with a listing of potential treatment agents they might consider using. Each agent was to be rated for when in the treatment sequence (1-8) physicians would consider using that drug if at all and when they would discontinue a current drug or when a drug had been added. The child had received extensive psychosocial interventions throughout the entire course of illness illustrated, but we decided not to further explore these for the sake of keeping the survey relatively short and focused. Moreover, a systematic literature on these psychosocial interventions exists. We and most of the authors consider these psychosocial therapies as first-line interventions, and we merely wanted to assess judgments about what might be done above and beyond these ongoing therapies.
We hypothesized that there would be great diversity of opinion and little consensus among the physicians about types and sequences of interventions. We and many others in the field had lobbied for several decades for more treatment research studies for children with bipolar disorder and its many comorbidities, but with limited success.4,5,7,8 We thought that exposing the lack of agreement on pharmacologic treatment even by experts in the field might help foster a greater focus on the need for a systematic treatment literature to better guide physicians. In addition, to the extent that there was some convergence of treatment suggestions, we thought that these recommendations could also be usefully relayed back to the child’s parents and their treating physician.
METHODS
We examined lists of physicians who had written widely on childhood or adult bipolar illness, who had attended meetings on this topic, and were known to the senior authors of this article. In December 2018, we sent these clinician investigators a graphic representation of the child’s longitudinal course of symptoms of anxiety, depression, ADHD, oppositional behavior, and mania along with a list of possible pharmacologic treatments that they might consider. These survey forms were mailed to 28 medical doctors (MDs) with expertise in childhood bipolar disorders and to 52 MDs involved in adult bipolar disorder treatment or research. By the end of January 2019, we received 8 completed survey forms from the child psychiatrists and 18 from adult psychiatrists.
- Among child and adult psychiatrists, there was little consensus about which drugs in which order should be used to treat residual symptoms of anxiety, attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder, and oppositional behavior in a child whose mania and depression had improved.
- The conduct and funding of a new round of treatment-related studies in children with bipolar disorder and its comorbidities could help generate more consistent approaches.
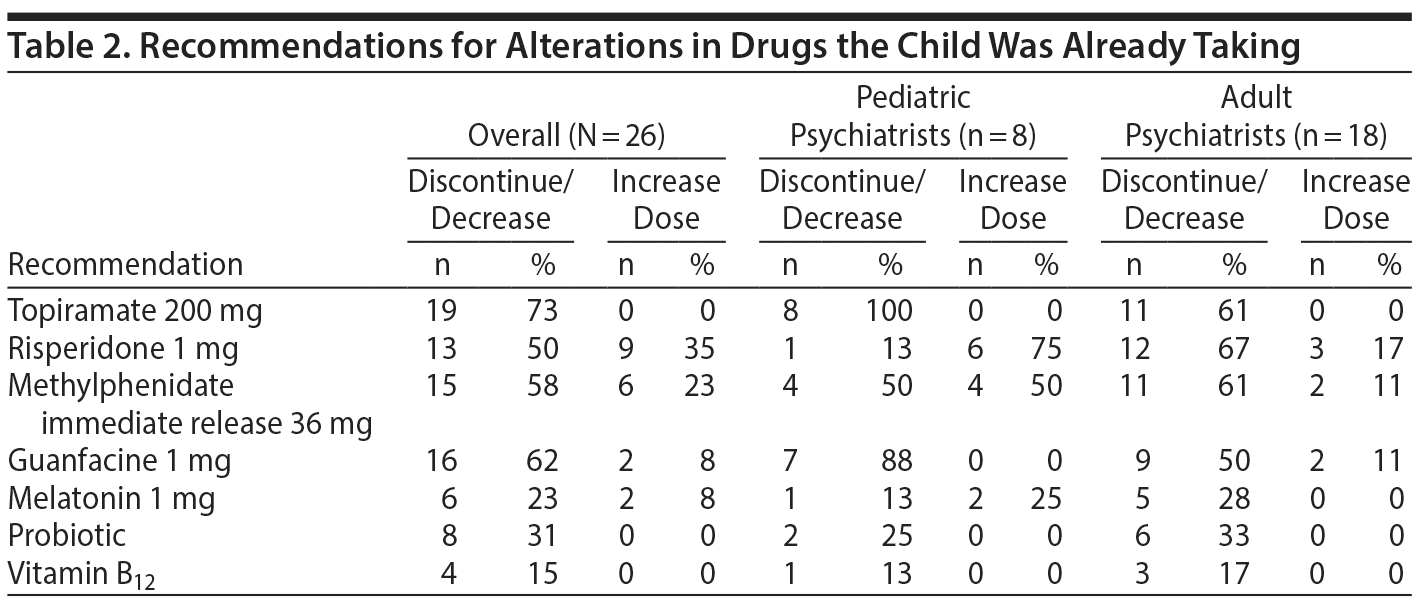
The survey listed lithium and 7 anticonvulsants, 9 atypical antipsychotics, 7 types of medications for ADHD, 7 supplements, 4 categories of antidepressants, 2 antiinflammatories and metformin, and all of the drugs this child had been given and was still on including risperidone 1 mg, topiramate 200 mg, methylphenidate 36 mg, guanfacine 1 mg, melatonin 1 mg, a probiotic, and vitamin B12. Each category of drugs had blank lines listed as “other” for inserting any other proposed treatment that was not already on the list. All of the drugs itemized in the survey are those listed in Table 1. In addition to rating the sequence (1-8) of when a physician would consider adding or discontinuing a given drug, a line for comments was available that could be used for notes about increasing or decreasing the dose of a drug. We tabulated the results of the 26 physicians together as well as the 8 child psychiatrists and the 18 adult psychiatrists separately so that the results and sequences from both groups could be compared and contrasted.
RESULTS
Course of Illness Rated Weekly by the Parents
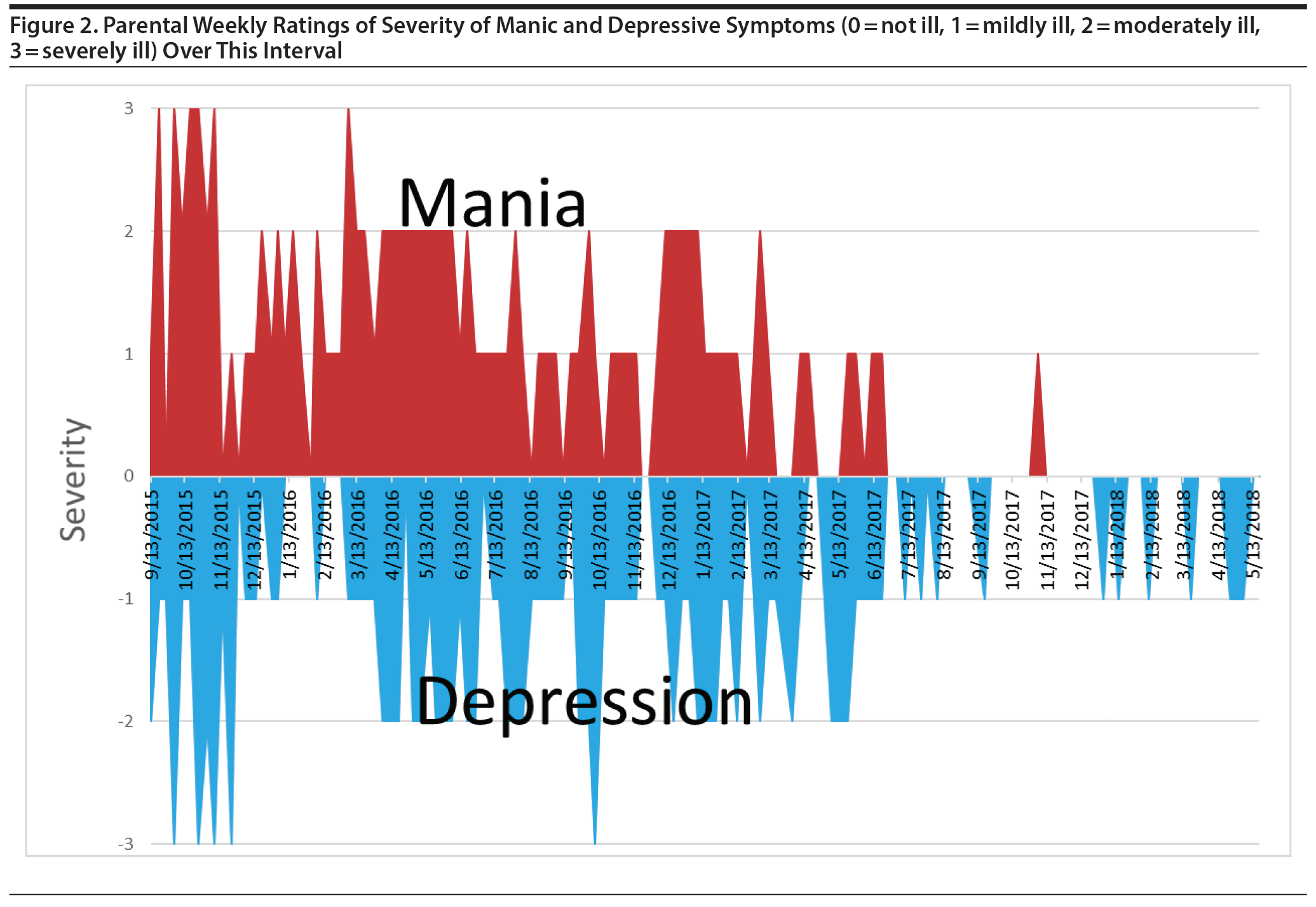
This child had a prolonged mania for about 1.5 years, often rated as a 3 = severe or a 2 = moderate as would be consistent with a diagnosis of bipolar I disorder. Depression was concomitantly rated as moderate to severe, consistent with a diagnosis of mixed or dysphoric mania (Figure 2). However, there were also periods of time when manic and depression severity was rated as 1 = mild, so it is unclear whether this was a continuous mixed manic episode or whether it had characteristics of bipolar disorder not otherwise specified wherein manic and depressive symptoms rapidly oscillate often many times within a single day over prolonged periods of time.7,9,10 Given the weekly intervals of the parental ratings, a bipolar I versus bipolar disorder not otherwise specified diagnosis cannot be readily distinguished.
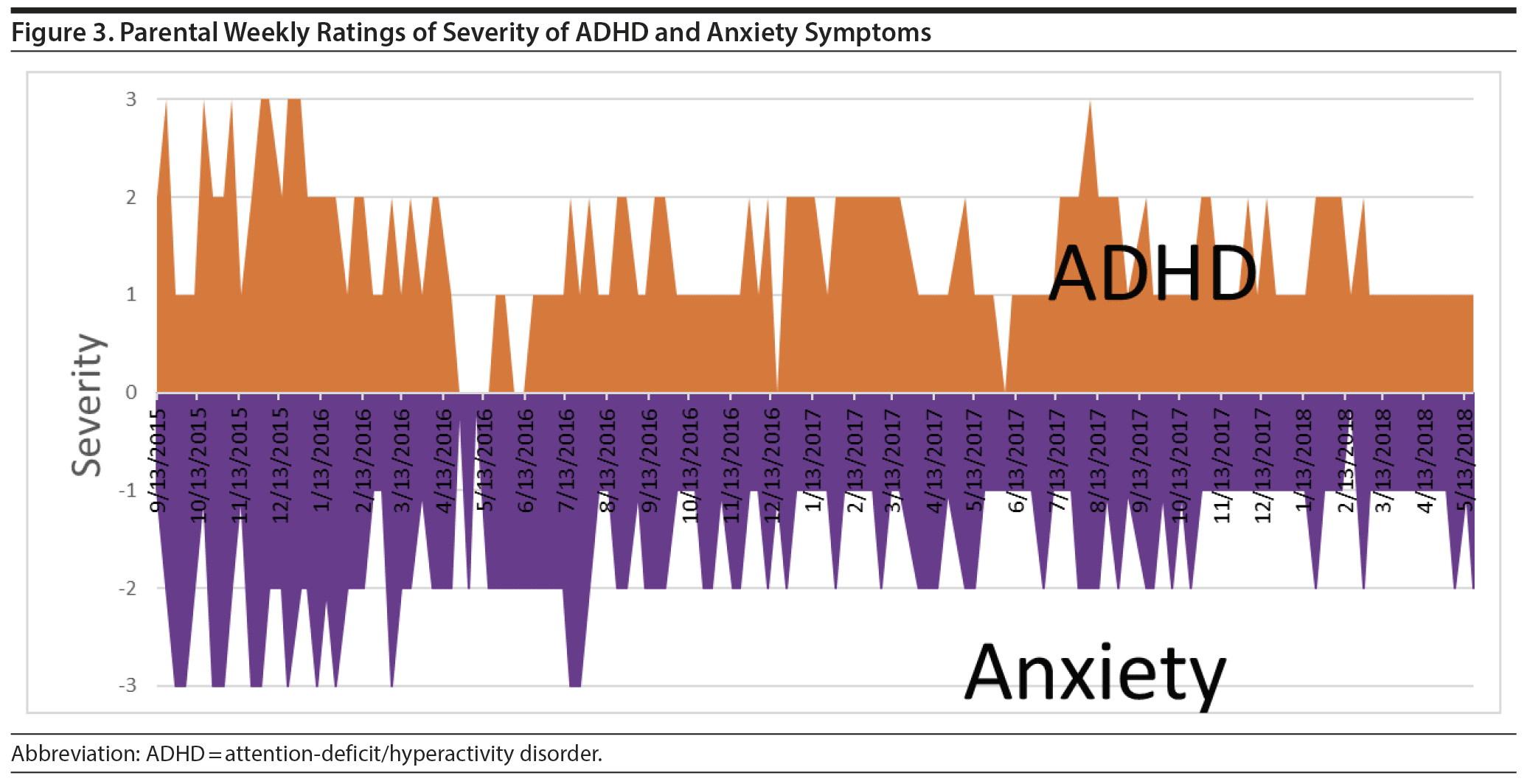
Initial attempts at treatment of the mania and depression were not successful. These included Ayur-ashwaganda, micro doses of lithium (9,600 ug/d), and hydroxy B12, as well as guanfacine (1 mg), melatonin (1 mg), and a probiotic. When risperidone (1 mg/d) was added, mania improved to mostly mild severity, but depression remained mild to moderate (Figure 1). When topiramate (200 mg/d) was added followed by methylphenidate (36 mg/d), manic and depressive symptoms were largely resolved. We had no information on the patient’s weight, so it was uncertain whether topiramate was being used to augment the psychotropic effects of risperidone or to address potential weight gain. Yet, for the last 10 months of ratings, considerable symptoms of anxiety, ADHD (Figure 3), and oppositional behavior continued (Figure 4). The severity and consistency of these symptoms suggested that they would have met criteria for an anxiety disorder comorbidity, a diagnosis of ADHD, and a disruptive behavioral disorder. However, these diagnoses were never formalized, so we have labeled them only as residual symptoms causing impairment rather than a specific comorbidity. It was at this juncture in the child’s course (resolution of mania and depression) that the MDs were asked to specify and rate their treatment options for these residual symptoms.
Overall Ratings of the 26 MD Responders to the Survey
As indicated in Table 1, the drugs most highly endorsed were lamotrigine: 69%, lithium: 62%, lurasidone: 62%, quetiapine: 54%, aripiprazole: 46%, and valproate: 42%. Among the antidepressants, 38% endorsed a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI), 12% a serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor, and 27% bupropion. There was a wide diversity of opinion about modifications of the current drugs, risperidone and methylphenidate, for the continued ADHD symptoms, but most recommended discontinuation of topiramate (Table 2). The differential and comparative suggestions of the child versus adult psychiatrists are noted below.
Treatment Suggestions/Sequences From 8 Child Psychiatrists
As illustrated in the middle rows of Table 1, there was a notable diversity of opinion among child psychiatrists about potential next steps that one would employ to address the continued areas of residual symptoms of anxiety, ADHD, and oppositional behavior.
Six of 8 (75%) raters suggested increasing the dose of risperidone, and all 8 suggested discontinuing topiramate. However, the suggestions for next steps varied from adding lithium in 4/8 (50%), with 3 recommending this as the first step, to adding lamotrigine in 4/8 (50%), with all 4 suggesting that they would do this early (in steps 1-3).
A switch to lurasidone was endorsed by 5/8 (62.5%), occurring at steps 2, 3, 3, 3, and 4, respectively. A switch to quetiapine was also suggested by 5/8 (62.5%), but generally later in the sequence. Of the other atypical antipsychotics, 3 suggested using aripiprazole, 2 cariprazine, and 2 ziprasidone. Only 1 of the child psychiatrists suggested use of valproate late in the sequence (and that was only very late at step 8).
Suggestions about treatment of ADHD symptoms showed no consensus: 4/8 would increase the dose of methylphenidate, while 4/8 would discontinue it; 2/8 would switch to an amphetamine, and 7/8 would discontinue guanfacine.
Additionally, 5/8 considered leaving metformin in the regimen (presumably for heading off weight gain and diabetes). Also, presumably to target anxiety or oppositionality, 4/8 (50%) suggested using an SSRI, 3/8 (38%) bupropion, 2/8 buspirone, 1/8 N-acetylcysteine, and 1/8 each vortioxetine, mirtazapine, and memantine. One MD suggested modafinil and 2 gabapentin.
Treatment Suggestions/Sequences From 18 Adult Psychiatrists
As illustrated in Table 1 (right rows), there was some divergence in the recommendations of the adult psychiatrists compared to the child psychiatrists. More adult MDs (12/18, 67%) suggested using lithium compared to 50% of the child MDs. Many more suggested using valproate (10/18, 56%) compared to the single late suggestion for valproate among the child MDs. Few adult psychiatrists (3/18) suggested increasing the dose of risperidone compared to 75% of the child MDs.
Similar to the endorsement of lamotrigine by the child MDs, 14/18 (78%) of the adult MDs suggested this drug. Also similar was the endorsement of the use of lurasidone in 11/18 (61%), although when they would do this varied widely. Two each would do this at steps 1 and 2, 3 at step 3, 1 late at step 6, and 4 at step 7. A switch to quetiapine was also highly endorsed (9/18, 50%) as was aripiprazole (9/18, 50%). Four suggested use of olanzapine, 4 cariprazine, and 3 ziprasidone.
Again. there was great diversity of opinion as to how to deal with the stimulants. For example, 3/18 recommended dose decreases, 3 dose discontinuation, 1 dose increase, and 4 to switch to a long-acting methylphenidate preparation and 1 to a long-acting amphetamine. Also, 9/18 suggested the discontinuation of guanfacine. One suggested using memantine. In contrast to the robust support of the child MDs, only 1/17 suggested continued use of metformin.
Among the antidepressants, similar to the child MDs, 6/18 (33.3%) suggested an SSRI and 4/17 (23.5%) bupropion. Among the single drugs suggested were minocycline, trimipramine, and asenapine.
DISCUSSION
As hypothesized, there was considerable diversity of opinion about use or not and the sequencing of agents in both the child and adult psychiatrist groups. Use of lamotrigine and lithium and a switch of risperidone to lurasidone or quetiapine were endorsed by 50%-75% of both groups, but the sequence of when they would be considered, if at all, varied widely. Major divergences in recommendations included dose increases of risperidone by the child MDs but not the adult MDs and endorsement of valproate by 56% of the adult MDs but only 1/8 (12%) of the child MDs. The adult MDs may have been making judgments on the basis of their experience in adults and may not have been as aware of the controlled data on the failure of valproate in childhood acute mania11 and its inferiority to risperidone12 and in prevention in high-risk patients.13
Likewise, the higher and earlier endorsement of lithium by the adult MDs may have been related to the increasing acceptance of lithium as the drug of choice in adults. Conversely, the data supporting a role for lithium in young children with bipolar disorder is more recent, which could have accounted for its lesser and later use suggested by the child MDs.14-16 Neither group had anything resembling consensus about use and management of stimulants or antidepressants.
Caveats and Limitations
Before discussing these findings and their potential implications, several methodological considerations need to be addressed. Only a small number of child psychiatrists who were mailed the survey completed it: 8/28 or 28.6%. Similarly, only 18/52 or 34.6% of adult MDs completed the survey. However, there is little reason to think that those who did not respond and return the survey would have had major differences or greater agreement on treatment than what we have seen here. From comments that various clinicians made on the survey, it was sometimes unclear that sequences involved discontinuation of a prior medication or whether more complex combination treatment strategies were often intended. There did appear to be differences in overall strategy from those endorsing simplification of the treatment regimen to those endorsing complex combination therapy that was not always evident from the way the forms were filled out.
The survey was not conducted in such a way that the data could be used to build consensus among experts as to the best treatments and their rank order. Alternative methods to obtain such data could be helpful in bridging the gap related to the paucity of controlled and comparative studies.
Several clinicians who were sampled were from non-US locations, but because of the small numbers from outside of the United States, comparisons could not be accurately portrayed. This could be particularly pertinent given that childhood-onset bipolar disorder appears to occur more widely in the United States compared to Canada and many European countries.17-20 The diagnoses of comorbidities that commonly occur in childhood-onset bipolar disorder, such as an anxiety disorder, ADHD, or oppositional defiant disorder, were not available or given to the raters, although the ratings of moderate symptom severity in these areas would most likely have reached diagnostic thresholds for these comorbidities.21,22 The longitudinal ratings by parents utilized here differ from many other cross-sectional diagnostic and rating scale assessments typically used for such a child, but may track symptom severity and variation more precisely than that available from cross-sectional scales.
In addition, data suggest that parental rating may be the most sensitive compared to self, teacher, or other ratings.23 How the severity of symptoms, rated as none = 0, mild = 1, moderate = 2, and severe = 3 in this child, would relate to quantitative rating scale measures for each of the symptoms areas is not known. However, parents were asked to base the rating of the symptoms on the severity of their impact and dysfunction they induced in the child’s usual family, social, and educational roles. The portrayal of marked improvement in the manic and depressive domains provides evidence that the ratings are sensitive to change and that parental rating can reveal clear differences in behavioral areas that improve and those that do not. This suggests, but does not prove, that parental ratings are not unduly influenced by the parent’s mood state, but are more likely accurate reflections of the discrete aspects of the child’s behavior.23
Early in this child’s mania, only low doses of lithium (lithium orotate) had been utilized prior to the switch to risperidone. It was unclear how many clinicians were cognizant of the use of this very low-dose lithium and how it may have impacted on their decision to return or not to a lithium carbonate trial. Several clinicians complained about not being given enough (any) information about other variables such as family history that could have helped guide therapeutic decisions. This child had a wide range of family, individual, and educational interventions,3 which for brevity and focus were not outlined or presented in the graphic, and how these and perhaps other choices of psychosocial approaches may have influenced drug choices is not clear. Since there were no comparable assessments of how clinicians might have chosen and sequenced treatment for a still symptomatic adult patient with bipolar disorder, it is possible that the wide range of opinions on how physicians would treat this childhood-onset illness would, to some extent, also be apparent in an adult patient as well.
Implications
Given that these quandaries about and limitations of the findings are not likely to make a major impact on the interpretation of the current survey findings, there are several take-away messages and clinical implications of these data. The first is that there is very little consensus as to how either child or adult psychiatrists would proceed to treat a preadolescent with only partially treated bipolar disorder. After the almost complete mood response to the antipsychotic, risperidone (in conjunction with several other agents), there was wide divergence in opinion as to the best approaches to the residual symptoms of anxiety, ADHD, and oppositionality. Guidelines for bipolar disorder in adults have become increasingly comprehensive and nuanced with attempts at integrating both the degree of evidence for efficacy of an approach and its side effects and long-term tolerability.24
The few published guidelines for childhood-onset bipolar disorder are more primitive and tend to focus on degree of improvement seen in the few available RCTs in bipolar I disorder25 and do not readily deal with the best approaches to achieve remission of either the primary mood symptoms or the many other problematic comorbidities or symptomatic realms seen in the current patient or others.22 The wide range of approaches and their sequencing that we have seen here most likely are an accurate reflection of a lack of general agreement about clinical treatment.
This range of opinions is likely attributable to the paucity of placebo-controlled RCTs and even fewer comparative practical clinical trials assessing the effectiveness and tolerability of 2 or more agents. In 1 of the few comparative clinical trials,15 risperidone was found to be more effective than lithium or valproate but was associated with more side effects including weight gain. The child MDs often opted for increasing risperidone before switching to lurasidone or quetiapine. It would be of great help to know which of the 2 later agents had superior effectiveness and tolerability in a head-to-head comparison, especially since lurasidone is now US Food and Drug Administration-approved for bipolar depression in children aged 10-17 years,26 while quetiapine failed to exceed placebo in youngsters with bipolar depression.27 Clinicians would appear to be proceeding with treatment on the basis of their best judgment and guesses, rather than a strong database, guidelines, or feedback from other physicians. This would appear to be extremely problematic and as illustrated in the current case example would likely be associated with long periods (months to years as seen here) of highly symptomatic and dysfunction behavior.
A difficult long-term course of illness was also the result seen in several prospective longitudinal follow-up studies28-30 in which children with bipolar disorder remained symptomatic, often for some two-thirds of the time of follow-up. Even in the study by Birmaher et al10 in which children were divided into 4 groups according to the trajectory of their outcome on follow-up, those in the best functioning groups still remained symptomatic. Those who did well tended to be treated with mood stabilizers, lithium, and atypical antipsychotics as generally recommended in the current survey. However, about half of the children in that study10 either never showed a good response or did so only late after a prolonged period of time symptomatic.
The study by Birmaher et al,10 which was characterized as a demonstration of a good outcome for those with childhood-onset bipolar disorder, was achieved with treatment by experts. However, in the United States, the majority of children with psychiatric illness are seen by pediatricians and those in primary care,31 so in these MDs with less experience and training in psychiatry, the lack of a systematic literature and consensus on treatment approaches is likely to be even more problematic. It would appear that the scant literature on treatment of children with bipolar disorder needs a major new infusion of studies on clinical efficacy and effectiveness. How this might be achieved is uncertain, as it does not appear to be an urgent goal of the current National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH) leadership. Possible approaches to fix the lack of treatment studies and funding are discussed in more detail elsewhere,4-6 but include specific set asides of NIMH and SAMSHA monies targeted for this purpose, creating an extensive treatment outcome network in academic centers and clinical care settings, and lobbying congress for a national clinical treatment initiative.
In the absence of such initiatives and major new treatment studies, it would appear helpful to emphasize the utility of a longitudinal numerical and graphic assessment of symptoms in each individual child such as that seen here (see www.bipolarnews.org, click on Child Network32). This or other detailed longitudinal approaches might help in early diagnosis and recognition of the need for treatment (see MyMoodMonitor or M3,33 Gaynes et al 2010,34 and the NIMH Life Chart Method or Personal Calendar available at www.bipolarnews.org35). It would also help, as seen in the current patient, with the ready visualization of the degree of improvement achieved and the need for sequential treatment revisions until a good response or remission is achieved.36 In the face of a panoply of potential treatment options and sequences,24,25,37-39 detailed longitudinal assessment of what approaches really work and are tolerated in a given individual child would appear to be one key to eventual treatment success.
Submitted: November 27, 2019; accepted March 24, 2020.
Published online: September 17, 2020.
Potential conflicts of interest: Dr Post has spoken for AstraZeneca, Sunovion, Janssen, Validus, and Takeda. Dr Findling receives or has received research support, acted as a consultant and/or served on a speaker’s bureau for Acadia, Aevi, Akili, Alcobra, Allergan, Amerex, American Academy of Child & Adolescent Psychiatry, American Psychiatric Press, Arbor, Bracket, Daiichi-Sankyo, Epharma Solutions, Forest, Genentech, Insys, Ironshore, KemPharm, Luminopia, Lundbeck, Merck, NIH, Neurim, Noven, Nuvelution, Otsuka, PCORI, Pfizer, Physicians Postgraduate Press, Receptor Life Sciences, Roche, Sage, Shire, Sunovion, Supernus Pharmaceuticals, Syneurx, Teva, TouchPoint, Tris, and Validus. Dr Rowe has no conflicts of interest related to the subject of this article.
Funding/support: None.
REFERENCES
1.Post R. Recognizing depression, anxiety, and externalizing behaviors in children of a parent with mood disorders. J Depress Anxiety. 2016;S2(14).
2.Post R. Children in the US are at high risk for psychiatric disorders: early monitoring by parents may enhance awareness and treatment. J Pediatr Neurol Med. 2016;3(110).
3.Post RM, Rowe M, Kaplan D, et al. A multisymptomatic child with bipolar disorder: how to track and sequence treatment. Prim Care Companion CNS Disord. 2017;19(4):17r02122. PubMed CrossRef
4.Post RM, Kowatch RA. The health care crisis of childhood-onset bipolar illness: some recommendations for its amelioration. J Clin Psychiatry. 2006;67(1):115-125. PubMed CrossRef
5.Post RM. Childhood-onset bipolar disorder: the perfect storm. Psychiatr Ann. 2009;39(10):879-886. CrossRef
6.Post RM, Altshuler LL, Kupka R, et al. More childhood onset bipolar disorder in the United States than Canada or Europe: implications for treatment and prevention. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2017;74(pt A):204-213. PubMed CrossRef
7.Post RM, Wozniak J. Survey of expert treatment approaches for children with bipolar disorder-not otherwise specified and bipolar I presentations. Psychiatr Ann. 2009;39(10):887-895. CrossRef
8.Post RM, Chang K, Frye MA. Paradigm shift: preliminary clinical categorization of ultrahigh risk for childhood bipolar disorder to facilitate studies on prevention. J Clin Psychiatry. 2013;74(2):167-169. PubMed CrossRef
9.Axelson D, Goldstein B, Goldstein T, et al. Diagnostic precursors to bipolar disorder in offspring of parents with bipolar disorder: a longitudinal study. Am J Psychiatry. 2015;172(7):638-646. PubMed CrossRef
10.Birmaher B, Gill MK, Axelson DA, et al. Longitudinal trajectories and associated baseline predictors in youths with bipolar spectrum disorders. Am J Psychiatry. 2014;171(9):990-999. PubMed CrossRef
11.Wagner KD, Redden L, Kowatch RA, et al. A double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial of divalproex extended-release in the treatment of bipolar disorder in children and adolescents. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2009;48(5):519-532. PubMed CrossRef
12.Geller B, Luby JL, Joshi P, et al. A randomized controlled trial of risperidone, lithium, or divalproex sodium for initial treatment of bipolar I disorder, manic or mixed phase, in children and adolescents. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2012;69(5):515-528. PubMed CrossRef
13.Findling RL, Frazier TW, Youngstrom EA, et al. Double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of divalproex monotherapy in the treatment of symptomatic youth at high risk for developing bipolar disorder. J Clin Psychiatry. 2007;68(5):781-788. PubMed CrossRef
14.Findling RL, Robb A, McNamara NK, et al. Lithium in the acute treatment of bipolar i disorder: a double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Pediatrics. 2015;136(5):885-894. PubMed CrossRef
15.Geller B, Tillman R, Bolhofner K, et al. Pharmacological and non-drug treatment of child bipolar I disorder during prospective eight-year follow-up. Bipolar Disord. 2010;12(2):164-171. PubMed CrossRef
16.Hafeman D, Rooks B, Merranko J, et al. Lithium versus other mood-stabilizing medications in a longitudinal study of bipolar youth [published online ahead of print July 29, 2019]. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. PubMed CrossRef
17.Etain B, Lajnef M, Bellivier F, et al. Clinical expression of bipolar disorder type I as a function of age and polarity at onset: convergent findings in samples from France and the United States. J Clin Psychiatry. 2012;73(4):e561-e566. PubMed CrossRef
18.Bellivier F, Etain B, Malafosse A, et al. Age at onset in bipolar I affective disorder in the USA and Europe. World J Biol Psychiatry. 2014;15(5):369-376. PubMed CrossRef
19.James A, Hoang U, Seagroatt V, et al. A comparison of American and English hospital discharge rates for pediatric bipolar disorder, 2000 to 2010. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2014;53(6):614-624. PubMed CrossRef
20.Post RM, Rowe M, Kaplan D, et al. The Child Network for parents to track their child’s mood and behavior. J Child Adolesc Psychopharmacol. 2017;27(9):840-843. PubMed CrossRef
21.Birmaher B, Axelson D, Monk K, et al. Lifetime psychiatric disorders in school-aged offspring of parents with bipolar disorder: the Pittsburgh Bipolar Offspring study. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2009;66(3):287-296. PubMed CrossRef
22.Mesman E, Birmaher BB, Goldstein BI, et al. Categorical and dimensional psychopathology in Dutch and US offspring of parents with bipolar disorder: a preliminary cross-national comparison. J Affect Disord. 2016;205:95-102. PubMed CrossRef
23.Youngstrom EA, Freeman AJ, Jenkins MM. The assessment of children and adolescents with bipolar disorder. Child Adolesc Psychiatr Clin N Am. 2009;18(2):353-390, viii-ix. PubMed CrossRef
24.Yatham LN, Kennedy SH, Parikh SV, et al. Canadian Network for Mood and Anxiety Treatments (CANMAT) and International Society for Bipolar Disorders (ISBD) 2018 guidelines for the management of patients with bipolar disorder. Bipolar Disord. 2018;20(2):97-170. PubMed CrossRef
25.Kowatch RA, Fristad M, Birmaher B, et al; Child Psychiatric Workgroup on Bipolar Disorder. Treatment guidelines for children and adolescents with bipolar disorder. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2005;44(3):213-235. PubMed CrossRef
26.DelBello MP, Goldman R, Phillips D, et al. Efficacy and safety of lurasidone in children and adolescents with bipolar i depression: a double-blind, placebo-controlled study. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2017;56(12):1015-1025. PubMed CrossRef
27.Findling RL, Pathak S, Earley WR, et al. Efficacy and safety of extended-release quetiapine fumarate in youth with bipolar depression: an 8 week, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. J Child Adolesc Psychopharmacol. 2014;24(6):325-335. PubMed CrossRef
28.Geller B, Tillman R, Bolhofner K, et al. Child bipolar I disorder: prospective continuity with adult bipolar I disorder; characteristics of second and third episodes; predictors of 8-year outcome. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2008;65(10):1125-1133. PubMed CrossRef
29.DelBello MP, Hanseman D, Adler CM, et al. Twelve-month outcome of adolescents with bipolar disorder following first hospitalization for a manic or mixed episode. Am J Psychiatry. 2007;164(4):582-590. PubMed CrossRef
30.Wozniak J, Petty CR, Schreck M, et al. High level of persistence of pediatric bipolar-I disorder from childhood onto adolescent years: a four year prospective longitudinal follow-up study. J Psychiatr Res. 2011;45(10):1273-1282. PubMed CrossRef
31.Anderson LE, Chen ML, Perrin JM, et al. Outpatient visits and medication prescribing for us children with mental health conditions. Pediatrics. 2015;136(5):e1178-e1185. PubMed CrossRef
32.Child Network. Bipolar Network News website. http://bipolarnews.org/?page_id=2630.
33.Welcome to My Mood Monitor. Mymoodmonitor website. http://www.mymoodmonitor.com/.
34.Gaynes BN, DeVeaugh-Geiss J, Weir S, et al. Feasibility and diagnostic validity of the M-3 checklist: a brief, self-rated screen for depressive, bipolar, anxiety, and post-traumatic stress disorders in primary care. Ann Fam Med. 2010;8(2):160-169. PubMed CrossRef
35.NIMH Life Chart Method or Personal Calendar. Bipolar Network News website. http://bipolarnews.org/?page_id=52.
36.Post RM, Leverish GS. Treatment of Bipolar Illness: A Casebook for Clinicians and Patients. New York, NY: WW Norton and Co; 2008:1-666.
37.Post RM. Treatment of bipolar depression: evolving recommendations. Psychiatr Clin North Am. 2016;39(1):11-33. PubMed CrossRef
38.Goldstein BI, Birmaher B, Carlson GA, et al. The International Society for Bipolar Disorders Task Force report on pediatric bipolar disorder: Knowledge to date and directions for future research. Bipolar Disord. 2017;19(7):524-543. PubMed CrossRef
39.Post RM, Goldstein B, Birmaher B, et al. Toward prevention of bipolar disorder in at-risk children: potential strategies ahead of the data. J Affect Disord. 2020;272:508-520. CrossRef
Enjoy this premium PDF as part of your membership benefits!